Answer: (d) no solution
Here, ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() and
and ![]()
For parallel lines, we have:
![]()
Sol:
The given system of equations can be written as:
![]() and
and ![]()
The given equations are of the following form:
![]() and
and ![]()
Here, ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
As a result, the given system has no solution.
The pair of equations 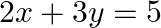 and
and 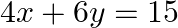 has
has
(a) a unique solution
(b) exactly two solutions
(c) infinitely many solutions
(d) no solution
(a) a unique solution
(b) exactly two solutions
(c) infinitely many solutions
(d) no solution
The pair of equations 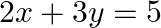 and
and 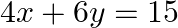 has
has
(a) a unique solution
(b) exactly two solutions
(c) infinitely many solutions
(d) no solution
(a) a unique solution
(b) exactly two solutions
(c) infinitely many solutions
(d) no solution
