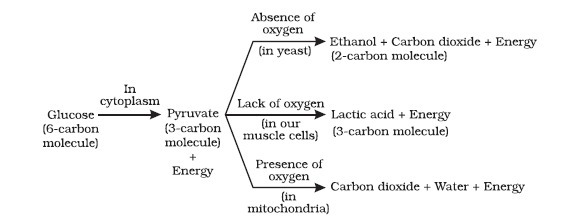
Glucose is initially broken down into pyruvate, a three-carbon molecule. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of all living things. The following stages further break down pyruvate.
In yeast:
Anaerobic respiration is the process of breaking down pyruvate in the absence of oxygen. Pyruvate is broken down in yeasts to produce CO2 and ethanol.
In Muscle Cells:
The energy demand of our muscular cells increases dramatically during strenuous physical activity. Anaerobic respiration in muscle cells compensates for this. Pyruvate is converted to lactic acid in muscle cells.
In Mitochondria:
Pyruvate is broken down in mitochondria during aerobic respiration (when oxygen is present). Pyruvate is decomposed here to create H2O and CO2. Aerobic respiration is the most common mode of respiration in most organisms.

![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{l} \square \vec{r}=(\hat{i}+\hat{j})+\lambda(2 \hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k}) \\ \vec{r}=(2 \hat{i}+\hat{j}-\hat{k})+\mu(3 \hat{i}-5 \hat{j}+2 \hat{k}) \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2f8ab5b81e582387cb9ae472791476e4_l3.png)