Solution:
We have 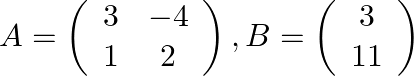 and
and 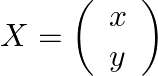 .
.
We need to find ![]() .
.
Now if number of columns in left matrix is equals to the number of rows in right matrix, multiplication of two matrices is possible.
Next discuss the order of the matrices which are given the order of matrix ![]() is
is ![]() , order of the matrix
, order of the matrix ![]() is
is ![]() 1 and order of the matrix
1 and order of the matrix ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
Therefore the multiplications we can proceed as
(i) The multiplication ![]() is possible.
is possible.
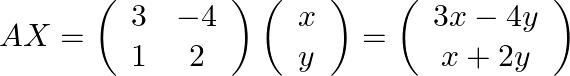
(ii)We have ![]() .
.
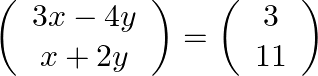
Thus we can write
![]()
On solving the equations we obtain
![]()

![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left[\begin{array}{cc} 3 & -4 \\ 1 & 2 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} \mathrm{x} \\ \mathrm{y} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{l} 3 \\ 11 \end{array}\right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-16dd3658e32c62682e7e1c991959454b_l3.png)