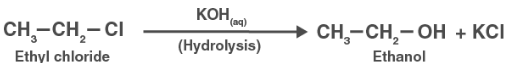
(i) Under normal circumstances, chlorobenzene does not hydrolyze. When heated in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623 K and a pressure of 300 atm, it hydrolyzes to produce phenol.
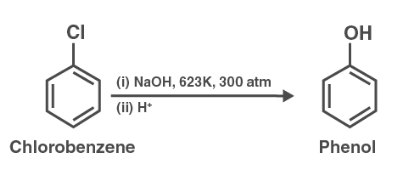
(ii) When ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH, it undergoes hydrolysis to form ethanol