Solution:
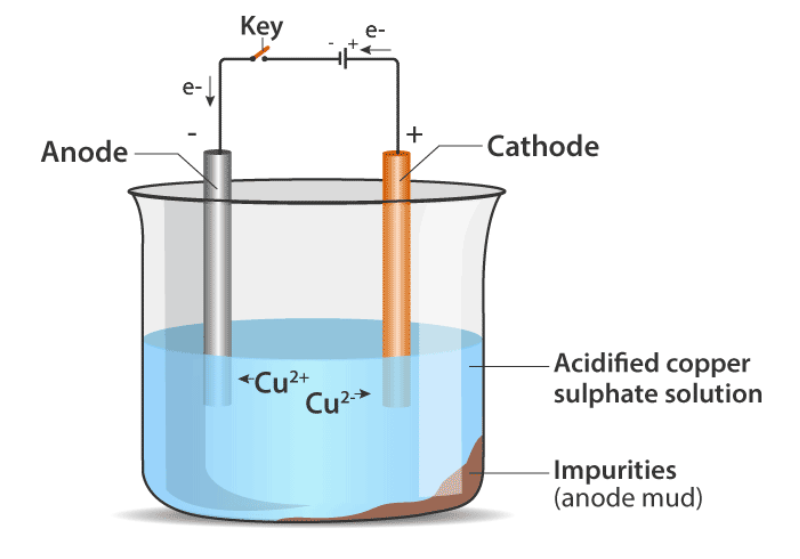
A broad block of impure metal is used as an anode (attached to the battery’s +ve connector) and a thin strip of pure metal is used as a cathode when electrolysis is used to refine an impure metal (connected to the -ve terminal of the battery). As an electrolyte, a water-soluble salt (of the metal to be refined) is used. The impure metal dissolves off the anode and enters the electrolyte solution when current passes across it. The electrolyte deposits on the cathode also include pure metal.
Copper electrolysis: An acidified copper sulphate (CuSO4 + dilute H2SO4) solution forms the electrolyte in an electrolytic tank. By connecting the positive terminal of a power source to a block of impure copper, an anode is created (battery). The cathode of the cell is a narrow strip of extremely pure copper metal. It is linked to the power supply’s negative terminal.
The cell is wired with a modest electric current. The electrolyte absorbs atoms from the anode. Copper sulphide is formed when copper from the anode is transformed. On the cathode, an equal amount of copper atoms from the solution are deposited. This is done to maintain the solution’s concentration. Because they are unable to displace copper from the sulphate solution, impurities from the anode block either remain in the solution or accumulate below the anode. Anode mud refers to the insoluble contaminants that remain in the electrolyte.
Copper sulphate solution contains ions of Cu+ and SO4–. The following reactions take place at the anode and cathode when an electric current is passed.
At cathode: Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
At anode: Cu -2e- → Cu2+
Pure copper is removed from the cathode. Some metals like gold, silver are present in the anode and can be recovered separately.
