Solution:
Given that ![]()
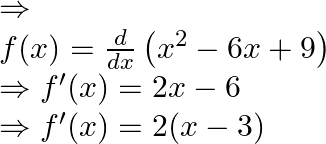
For ![]() let us find critical point, we must have
let us find critical point, we must have
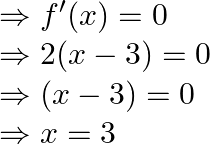
So, ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]() if
if ![]()
Therefore, ![]() increases on
increases on ![]() and
and ![]() is decreasing on interval
is decreasing on interval ![]()
Let’s find the coordinates of point
Eq. of curve is ![]()
Slope of this curve is given by
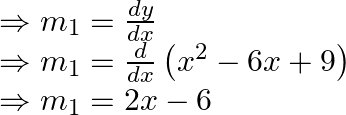
Eq. of line is ![]()
Slope of this curve is given by
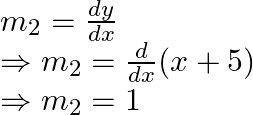
As slope of curve is parallel to line
So, they follow the relation
Therefore putting the value of ![]() in equation of curve, we obtain
in equation of curve, we obtain
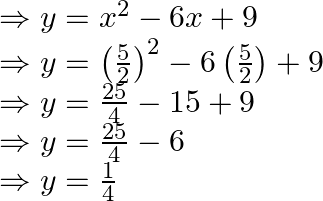
Therefore the required coordinates is ![]()
