As we know that vapour pressure of water, ![]() of
of ![]()
Weight of water, ![]()
Weight of urea, ![]()
Molecular weight of water, ![]()
Molecular weight of urea, ![]()
We must now determine the vapour pressure of water in the solution. Vapour pressure is denoted by.
As a result of Raoult’s law, we now have:
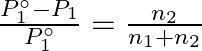
![]()
![]()
![]() of
of ![]() As a result, the vapour pressure of water in the given solution is
As a result, the vapour pressure of water in the given solution is ![]() of
of ![]() and its relative lowering is 0.0173.
and its relative lowering is 0.0173.
