Solution: The potential difference across $4 \Omega$ resistor is potential drop by the $4 \Omega$ resistor.$V=I R=1 \times 4=4 V$The power dissipated in $4 \Omega$ resistor$$P=I^{2} R=1^{2} \times...
Find out the following in the electric circuit given in Figure 12.9
Find out the following in the electric circuit given in Figure 12.9
(a) Effective resistance of two 8 Ω resistors in the combination
(b) Current flowing through 4 Ω resistor
Solution: (a) Since, two $8 \Omega$ resistors are in parallel, then their effective resistance $R_{p}$ is given by$$\begin{aligned}\frac{1}{R_{p}}...
What is Joule’s heating effect? How can it be demonstrated experimentally? List its four applications in daily life.
Solution: According to the Joules heating effect, the amount of heat that a resistor produces is For the given resistor, the voltage is directly proportional to the square of the current.Resistance...
How will you conclude that the same potential difference (voltage) exists across three resistors connected in a parallel arrangement to a battery?
Solution: Create a circuit with three resistors (R1, R2, and R3) connected in parallel, as shown in the diagram below: Take a reading of the potential difference between three resistors that are...
How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of the circuit containing three resistances in series connected to a battery?
Solution: To construct the circuit, connect three resistors R1, R2, and R3 in series.Make use of an ammeter to observe the changes that have occurred in the current flow.Remove R1 and measure the...
What is electrical resistivity of a material? What is its unit? Describe an experiment to study the factors on which the resistance of conducting wire depends.
Answer: The ability of a conductor to resist the flow of electric current is an inherent property of the conductor itself. Each material's resistance is distinct from the others. Resistance is...
State Ohm’s law? How can it be verified experimentally? Does it hold good under all conditions? Comment.
Answer: Ohm’s law states that at constant temperature potential difference (voltage) across an ideal conductor is proportional to the current through it. V/I = R Ohm's law is being checked for...
Three incandescent bulbs of 100 W each are connected in series in an electric circuit. In another circuit, another set of three bulbs of the same wattage are connected in parallel to the same source.
(a) Will the bulb in the two circuits glow with the same brightness? Justify your answer.
(b) Now let one bulb in both the circuits get fused. Will the rest of the bulbs continue to glow in each circuit? Give reason.
Answer: a) In a series configuration, the resistance of the bulbs is three times greater than the resistance of a single bulb. As a result, when compared to the current in each bulb in the parallel...
B1 , B2, and B3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in Figure 12.8. When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by ammeter A.
What happens to the glow of the other two bulbs when the bulb B1 gets fused?
What happens to the reading of A1 , A2 , A3 and A when the bulb B2 gets fused?
Solution: In a parallel circuit, the potential difference does not become divided. As a result, when bulb one is fused, the glowing of the other bulbs will not be affected. 3 Amperes are being...
B1, B2, and B3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in Figure 12.8. When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by ammeter A. How much power is dissipated in the circuit when all the three bulbs glow together?
Solution: Evaluating the value, R= V/I = 4.5V/3A= 1.5Ω As we know that, substituting the value of parameters in P= I2R, we get = (3A)2 x 1.5 Ω = 13.5 W
Why is the parallel arrangement used in domestic wiring?
Answer: Parallel wiring is commonly used in domestic wiring because it ensures that the potential difference between each electrical appliance is the same across the board.
A current of 1 ampere flows in a series circuit containing an electric lamp and a conductor of 5 Ω when connected to a 10 V battery. Calculate the resistance of the electric lamp. Now if the resistance of 10 Ω is connected in parallel with this series combination, what change (if any) in current flowing through 5 Ω conductor and potential difference across the lamp will take place? Give reason.
Solution: Given: I= 1 A, V= 5 V 1) Let R be the resistance of the electric lamp. In series total resistance = 5 + R I = v/r 1 = 10/5+R R = 5 ohm 2) V across Lamp + conductor = 10 V V acoess Lamp =...
What is the commercial unit of electrical energy? Represent it in terms of joules.
Solution: Electrical energy is a term that is used to refer to energy that has been converted from electric potential energy when it is used informally. Commercial unit of electrical energy is...
What is electrical resistivity? In a series electrical circuit comprising a resistor made up of a metallic wire, the ammeter reads 5 A. The reading of the ammeter decreases to half when the length of the wire is doubled. Why?
Answer: The resistivity of a conductor is defined as the property of the conductor that prevents the flow of electric current. The resistance of a particular material is one-of-a-kind. Resistance is...
How does the use of a fuse wire protect electrical appliances?
Answer: The resistance of fuse wire is much higher than that of the main wiring. The electric current increases by a significant amount when this occurs. The fuse wire melts, causing the circuit to...
Draw a circuit diagram of an electric circuit containing a cell, a key, an ammeter, a resistor of 2 Ω in series with a combination of two resistors (4 Ω each) in parallel and a voltmeter across the parallel combination. Will the potential difference across the 2 Ω resistor be the same as that across the parallel combination of 4Ω resistors? Give reason.
Solution: The circuit diagram is: The following equation can be used to calculate the total resistance of a parallel combination of 40 resistors: $\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{2}$$R...
Should the resistance of an ammeter be low or high? Give reason.
Answer: The resistance of an ammeter should be low because the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit, and if the resistance of the circuit is too high, no current will flow through it.
Three 2 Ω resistors, A, B and C, are connected as shown in Figure 12.7. Each of them dissipates energy and can withstand a maximum power of 18W without melting. Find the maximum current that can flow through the three resistors?
Solution: We know that Current $P = I ^{2} R$ Evaluating the value,$$18 W = l ^{2} \times 2 \Omega \I ^{2}=18 W / 2 \Omega \ $$ =9 A I =3 AThis is the maximum current that can flow through the three...
A child has drawn the electric circuit to study Ohm’s law as shown in Figure 12.6. His teacher told that the circuit diagram needs correction. Study the circuit diagram and redraw it after making all corrections.
Solution: Specifically, the ammeter has been connected in parallel with the voltmeter, which is not the correct way to connect the two metres. The ammeter should be connected in series with the...
Unit of electric power may also be expressed as
(a) volt-ampere
(b) kilowatt-hour
(c) watt-second
(d) joule second
Solution: The answer is (a) volt-ampere The apparent power of an electrical circuit is measured in volt-amperes (VA), which is the unit of measurement. A watt-second (also spelled watt-second,...
Two resistors of resistance 2 Ω and 4 Ω when connected to a battery will have
(a) same current flowing through them when connected in parallel
(b) same current flowing through them when connected in series
(c) the same potential difference across them when connected in series
(d) different p
Solution: The answer is (b) same current flowing through them when connected in series When using a series combination, the current is not divided into branches because the resistor receives a...
An electric kettle consumes 1 kW of electric power when operated at 220 V. A fuse wire of what rating must be used for it?
(a) 1 A
(b) 2 A
(c) 4 A
(d) 5 A
Solution: The answer is (d) 5 A We know, P=V x I Substituting , 1000 w = 220v x I I =1000w/220v = 4.54 A = 5 A
In an electrical circuit, two resistors of 2 Ω and 4 Ω respectively are connected in series to a 6 V battery. The heat dissipated by the 4 Ω resistor in 5 s will be
(a) 5 J
(b) 10 J
(c) 20 J
(d) 30 J
Solution: Answer is (c) 20 J Equivalent resistance of the circuit is R = 4+2 = 6Ω current, I= V/R = 6/6= 1A the heat dissipated by 4-ohm resistor is, H = I2Rt = 20J
In an electrical circuit, three incandescent bulbs A, B and C of rating 40 W, 60 W and 100 W respectively are connected in parallel to an electric source. Which of the following is likely to happen regarding their brightness?
(a) The brightness of all the bulbs will be the same
(b) The brightness of bulb A will be the maximum
(c) The brightness of bulb B will be more than that of A
(d) The brightness of bulb C will be less than that of B
Solution: Answer is (c) Brightness of bulb B will be more than that of A Due to the fact that the bulbs are connected in parallel, their combined resistance will be less than the arithmetic sum of...
The resistivity does not change if
(a) the material is changed
(b) the temperature is changed
(c) the shape of the resistor is changed
(d) both material and temperature are changed
Solution: Answer is (c) the shape of the resistor is changed We will be re-arranging the terms we will receive, =A/RlAs a result, the resistivity of the material will be determined by its area and...
If the current I through a resistor is increased by 100% (assume that temperature remains unchanged), the increase in power dissipated will be
(a) 100 %
(b) 200 %
(c) 300 %
(d) 400 %
Solution: Answer is (c) 300 % The amount of heat generated by a resistor is proportional to the square of the current flowing through it. As a result, when the current is doubled, the dissipation of...
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively (Figure.12.5). Which of the following is true?
(a) R1 = R2 = R3
(b) R1 > R2 > R3
(c) R3 > R2 > R1
(d) R2 > R3 > R1
Solution: The answer is (c) R3 > R2 > R1 Resistance is inversely proportional to the amount of current flowing through it. Because the highest resistance will result in the least amount of current...
A cylindrical conductor of length l and uniform area of cross section A has resistance R. Another conductor of length 2l and resistance R of the same material has an area of cross-section
(a) A/2
(b) 3A/2
(c) 2A
(d) 3A
Solution: Answer is (c) 2A Explanation: We are well aware of this. R is equal to (L/A). The resistance of a wire of length L is denoted byThe area of the cross-section is denoted by the letter A.The...
Which of the following represents voltage?
(a)Work done/ Current×Time
(b) Work done × Charge
(c)Workdone×TimeCurrent
(d) Work done × Charge × Time
Solution: The answer is a) Explanation: Electric potential is the work done per unit charge. Electric Potential=Charge Work Done Again, Charge=Current×Time...
What is the minimum resistance which can be made using five resistors each of 1/5 Ω?
(a) 1/5 Ω
(b) 1/25 Ω
(c) 1/10 Ω
(d) 25 Ω
Solution: Answer is (b) 1/25 Ω Explanation: When resistors are connected in series, the resistance is reduced to a minimum. 1/R = 5 + 5 + 5 +5 +5= 25 Ω R=1/25Ω
The proper representation of the series combination of cells (Figure 12.4) obtaining maximum potential is
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
Solution: The answer is (a) (i) Explanation: The positive terminal of the next cell is direct across from the negative terminal of the previous cell in this arrangement.
Identify the circuit (Figure 12.3) in which the electrical components have been properly connected.
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
Solution: The answer is (b) (ii) Explanation: For current to flow, an electrical circuit must be closed. An open circuit can result from improperly connected components. An ammeter measures the...
A current of 1 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb. Number of electrons passing through a cross-section of the filament in 16 seconds would be roughly
(a) 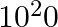
(b) 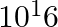
(c) 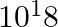
(d) 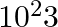
Solution: Answer is (a) 1020 Given $: I =1 A , t =16 s , e =1.6 \times 10^{-19} C$ Step 1: The filament draws current from the power supply. $I =\frac{ Q }{ t }=\frac{ Ne }{ t } \quad ($ Since $Q =...
Electrical resistivity of a given metallic wire depends upon
(a) its length
(b) its thickness
(c) its shape
(d) nature of the material
Solution: The answer is (d) nature of the material The resistivity of a material is an inherent property of the material. As an intensive property, it does not scale with the system's size, even if...
In the following circuits (Figure 12.2), the heat produced in the resistor or combination of resistors connected to a 12 V battery will be
(a) same in all the cases
(b) minimum in case (i)
(c) maximum in case(ii)
(d) maximum in case(iii)
Solution: The answer is (c) maximum in case(ii) In this example, two transistors are connected in series. Because they are connected in parallel, the total resistance in figure (iii) will be less...
A cell, a resistor, a key, and ammeter are arranged as shown in the circuit diagrams of Figure12.1. The current recorded in the ammeter will be
(a) maximum in (i)
(b) maximum in (ii)
(c) maximum in (iii)
(d) the same in all the cases
Solution: The answer is (d) the same in all the cases Because there are no modifications to any of the circuits, the current in all of the circuits will be the same.
