(c) the meter reads not v but ![]() and is calibrated to read
and is calibrated to read ![]()
When a voltage measuring device is connected to AC mains, the meter shows the steady input voltage of 220V. This means
(a) input voltage cannot be AC voltage, but a DC voltage.
(b) maximum input voltage is 220V.
(c) the meter reads not v but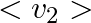 and is calibrated to read
and is calibrated to read 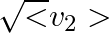 .
.
(d) the pointer of the meter is stuck by some mechanical defect.
(a) input voltage cannot be AC voltage, but a DC voltage.
(b) maximum input voltage is 220V.
(c) the meter reads not v but
(d) the pointer of the meter is stuck by some mechanical defect.
When a voltage measuring device is connected to AC mains, the meter shows the steady input voltage of 220V. This means
(a) input voltage cannot be AC voltage, but a DC voltage.
(b) maximum input voltage is 220V.
(c) the meter reads not v but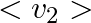 and is calibrated to read
and is calibrated to read 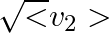 .
.
(d) the pointer of the meter is stuck by some mechanical defect.
(a) input voltage cannot be AC voltage, but a DC voltage.
(b) maximum input voltage is 220V.
(c) the meter reads not v but
(d) the pointer of the meter is stuck by some mechanical defect.
