The possible outcomes when a die is thrown are ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Then the sample space is,
![]()
So, ![]()
(i) Suppose, ![]() be the event having sum of numbers as
be the event having sum of numbers as ![]() .
.
The sample space is, ![]()
So, ![]() .
.
![]()
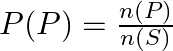
Therefore, ![]() .
.
(ii) Suppose ![]() be the event having sum of number as
be the event having sum of number as ![]() .
.
The sample space is ![]()
So, ![]() .
.
![]()
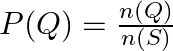
Therefore, ![]() .
.
