Refractive index = Real depth / Apparent depth
Solution:
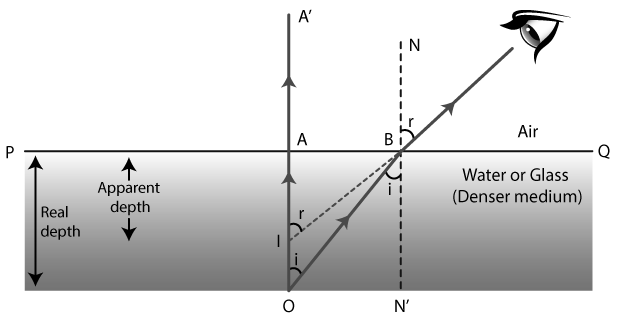
Take a look at a ray of light. OA is generally incident on the surface PQ. It follows AA’ in a straight line. Consider another beam from O that strikes OB at an angle of i. This beam is bent and travels through BC. The beam BC appears to originate from point I, which is the virtual image of O acquired by reversing the production of A’A and BC. As a result, AI depicts the apparent depth, which is lower than the true depth.
Because AO and BN’ are parallel and OB is a cross-sectional line,
we can write => ∠AOB = ∠OBN1 = i
Similarly, IC is the transversal line and IA’ and BN are parallel, so
we can write => ∠BIA’ = ∠CBN = r
In right-angle triangle BAO => sin i = BA / OB and
And in right-angle triangle IAB => sin r = BA / IB
By Snell’s law, for refraction from medium to air we can write
m μa = sin i / sin r =
(BA / OB) / (BA / IB)
m μa = IB / OB
Therefore, refractive index of medium with respect to air can be written as
a μm = 1 / m μa
a μm = OB / IB
The object is viewed from a point vertically above the object O, since point B is very close to the point A.
Therefore, IB = OA
Thus, a μm = OA / IA
a μm = Real depth / Apparent depth
