Solution:
Conductivity:
The conductivity of a solution is defined as the conductance of a solution with a length of 1 cm and an area of cross-section of 1 sq. cm and a cross-sectional area of 1 sq. cm. In the physical world, specific conductance is the inverse of resistivity.
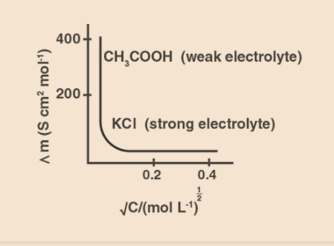
Molar conductivity
It is defined as the conductance of volume V of a solution containing 1 mole of electrolyte and maintained between two electrodes with an area cross-section A and a distance equal to the unit length of the solution at a certain concentration.
When the concentration of a substance is reduced, the molar conductivity increases. In this case, it is because dilution raises the total volume V (the total volume V of the solution containing one mole of the electrolyte). The variation is given below: