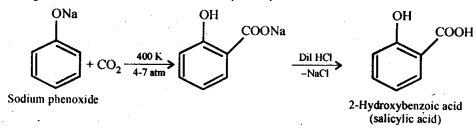
(i) Kolbe’s reaction: When sodium phenoxide is heated with C02 at 400°C under 4-7 atmospheres and then acidified, the main result is 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (salicylic acid), with a minor amount of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. This reaction is called Kolbe’s reaction.
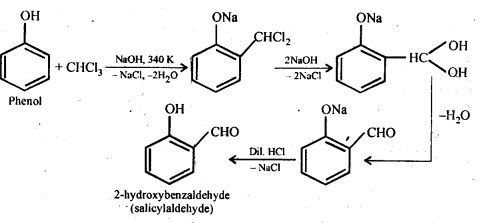
(ii) The main product of the Reimer-Tiemann reaction is 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde), which is produced by treating phenol with CHC13 in the presence of aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide at 340 K and then hydrolyzing the resultant product. The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is the name for this reaction.