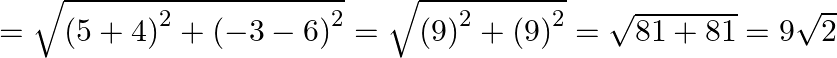Solution:
Given: PQ = QR because Q (0, 1) is equidistant between P (5, – 3) and R (x, 6).
Step 1: Using the distance formula, calculate the distance between PQ and QR.
PQ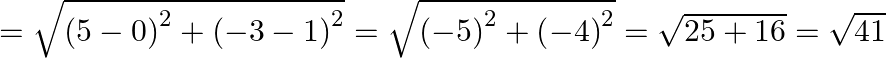
QR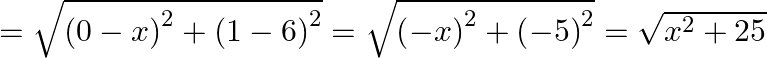
Step 2: Use PQ=QR
To omit the square root, square both sides.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
R (4, 6) or R (-4, 6) will be the coordinates of Point R.
If R (4, 6), then
QR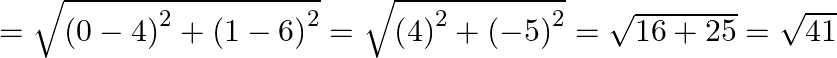
PR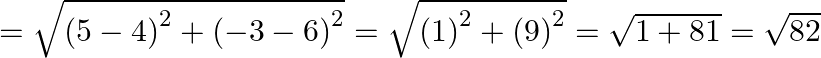
If R (-4, 6), then,
QR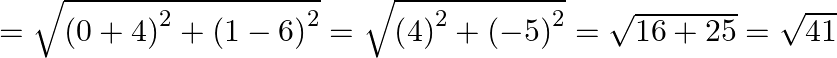
PR