On the off chance that we need to demonstrate that the given three focuses
![]()
are collinear, then, at that point, we need to likewise demonstrate that the line going through the focuses
![]()
additionally goes through the point
![]()
By utilizing the equation,
The condition of the line going through the focuses
![]()
is given by

![]()
![]()
![]()
On the off chance that
![]()
goes through
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The line going through the focuses
![]()
likewise goes through the point
![]()
Thus demonstrated. The given three focuses are collinear.

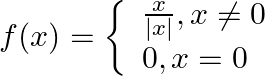 . Show that
. Show that 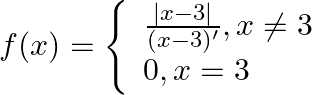 . Show that
. Show that