A real function f is said to be continuous at x = c, where c is any point in the domain of f if

h is a very small positive number. i.e. left hand limit as x → c (LHL) = right hand limit as x → c (RHL) = value of function at x = c.
A function is continuous at x = c if

From equation 1, f(x) is changing its expression at x = 2
Given, f (x) is continuous everywhere

4+2a + b = 8
∴ 2a + b = 4
∴ b = 4 – 2a …………… equation 2
Also from equation 1, it is clear that f(x) is also changing its expression at x = 4
Given, f (x) is continuous everywhere

∴ 8a + 5b = 14 ……………….Equation 3
Putting value of a from equation 2 to equation 3
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \therefore ~8a\text{ }+\text{ }5\left( 4-2a \right)\text{ }=\text{ }14 \\ \Rightarrow ~2a\text{ }=\text{ }6 \\ \therefore ~a\text{ }=\text{ }6/2 \\ =\text{ }3 \\ \therefore ~b\text{ }=\text{ }4\text{ }-\text{ }2\times 3\text{ }=-\text{ }2 \\ Thus,\text{ }a\text{ }=\text{ }3\text{ }and\text{ }b\text{ }=-\text{ }2 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-307aa7f8ef23abcfd7f7710c1dfc4514_l3.png)

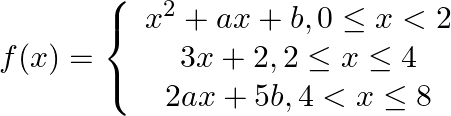 If f is continuous on [0, 8], find the values of a and b.
If f is continuous on [0, 8], find the values of a and b.