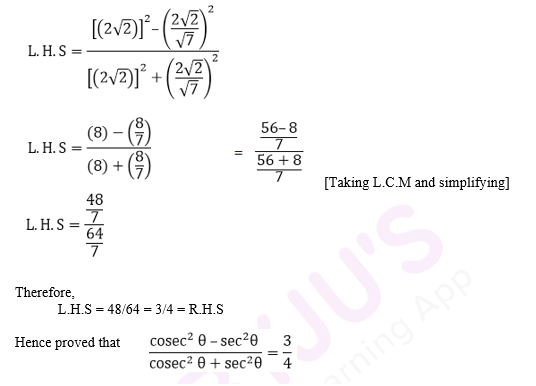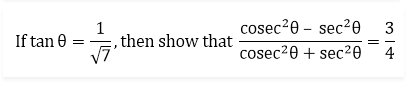
Solution:
Given, tan θ =
![]()
By definition, we know that
tan θ = Perpendicular side opposite to ∠θ / Base side adjacent to ∠θ
![]()
On comparing equation
![]()
Perpendicular side opposite to ∠θ =
![]()
Base side adjacent to ∠θ =
![]()
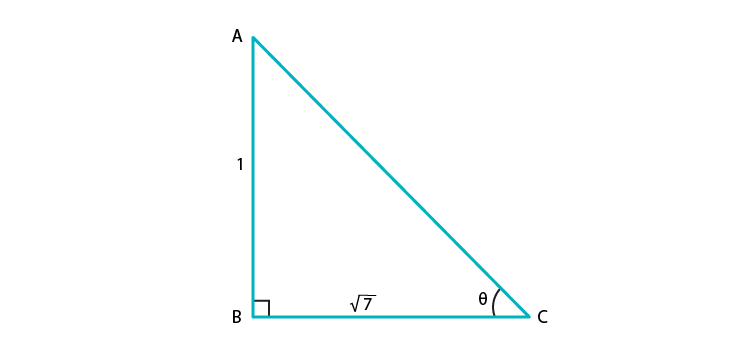
Thus, the triangle representing ∠ θ is,
Hypotenuse AC is unknown and it can be found by using Pythagoras theorem
By applying Pythagoras theorem, we have
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
AC2 =
![]()
AC 2 =
![]()
AC2 =
![]()
AC =
![]()
⇒ AC =
![]()
By definition,
sin θ = Perpendicular side opposite to ∠θ / Hypotenuse = AB / AC
⇒ sin θ =
![]()
And, since cosec θ =
![]()
⇒ cosec θ =
![]()
Now,
cos θ = Base side adjacent to ∠θ / Hypotenuse = BC / AC
⇒ cos θ =
![]()
And, since sec θ =
![]()
⇒ sec θ =
![]()
Taking the L.H.S of the equation,
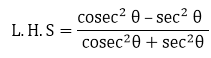
Substituting the value of cosec θ and sec θ from equation
![]()