(c) A card is selected from a pack of ![]() cards.
cards.
Suppose ![]() be the event of drawing an ace.
be the event of drawing an ace.
We have four aces in a pack.
So, ![]() .
.
![]()
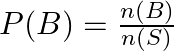
![]()
Therefore, ![]() .
.
(d) Suppose, ![]() be the event of drawing a black card.
be the event of drawing a black card.
We have 26 black cards in a pack.
So, ![]() .
.
![]()
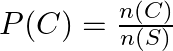
![]()
Therefore, ![]() .
.
(c) A card is selected from a pack of ![]() cards.
cards.
Suppose ![]() be the event of drawing an ace.
be the event of drawing an ace.
We have four aces in a pack.
So, ![]() .
.
![]()
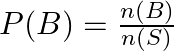
![]()
Therefore, ![]() .
.
(d) Suppose, ![]() be the event of drawing a black card.
be the event of drawing a black card.
We have 26 black cards in a pack.
So, ![]() .
.
![]()
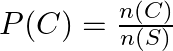
![]()
Therefore, ![]() .
.