The right option for measuring current unit is d) Ampere.
Q18. How does the resistance of a conductor depend on:c) temperature of the conductor
Answer: c) As the temperature rises, the material's resistance rises as well.
As illustrated in the diagram, three resistors are connected: A current of one ampere flows through resistor 5. What are the possible differences between AB and AC?
Difference in potential across AB = IR3 = 1 × 5 = 5V Between B and C, the equivalent resistance is 1/R’ = 1/R1 + 1/R2 = 1/10 + 1/15 = 5/30 R’ = 6Ω Total resistance...
As illustrated in the diagram, three resistors are connected: A current of one ampere flows through resistor 5. a) How much current is flowing via the other two resistors? b) How much total resistance do you have?
Answer: Based on the circuit diagram above; a) The total current is 1 amp when I insert the parallel combination of resistances R1 and R2. The current flow through R1 is I1, while the current...
Q18. How does the resistance of a conductor depend on: a) length of the conductor b) area of cross-section of the conductor
Answer: a) The resistance of a conductor is proportional to its length. The material's resistance diminishes as the length of the material rises, and vice versa. b) The resistance of a conductor is...
Q17. Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material when connected to the same source? Give reason for your answer.
Answer: Because the resistance of a thick wire is lower than that of a thin wire, current flow will be easier in a thick wire than in a thin wire.
Q16. a) Give two examples of substances which are good conductors of electricity. Why do you think they are good conductors of electricity? b) Calculate the resistance of a copper wire 1.0km long and 0.50mm diameter if the resistivity of copper is 1.7×10-8Ωm.
Answer: a) Two examples of substances that are good conductors of electricity are silver and copper. These two metals have free electrons that are available for conduction. b) Given in question : l...
A 6V battery is linked in series with a 20 resistance electric bulb and a 4 resistance cable. Create a circuit schematic and perform the following calculations: c) potential difference between the electric bulb and the resistance wire d) potential difference between the electric bulb and the resistance wire
Answer: c) Difference in potential across the bulb = IR1 = 0.25 20 = 5V d) Difference in potential across the resistance wire = IR2 = 0.25 4 = 1V
Q15. a) Write down an expression for the resistance of a metallic wire in terms of the resistivity. b) What will be the resistance of a metal wire of length 2 metres and area of cross-section 1.55×10-6m2, if the resistivity of the metal be 2.8×10-8Ωm?
Answer: a) Following is the expression for the resistance of a metallic wire in terms of the resistivity: R = ρl/A Where, R is the resistance of the wire , ρ is the resistivity of the wire , A is...
Q14. a) What do you understand by the “resistivity” of a substance? b) A wire is 1.0m long, 0.2 mm in a diameter and the has a resistance of 10Ω. Calculate the resistivity of its material?
Answer: a) Resistivity is defined as the characteristic property of a substance which is dependent on the nature of the substance and the temperature of the substance used in the conductor. It is...
Q13. Fill in the following blanks with suitable words: Resistance is measured in ………… the resistance of a wire increases as the length ………….. as the temperature ……… and as the cross-sectional area ……..
Answer: Ohm, increases, increases, and decreases respectively .
A 6V battery is linked in series with a 20 resistance electric bulb and a 4 resistance cable. Create a circuit schematic and perform the following calculations: a) The circuit’s total resistance b) the amount of electricity flowing through the circuit
a) given R1=20 , R2 =4, Total resistance of the circuit is given as: R = R1 + R2 = 20 + 4 = 24Ω b) We know that, V = IR Therefore, 6 = 24I I = 6/24 = 0.25amp
How many electrons are flowing per second past a point in a circuit in which there is a current of 5A?
Given that, Current, I $=5 \mathrm{~A}$ Time taken, $t=1 \mathrm{~s}$ We already know that, $\text{I}=\text{Q}/\text{t}$ $\text{Q}=\text{I}\times \text{t}=5\times 1=5\text{C}$ Total number of...
Consider the circuit given below where A, B, and C are three identical light bulbs of constant resistance. a) List the bulbs in order of increasing brightness b) If C burns out, what will be the brightness of A now compared with before?
Answer: a) Because it receives greater voltage than the other two, C will be the brightest of the three. However, as they are in a series combination, A and B will be equally brilliant. b) If C...
Q12. a) How does the resistance of a pure metal change if its temperature decreases? b) Hoes does the presence of impurities in a metal affect its resistance?
Answer: a) As the temperature drops, the material's resistance drops as well. b) The presence of impurities in a metal enhances the material's resistance.
Q11. Which has more resistance: a) A long piece of nichrome wire or a short one? b) A thick piece of nichrome wire or a thin piece?
Answer: Following has more resistance: a) A long piece of nichrome wire . b) A thin piece of nichrome wire .
a) Draw a circuit diagram showing two lamps, one cell, and a switch connected in series. b) How can you change the brightness of the lamps?
Answer: a) b) By connecting the lamps in parallel, the lamp's brightness can be adjusted.
Q10. Why are the coils of electric iron and electric toasters made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
Answer: Electric iron and toaster coils are composed of an alloy rather than a pure metal for the following reasons: a) When compared to pure metal, an alloy's resistivity is higher. b) At high...
Using the circuit given below, state which of the following statement is correct? a) When S1 and S2 are closed, lamps A and B are lit b) With S1 open and S2 closed, A is lit and B is not lit c) With S2 open and S1 closed A and B are lit d) With S1 closed and S2 open, lamp A remains lit even if lamp B gets fused
Answer: The correct answer is c) A and B are illuminated when S2 is open, and S1 is closed.
Q9. Give two reasons why nichrome alloy is used for making the heating elements of electrical appliances.
Answer: The following are the two reasons why nichrome alloy is utilised to make electrical device heating elements: a) Nichrome has a very high resistance. b) At high temperatures, nichrome does...
An electric heater is connected to the 230V mains supply. A current of 8A flows through the heater. a) How much charge flows around the circuit each second? b) How much energy is transferred to the heater each second?
Given that, Potential difference $=230 \mathrm{~V}$ Current, I $=8 \mathrm{~A}$ a) $I=Q / t$ $8=\mathrm{Q} / 1$ $\mathrm{Q}=8 \times 1=8 \mathrm{C}$ Hence, the current is $8 \mathrm{C}$. b) We...
The lamps in a household circuit are connected in parallel because: a) this way they required less current b) if one lamp fails the others remain lit c) this way they require less power d) if one lamp fails the others also fail
Answer: The correct option is b) if one lamp fails, the others remain lit. The current going through the bulbs is different when they are connected in parallel. As a result, even if one lamp burns...
Q8. What is nichrome? State its one use.
Answer: Nickel, chromium, manganese, and iron are used to make nichrome alloys. Nichrome's resistivity is 60 times higher than copper's. It is utilised in the manufacture of the heating elements...
c) An electrician has wired a house in such a way that if a lamp gets fused in one room of the house, all the lamps in other rooms of the house stop working. What is the defect in the wiring? d) Draw a circuit diagram showing two electric lamps connected in parallel together with a cell and a switch that works both lamps. Mark an A enclosed in a circle on your diagram to show where an ammeter should be placed to measure the current.
Answer: c) All of the lamps are linked together in a series combination. d)
Q7. Name the material which is used for making the heating element of an electric iron.
Answer: The substance used to make the heating element of an electric iron is nichrome.
a) Which is the better way to connect lights and other electrical appliances in domestic wiring: series circuits or parallel circuit? Why? b) Christmas tree lamps are usually wired in series. What happens if one lamp breaks?
Answer: a) When it comes to household wiring, parallel circuits are preferable over series circuits. This is because when one of the electrical appliances fails, it affects the others. b) The bulbs...
Q6. Why are copper and aluminum wires usually used for electricity transmission?
Answer: Because copper and aluminium wires have low resistivities, they are employed for power transmission.
Draw a circuit diagram to show how 3 bulbs can be lit from a battery so that 2 bulbs are controlled by the same switch while the third bulb has its own switch.
If the amount of electric charge passing through a conductor in 10 minutes is 300C, the current flowing is: a) 30A b) 0.3A c) 0.5A d) 5A
Given, Charge moved $=300 \mathrm{C}$ Time taken $=10$ mins Current $=?$ $\mathrm{I}=\mathrm{Q} / \mathrm{t}$ By substituting the values, we get $\mathrm{I}=0.5 \mathrm{~A}$ hence, the correct...
Q5. Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor of electricity?
Answer: Between iron and mercury, iron is a better electrical conductor. Iron has a lower resistance than mercury, and we know resistance is inversely proportional to current. As a result, as...
A 9V battery is linked in series with resistors 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, and 12 in series. What would be the current flow via the 12 resistor?
Answer Given, R1 = 0.2 Ω R2 = 0.3 Ω R3 = 0.4 Ω R4 = 0.5 Ω R5 = 12 Ω V = 9V Therefore, the resultant resistance is given as: R = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4 + R5 = 0.2 + 0.3 + 0.4 + 0.5 + 12 = 13.4 Ω...
If the current through a flood lamp is 5A, what charge passes in 10 seconds? a) 0.5C b) 2C c) 5C d) 50C
Given that, Current, I $=5 \mathrm{~A}$ Time taken, $t=10 \mathrm{~s}$ Charge moved, $Q=$ ? $\text{I}=\text{Q}/\text{t}$ $\text{Q}=\mid \times \text{t}$ $\text{Q}=50\text{C}$ hence, the correct...
Q4. Name the material which is the best conductor of electricity.
Answer: The best conductor of electricity is silver metal. This is due to the fact that, in comparison to other metals, the electrons in silver metal are open for free mobility.
Q3. On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
Answer: The resistance of a conductor is determined by the following factors: a) The conductor's length . b) The conductor's cross-section .al area c) The conductor's temperature . d) The type of...
If you were going to connect two light bulbs to one battery, would you use a series or a parallel arrangement? Why? Which arrangement takes more current from the battery?
Answer: When the configuration is parallel, the battery's current consumption is higher. Any problem in one bulb will not influence the other operation because the bulbs are in a parallel...
Consider the circuits given below: a) In which circuit are the lamps dimmest? b) In which circuit or circuits are the lamps of equal brightness to the lamps in circuit? c) Which circuit gives out the maximum light?
Answer: Following is the right answer: c) The most significant amount of light is produced in the circuit (i). The resistance in the circuit is minimal because only one bulb is used, resulting in...
Consider the circuits given below: a) In which circuit are the lamps dimmest? b) In which circuit or circuits are the lamps of equal brightness to the lamps in circuit? c) Which circuit gives out the maximum light?
Answer: The following are the correct answers: a) The lamps in the circuit (ii) are the dimmest. Because the bulbs are connected in series, lowering the voltage in the rotation. b) The lamps in the...
Explain the terms “series combination” and “parallel combination” of resistance with graphics. In that situation, the resulting resistance is as follows: a) fewer b) more than either individual resistance?
Answer: When two or more resistances are connected end to end in a series combination, the resistances are said to be connected in series. The sum of all individual resistances equals the sum of any...
Q2. If the length of a wire is doubled by taking more of wire, what happens to its resistance?
Answer: When the length of the wire is twice, the resistance of the wire doubles. Because resistance is proportional to length, yet area of cross section is inversely related to resistance, this is...
Ten bulbs are connected in a series circuit to a power supply line. Ten identical bulbs are connected in a: a) an identical power supply line b) which circuit would have the highest voltage across each bulb? c) in which circuit would the bulbs be brighter? d) in which circuit, if one bulb blows out, all others will stop glowing? e) which circuit would have less current in it?
Answer: The following are the right answers: c) When a parallel circuit is employed, the appliance's operation can be regulated by individual switches. d) When appliances are linked in parallel,...
Ten bulbs are connected in a series circuit to a power supply line. Ten identical bulbs are connected in a: a) an identical power supply line b) which circuit would have the highest voltage across each bulb? c) in which circuit would the bulbs be brighter? d) in which circuit, if one bulb blows out, all others will stop glowing? e) which circuit would have less current in it?
Answer: The following are the correct answers: a) The circuit must be parallel to have an identical power supply line. b) Each bulb will have the highest voltage when the circuit is parallel.
How much energy is consumed when a current of 5 ampere flows through the filament of a heater having resistance of 100 ohms for two hours? Express it in joules.
Answer: Given in the question, I = 5A R = 100 ohm T = 2 hours It is known to us that, Energy consumed = P × T = I2RT Substituting the values, Energy consumed = 5kWh 1kWh = 3.6 × 106J Therefore we...
In the circuit below, get the current in each resistor:
Answer: Given, R1 = 6Ω R2 = 4 Ω V = 24V The two resistances are linked in parallel, according to the circuit schematic. Therefore, Current across R1 = I1 = V/R1 = 24/6 = 4amp Current across R2 = I2...
Q1. What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thicker?
Answer: As the thickness of the conductor is increased, the resistance of the conductor decreases. This is because: R = (ρl)/(A) Where,R is the resistance . l is the length of the conductor , A is...
Define watt-hour. How many joules are equal to 1 watt-hour?
Answer: The quantity of electrical energy consumed when a 1 watt electrical appliance is used for 1 hour is measured in watt-hours. 1 watt-hour = 3600 joules.
Give three reasons why different electrical appliances in a domestic circuit are connected in parallel.
Answer: In a household circuit, different electrical appliances are linked in parallel because: a) The voltage distribution from the power supply line to each appliance is the same. b) Individual...
Calculate the total resistance in each situation as follows:
Given that R1 = 4Ω R2 = 4 Ω R3 = 3 Ω From the given circuit diagram, 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 1/R = ¼ + ¼ R = 2 Ω Total resistance = R + R3 = 2 + 3 = 5 Ω
Q14. Classify the following into good conductors, resistors, and insulators: Rubber, mercury, nichrome, polythene, aluminium, wood, manganin, bakelite, iron, paper, thermocol, metal coin
Answer: Conductor: mercury, aluminium, iron, metal coin . Resistor: manganin, nichrome . Insulator: rubber, polythene, wood, bakelite, paper, thermocol .
Calculate the total resistance in each situation as follows:
a) Given that R1 = 500Ω R2 = 1000Ω From the above circuit diagram, R = R1 + R2 = 500 + 1000 =1500Ω b) Given that R1 = 2Ω R2 = 2Ω From the given circuit diagram, 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 1/R = ½ + ½...
Define watt. Write down an equation linking watts, volts, and ampere.
Answer: The equation that connects watts, volts, and ampere is as follows: 1 watt = 1 volt × 1 ampere
Q13. Distinguish between good conductors, resistors, and insulators. Name two conductors, two resistors, and two insulators.
Answer: The following are the differences between excellent conductors, resistors, and insulators: Good conductors are those materials that have a low or negligible electrical resistance. Conductors...
A wire with resistance R is sliced into two sections of equal length. The two halves are connected in a parallel manner. What is the combination’s resistance?
Answer: Given that each part's resistance is R/2 Let's call the resulting resistance R'. 1/R’ = 2/R + 2/R R’ = R/4
What current will be taken by a 920W appliance if the supply voltage is 230V?
Answer: Given in the question, P = 920W V = 230V I = ? It is known to us that, P = VI 920 = 230I I = 920/230 I = 4A
Why is a series arrangement not used for connecting domestic electrical appliances in a circuit?
When connecting residential electrical appliances in a circuit, a series configuration is not used since if one of the electrical appliances fails, it affects all of the others. In addition, the...
An electric lamp is labelled 12V, 36W. This indicates that it should be used with a 12V supply. What other information does the label provide?
Answer: Another piece of information offered by the label is that the rate of energy consumption is 36J/s.
If the potential difference between the end of a wire of fixed resistance is doubled, by how much does the electric power increase?
Answer: We are aware of this, P =V2/R R is constant V is doubled Therefore, P = 2(V2)/R P = 4V/R As a result, when the resistance is doubled, the power is multiplied by four.
Which of the following resistor configurations, A or B, has the lowest total resistance?
Answer: The following is estimated when the resistance configuration from A is combined with the resistance arrangement from B: 1/R = 1/10 + 1/1000 = (100+1)/1000 R = 1000/101...
Draw a circuit diagram to show how two 4V electric lamps can be lit brightly from two 2V cells.
Answer: The circuit schematic below shows two 4V bulbs that are connected in parallel with 2V cells.
What is the meaning of the symbol kWh? Which quantity does it represent?
Answer: kWh stands for kilowatt-hour and is the commercial unit of electrical energy.
Which quantity has the unit of watt?
Answer: Electric power is measured in watts.
Name the quantity whose unit is kilowatt and kilowatt-hour.
Answer: Electric power is measured in kilowatts, and electric energy is measured in kilowatt-hours.
What is the SI unit of electric energy and electric power?
Answer: The joule is the SI unit of electric energy, and the watt is the SI unit of electric power.
Q12. Fill in the following blanks with a suitable word: Ohm’s law states a relation between potential difference and ……
Answer: The relationship between potential difference and current is described by Ohm's law.
An electric bulb is rated at 220V, 100W. What is its resistance?
Answer: It is given in the question, V = 220V P = 100W R = ? We know that, R = V2/P R = 484 ohm
Name the commercial unit of electric energy.
Answer: The kilowatt-hour is the commercial unit of electric energy.
Show how two 4 ohm resistors are connected to generate a total resistance of a) 2 ohms b) a resistance of 8 ohms
Answer: a) If you join them in parallel, 1R = 14 + 14 = 2/4 = 1/2 As a result, R = 2 ohm. b) By joining them in a sequence, R = 4 + 4 = 8 As a result, R = 8 ohm.
What are the various results of merging two resistances, one of value 2 ohm and the other of value 6 ohm?
Answer: given R1 = 2 Ohm R2 = 6 Ohm Let case 1 be parallel combination 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 1/R = ½ + 1/6 = 4/6 R = 6/4 = 1.5 ohm Let case 2 be series combination R = R1 + R2 = 2+6 = 8...
Which type of circuit, series or parallel, is preferred while connecting a large number of bulbs: a) for decorating a hotel building from outside? b) for lighting inside the rooms of the hotel?
Answer: When the following type of circuit is used: a) The exterior of the hotel will be decorated in a series manner. The exterior lights do not need the same voltage difference b) lighting the...
Q11. A current of 5 amperes flows through a wire whose ends are at a potential difference of 3 volts. Calculate the resistance of the wire.
Answer: Given in question : Current, I = 5A Potential difference, V = 3V We know that, V = IR Therefore, 3 = 5 × R R = 3/5 = 0.6 Ohms
Which one has a higher electrical resistance: a 100 watt bulb or a 60 watt bulb?
Answer: Because we know that power is inversely related to resistance, a 60 watt bulb has a larger electrical resistance than a 100 watt bulb.
Two resistances, X and Y, are connected in series and parallel, respectively. Which means that the combined resistance will be lower than either of the separate resistances?
Answer: The resultant resistance will be less than either of the individual resistances when the two resistances X and Y are coupled in parallel.
Q10. A resistance of 20 ohms has a current of 2 amperes flowing in it. What potential difference is there between its ends?
Answer: Given in question : Resistance, R = 20 Ohms Current, I = 2 amp We know that, V = IR Therefore, V = 2 × 20 = 40V
How should the two 2 ohm resistances be put together to form a 1 ohm equivalent resistance?
Answer: The two resistances of 2 ohms must be connected in parallel to produce an equivalent resistance of 1 ohm.
Q9. A potential difference of 20V is applied across the ends of a resistance of 5 ohms. What current will flow in the resistance?
Answer: Given in question : Potential difference, V = 20V Resistance, R = 5 Ohms Current, I = ? We know that, V = IR 20 = I × 5 I = 20/5 = 4A
What will the overall resistance be if three 3 ohm resistances are connected in parallel?
Answer: Given, R1 = R2 = R3 = 3Ω 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 = 1/3 + 1/3 + 1/3 = 3/3 = 1 Therefore, R = 1Ω
What happens to the other bulbs in a parallel circuit if one bulb blows off?
Answer: When the bulbs are connected in a parallel configuration, they continue to glow. This occurs because the electricity flow is not disrupted, and the voltage differential between the other...
State two factors on which the electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance depends.
Answer: The electrical energy required by an electrical equipment is determined by the following two factors: a) The appliance's usage time b) The appliance's power rating
Q8. Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is halved. By how much does the current change?
Answer: Given in question : Potential difference = constant Also, we know that, V = IR I = V/R Given that V is constant, therefore, I will be proportional to 1/R. Therefore, when R is halved, I also...
In parallel, state the law of resistance combination.
Answer: The reciprocal of the combined resistance of a number of parallel resistances is equal to the total of the reciprocals of all the individual resistances, according to the law of parallel...
Q7. Which has less electrical resistance: a thin wire or a thick wire of the same length and same material?
Answer: Because the number of electrons present in the thick wire is more than that of the thin wire, a thick wire of the same length and substance will have less electrical resistance.
What happens to the other bulbs in a series circuit if one bulb blows off?
Answer: All of the other bulbs stop glowing when the bulbs are joined in series. Because the electrical appliances work on a definite voltage difference and in the series combination, the voltage...
What will the resultant resistance be if five 0.2 ohm resistances are linked in series?
Answer: The cumulative resistance of any number of resistances connected in series equals the individual resistances, according to the law of series combination of resistances. R = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4...
Q6. State the factors on which the strength of electric current flowing in a given conductor depends.
Answer: The following are the factors that influence the strength of an electric current flowing through a conductor: a) The voltage (or potential difference) between the conductor's ends b) The...
Are the lights in your house wires in series?
Answer: In our homes, the lights are not connected in a series. They are linked in a parallel manner. The home's electric appliances are connected in parallel combinations to achieve the same...
Q5. Keeping the resistance constant, the potential difference applied across the ends of a component is halved. By how much does the current change?
Answer: Given in question : Resistance = constant We know that V = IR When resistance, R is constant, V is proportional to I Therefore, when V is halved, I also becomes half.
Give the law of series resistance combination.
Answer: According to the law of series combination of resistances, the combined resistance of any number of resistances connected in series equals the individual resistances.
Q4. What is the general name of the substances having infinitely high electrical resistance?
Answer: Insulators are materials with an infinitely high electrical resistance.
Q3. Name the physical quantity whose unit is “ohm”.
Electric resistance is a physical quantity with an ohm unit.
Q2. Name the unit of electrical resistance and give its symbol.
Electrical resistance is measured in Ohms. The ohm symbol is as follows:Ω
Which electric heating devices in your home do you think have resistors which control the flow of electricity?
Answer The electric heating devices with resistors that control the flow of electricity are as follows: a) Iron (electric) c) Heater for the room c) Thermostat d) Oven (electric)
An electric iron is connected to the mains power supply of 220V. When the electric iron is adjusted at ‘minimum heating’ it consumes a power of 360W but at ‘maximum heating’ it takes a power of 840W. Calculate the current and resistance in each case.
Answer Given, 220 volts 360W = Pmin 840 W (Pmax) When the heat is turned down to a bare minimum, VI = Pmin I220 = 360 1.63 amps I V/I = R R = 1.63/1.63/1.63/1.63/1.63/1.63 134.96 ohms R = 134.96...
Two exactly similar heating resistances are connected in series and in parallel in two different circuits one by one. If the same current is passed through both the combinations, is more heat obtained per minute when they are connected in series or when they are connected in parallel? Give reason for your answer.
Answer More heat is obtained each minute when the heating resistances are connected in series. This is due to the fact that the overall resistance in a series configuration is higher than the total...
Name the law which relates the current in a conductor to the potential difference across its ends.
Ohm's law is a law that connects the current in a conductor to the potential difference between its ends. The conductor is the type of metal which allows the electrical current to flow through it.
a) How does the wire in the filament of a light bulb behave differently to the other wires in the circuit when the current flows? b) What property of the filament wire accounts for this difference?
Answer a) The behaviour of the filament wire in a light bulb differs from the behaviour of the other wires in the circuit, since the filament wire becomes white hot while the other wires do not. b)...
The electrical resistivities of four materials P, Q, R, and S are given below: P: 6.84 × 10-8Ωm Q: 1.70 × 10-8Ωm R: 1.0 × 1015Ωm S: 11.0 × 10-7Ωm Which material will you use for making: a) heating element of electric iron b) connecting wires of electric iron c) covering of connecting wires Give reason for your choice in each case.
Answer a) An electric iron's heating element is S, which has a high resistance. This is a nichrome substance. b) An electric iron's connecting wires are Q because they have a low resistance. Copper...
If 20C of charge pass a point in a circuit in 1s, what current is flowing?
Answer: Given the information in the question: Charge moved, Q = 20C Time is taken, t = 1s To find, Current, I We know that the current is calculated as follows: I = Q/t We get by substituting the...
If the current flowing through a fixed resistor is halved, the heat produced in it will becomes: a) double b) one-half c) one-fourth d) four times
Answer c) four times is the correct answer. When the current flowing through a fixed resistor is cut in half, the heat generated in the resistor increases to four times its original value.
Which of the following is the most likely temperature of the filament of an electric light bulb when it is working on the normal 220V supply line? a) 500°C b) 1500°C c) 2500°C d) 4500°C
Answer b) 2500°C is the correct answer.
In a filament types light bulb, most of the electric power consumed appears as: a) visible light b) infrared rays c) ultraviolet rays d) fluorescent light
Answer B) infrared rays is the right answer. Infrared rays are produced by the electric power consumed by a filament type light bulb.
Which of the following characteristics is not suitable for a fuse wire? a) thin and short b) thick and short c) low melting point d) higher resistance than rest of wiring
Answer b) thick and short is the correct answer. When a fuse wire is thick, there are more electrons available, which is not a desirable feature of a fuse wire.
The heat produced in a wire of resistance ‘x’ when a current ‘y’ flows through it in time ‘z’ is given by: a) x2 × y × z b) x × z × y2 c) y × z2 × x d) y × z × x
Answer b) x z y2 is the correct answer.
The elements of electric heating devices are usually made of: a) tungsten b) bronze c) nichrome d) argon
Answer c) nichrome is the correct answer. Nichrome is used to make the components of electric heating equipment.
An electric fuse works on the: a) chemical effect of current b) magnetic effect of current c) lighting effect of current d) heating effect of current
Answer The correct answer is d) present heating impact. The working principle of an electric fuse is the heating effect of current.
The current passing through an electric kettle has been doubled. The heat produced will becomes: a) half b) double c) four times d) one-fourth
Answer c) four times is the correct answer. When the current in an electric kettle is doubled, the heat produced increases by four times.
The heat produced by passing an electric current through a fixed resistor is proportional to the square of: a) magnitude of resistance of the resistor b) temperature of the resistor c) magnitude of current d) time for which current is passed
Answer The correct answer is c) present magnitude. The heat generated by an electric current travelling through a fixed resistor is proportional to the square of the current magnitude.
Name the unit of electrical resistance and give its symbol.
Answer: An object's electrical resistance is a measure of its resistance to the flow of electric current. Electrical resistance is measured in Ohms. The ohm symbol is as follows: Ω
100 joules of heat is produced per second in a 4ohm resistor. What is the potential difference across the resistor?
Answer Given, 100J = H T = 1 second 4 ohms R = 4 ohms R = 4 ohm We are aware of this. I2RT = H I2 x 4 x 1 = 100 I2 = 100/4 5 amps = I IR = V 5 x 4 = V V equals 20
A resistance of 25Ω is connected to a 12V battery. Calculate the heat energy in joules generated per minute
Answer Given, R equals 25 V Equals 12 volts T = 60 seconds ? = H IR = V I=12/25 I=0.48 amp We are aware of this. H=I^2 RT H=345.6J
An electric heater of resistance 8Ω takes a current of 15A from the mains supply line. Calculate the rate at which heat is developed in the heater.
Answer Given, 8 ohm R Equals 8 ohm R = 8 ohm 15 amps = I T = 1 second We are aware of this. I2RT = H 1800 J/s H
A heating coil has a resistance of 200Ω. At what rate will heat be produced in it when a current of 2.5A flows through it?
Answer Given, R = 200 ohms ohms ohms ohms 2.5 amps I T = 1 second We are aware of this. I2RT = H 1250 J/s H
Name the law which relates the current in a conductor to the potential difference across its ends.
Answer: Ohm's law is a law that connects the current in a conductor to the potential difference between its ends.
When a current of 4amp passes through a certain resistor for 10 minutes, 2.88 × 104 J of heat are produced. Calculate a) the power of the resistor b) the voltage across the resistor
Answer Given, 4 amps = I T = 10 minutes = 600 seconds 2.88 104 J H = 2.88 104 J H = 2.88 104 J H = 2.88 104 a) We are aware of this. I2RT = H 42600R = 28800R...
Explain why, tungsten is used for making the filaments of an electric bulb.
Answer Because tungsten has an extremely high melting point, it is utilised to make electric bulb filaments. This means that the filament will continue to burn hot but will not melt. Tungsten is...
State three factors on which the heat produced by an electric current depends. How does it depend on these factors?
Answer The three elements that influence the amount of heat created by an electric current are as follows: a) The amount of heat produced is proportional to the square of the current. b) The amount...
Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow hot while the heating element does?
Answer Electrical resistivity is a measurement of how well a substance resists the passage of electricity, whereas conductivity is a measure of how easily electricity flows. The heater's heating...
Explain why, filament type electric bulbs are not power efficient.
Answer Filament-type electric bulbs are inefficient because they waste the majority of their electricity as heat, with only a small portion converted to light.
Name two gases which are filled in filament type electric light bulbs.
Answer The two gases that are used to fill filament type electric light bulbs are as follows: Argon (a) Nitrogen (b)
Name two devices which work on the heating effect of electric current.
Answer The two devices that work on the heating effect of an electric current are as follows: a) An electric space warmer b) Fuse (electric)
Which effect of current is utilized in the working of an electric fuse?
Answer An electric fuse works by utilising the heating impact of current.
Which effect of current is utilized in an electric light bulb?
Answer An electric light bulb makes use of the current's heating effect.
Name two effects produced by electric current.
Answer The two impacts of electric current are as follows: a) Effect of heating b) Magnetic attraction
If the current passing through a conductor is doubled, what will be the change in heat produced?
Answer When the current going through a conductor is doubled, the amount of heat produced quadruples. This is due to the fact that the amount of heat produced is proportional to the square of the...
How does the heat H produced by a current passing through a fixed resistance wire depend on the magnitude of current I?
Answer: The amount of heat created by a current flowing through a fixed resistance wire is exactly proportional to the amount of current I flowing through the wire.
What do the following symbols mean in circuit diagrams?
Answer: a) In the circuit schematic, the symbol above denotes variable resistance. b) In the circuit schematic, the symbol above represents a closed plug key.
Compare how an ammeter and a voltmeter are connected in a circuit?
Answer: The ammeter is connected in series in an electric circuit, while the voltmeter is connected in parallel.
Which of the two is connected in series: ammeter or voltmeter?
Answer: The ammeter is linked in series with the voltmeter in place of the ammeter.
a) How many milliamperes are there in 1 ampere? b) How many microamperes are there in 1 ampere?
Answer: a)This table shows how many milliamperes there are in a single ampere: 1 amp = 103 milliamp b) The following is of the microamperes that are contained inside one ampere: 1 amp = 106 micro...
What is the unit of electric current?
Answer: The unit of electric current is ampere. Current is denied when the rate at which charge flows through the conductor is less than a certain threshold.
Which of the following equations shows the correct relationship between electrical units? 1A = 1C/s or 1C = 1A/s
Answer: The correct is 1A = 1C/s Current is denied when the rate at which charge flows through the conductor is less than a certain threshold. As a result, the right relationship is I=q/t, where q...
a) In which direction does conventional current flow around a circuit? b) In which direction do electrons flow?
Answer: a) Traditional current is carried from the positive terminal of the batter to its negative terminal in the outer circuit. b) In a battery, electrons move from the negative terminal to the...
Which particles constitute the electric current in a metallic conductor?
Answer: An electric current in a metallic conductor is made up of electrons, which are the particles that make up the current.
What actually travels through the wires when you switch on a light?
Answer: When the light is turned on, there is an increase in the flow of electrons across the wires.
What is the flow of charge called?
Answer: Electric current is the term used to describe the passage of charge. A conductor's electric current can be defined as the rate at which negative charges flow through it. Alternately, it can...
By what name is the physical quantity coulomb/second called?
Answer: The physical quantity coulomb/second is referred to as the ampere in the scientific community. It is defined as the elementary charge e, which has a value of 1.602 × 10-19 and is expressed...
The atoms of copper contain electrons and the atoms of rubber also contain electrons. Then why does copper conduct electricity but the rubber does not conduct electricity?
Answer: Copper atoms possess electrons, as do rubber atoms, however copper conducts electricity while rubber does not because copper contains unbound electrons held loosely together by the nucleus...
Three 2V cells are connected in series and used as battery in a circuit. a) What is the p.d at the terminals of the battery? b) How many joules of electric energy does 1C gain on passing through one cell and all the three cells?
Answer: a) As an example, if three cells, each having a voltage of 2 volts, are connected in series for the purpose of building a battery, the total potential difference between the terminals of the...
One coulomb charge is equivalent to the charge obtained in: a) 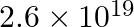 electrons b)
electrons b) 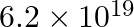 electrons c)
electrons c)  electrons d)
electrons d)  electrons
electrons
Answer: The correct option is d) 6.25×1018 electrons There are 6.25×1018 electrons in a one-coulomb charge. A coulomb is a charge carried by an ampere per the second current. 1C=1A * 1s We know...
The unit for measuring potential difference is: a) Watt b) Ohm c) Volt d) kWh
Answer: It is c) Volt that is the correct answer. For measuring the potential difference, the volt is the unit of measurement.
Which of the following units could be used to measure electric charge? a) Ampere b) Joule c) Volt d) Coulomb
Answer: The correct choice is d) Coulomb's law. Coulomb is a unit of measurement for electric charge that is used in science.
The device used for measuring potential difference is known as: a) Potentiometer b) Ammeter c) Galvanometer d) Voltmeter
Answer: It is d) Voltmeter that is the correct answer. A voltmeter is a gadget that is used to measure the difference between two potentials.
The work done in moving a unit charge across two points in an electric circuit is a measure of: a) Current b) Potential difference c) Resistance d) Power
Answer: It is b) Potential difference that is the correct answer. The potential difference between two places in an electric circuit is a measure of the amount of work required to move a unit charge...
e) State whether a voltmeter has a high resistance or a low resistance. Give reason for your answer.
Answer: In order to function, the resistance of the voltmeter must be high since it must draw only a small amount of current from an electric circuit.
c) What is the potential difference between the terminals of a battery if 250 joules of work is required to transfer 20 coulombs of charge from one terminal of battery to the other?
d) What is a voltmeter? How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points. Explain with the help of a diagram.
c) Given, Work done = 250J Charge moved = 20C To find Potential difference We know that potential difference is given as Potential difference = (Work done)/(Charge moved) p.d = (250)/(20) = 12.5...
a) What do you understand by the term “potential difference”? b) What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 volt?
Answer: a) The potential difference between two points is defined as the amount of work required to move a unit positive charge from one point to the other point. b) A 1-volt difference in potential...
a) Name a device that helps to measure the potential difference across a conductor. b) How much energy is transferred by a 12V power supply to each coulomb of charge which it moves around a circuit?
Answer: a) Voltmeter: a device that helps to measure the potential difference across a conductor. b) Given in question: Potential difference = 12V Charge moved = 1C To find, Work done We know that...
a) State the relation between potential difference, work done, and charge moved. b) Calculate the work done in moving a charge of 4 Coulomb from a point at 220 Volts to another point at 230 Volt.
Answer: a) The relation between potential difference, work done, and charge moved: Potential difference = (Work done)/(Charge moved) b) Given information in question: V1 = 220V V2 = 230V Charge...
What do you understand by the term “electric potential” at a point? What is the unit of electric potential?
Answer: The electric potential at a given point is defined as the amount of work required to move a unit positive charge from infinity to a specific point in space. The unit of electric potential is...
Which of the following are conductors and which are insulators? Sulphur, silver, copper, cotton, aluminium, air, nichrome, graphite, paper, porcelain, mercury, mica, Bakelite, polythene, manganin
Answer: Conductors are defined as the materials that allow an electric current to flow across their surfaces. Almost all metals are examples of conductors, including gold and silver. Insulators are...
What is meant by conductors and insulators? Give two examples of conductors and two of insulators.
Answer: Conductors are defined as the materials that allow electric current to flow across their surfaces. Almost all metals are examples of conductors, including gold and silver. The following are...
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words: a) Potential difference is measured in …………… by using a ……….. placed in …………… across a component. b) Copper is a good ……….. plastic is an …………….
Answer: a) Volts, voltmeter, parallel b) Conductor, insulator
Define one coulomb charge.
Answer: A coulomb is the amount of charge produced by a one-ampere current flowing for one second.
From a uniform disc of radius  , a circular hole of radius
, a circular hole of radius 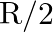 is cut out. The centre of the hole is at
is cut out. The centre of the hole is at 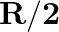 from the centre of the original disc. Locate the centre of gravity of the resulting flat body
from the centre of the original disc. Locate the centre of gravity of the resulting flat body
Let the unit area of the original disc be $\sigma$ The radius of the original disc is given as $2r$ Mass of the original disc can be calculated as $m=\pi\left(2 r^{2}\right) \sigma=4 \pi r^{2}...
A rope of negligible mass is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 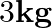 and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
Mass of the hollow cylinder is given as $m=3 \mathrm{~kg}$ Radius of the hollow cylinder is given as $r=40 \mathrm{~cm}=0.4 \mathrm{~m}$ So, force applied will be $F=30 \mathrm{~N}$ Calculating the...
(a) A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 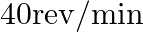 . How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to
. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 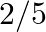 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction
times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction
(b) Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
(a) Initial angular velocity, is given as $\omega_{1}=40 \mathrm{rev} / \mathrm{min}$ Suppose the final angular velocity be $\omega_{2}$ Let the moment of inertia of the boy with stretched hands be...
A solid cylinder of mass 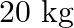 rotates about its axis with angular speed
rotates about its axis with angular speed 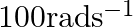 . The radius of the cylinder is
. The radius of the cylinder is 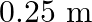 . What is the kinetic energy associated with the rotation of the cylinder? What is the magnitude of angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis?
. What is the kinetic energy associated with the rotation of the cylinder? What is the magnitude of angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis?
Mass of the cylinder is given as $m=20 \mathrm{~kg}$ Angular speed is given as $\omega=100 \mathrm{rad} \mathrm{s}^{-1}$ Radius of the cylinder is given as $r=0.25 \mathrm{~m}$ So, the moment of...
(a) Find the moment of inertia of a sphere about a tangent to the sphere, given the moment of inertia of the sphere about any of its diameters to be 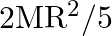 , where
, where 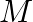 is the mass of the sphere and
is the mass of the sphere and 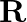 is the radius of the sphere.
is the radius of the sphere.
(b) Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius 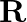 about any of its diameters to be
about any of its diameters to be 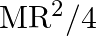 , find its moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge.
, find its moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge.
The moment of inertia of a sphere about its diameter is $=2 \mathrm{MR}^{2} / 5$ and is also shown in the figure, As the the theorem of parallel axes says, M.I of a sphere about a tangent to the...
A 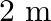 irregular plank weighing
irregular plank weighing 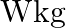 is suspended in the manner shown below, by strings of negligible weight. If the strings make an angle of
is suspended in the manner shown below, by strings of negligible weight. If the strings make an angle of 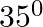 and
and 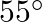 respectively with the vertical, find the location of center of gravity of the plank from the left end.
respectively with the vertical, find the location of center of gravity of the plank from the left end.
Following is the FBD(Free Body Diagram) for the above figure: Length of the plank is given as $\mid=2 \mathrm{~m}$ $\theta_{1}=35^{\circ}$ and $\theta_{2}=55^{\circ}$ Let the tensions produced in...
Two particles, each of mass 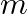 and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance
and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance 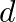 . Show that the angular momentum vector of the two-particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken
. Show that the angular momentum vector of the two-particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken
Considering three points $Z, C$ and $X$ : Angular momentum at Z will be given as, $\mathrm{Lz}=\mathrm{mv} \times 0+\mathrm{mv} \times \mathrm{d}$ $=\mathrm{mvd}-(1)$ Angular momentum about $x$ will...
Show that 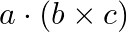 is equal in magnitude to the volume of the parallelepiped formed on the three vectors,
is equal in magnitude to the volume of the parallelepiped formed on the three vectors,  and
and 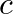 .
.
Let the parallelepiped formed be: where, $\overrightarrow{O J}=\vec{a}, \overrightarrow{O L}=\vec{b}$ and $\overrightarrow{O K}=\vec{c}$ $\hat{n}$ is a unit vector along $\mathrm{OJ}$ and is...
A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed 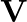 on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
The child and the trolley are one system, and the youngster's movement within the cart is entirely internal. The velocity of the system's centre of mass will not change because there is no external...
A star  times the mass of the sun and collapsed to a size of 12 km rotates with a speed of
times the mass of the sun and collapsed to a size of 12 km rotates with a speed of  rev. per second. (Extremely compact stars of this kind are known as neutron stars. Certain stellar objects called pulsars belong to this category). Will an object placed on its equator remain stuck to its surface due to gravity? (mass of the sun
rev. per second. (Extremely compact stars of this kind are known as neutron stars. Certain stellar objects called pulsars belong to this category). Will an object placed on its equator remain stuck to its surface due to gravity? (mass of the sun 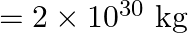 ).
).
If the outward centrifugal force is lesser than the inward gravitational pull, any matter will remain stuck to the surface. Gravitational force is given by the relation: $f_{G}=\frac{G M m}{R^{2}}$...
What is the unit of electric charge?
Answer: The unit of electric charge is the coulomb (coulomb). In electrical engineering, the term "coulomb" refers to the charge that is transferred with the help of a constant current of one ampere...
Two stars each of one solar mass 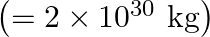 are approaching each other for a headon collision. When they are a distance
are approaching each other for a headon collision. When they are a distance 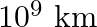 , their speeds are negligible. What is the speed with which they collide? The radius of each star is
, their speeds are negligible. What is the speed with which they collide? The radius of each star is 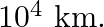 Assume the stars to remain undistorted until they collide. (Use the known value of G).
Assume the stars to remain undistorted until they collide. (Use the known value of G).
Mass of each star is given as $M=2 \times 10^{30} \mathrm{~kg}$ Radius of each star is given as $R=10^{4} \mathrm{~km}=10^{7} \mathrm{~m}$ Distance between the stars is given as $r=10^{9}...
How much work is done in moving a charge of 2C across two points having a potential difference of 12V?
Answer: Given, Potential difference = 12V Charge moved = 2C To find, Work done We know that the work done is given as Work done = p.d × charge moved = 12 × 2 = 24J So, to move a 2C charge with a 12V...
A rocket is fired vertically with a speed of 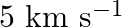 from the earth’s surface. How far from the earth does the rocket go before returning to the earth? Mass of the earth
from the earth’s surface. How far from the earth does the rocket go before returning to the earth? Mass of the earth 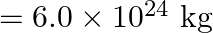 ; mean radius of the earth
; mean radius of the earth 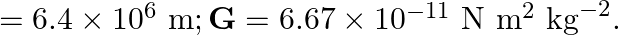
Velocity of the missile is given as $v=5 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ Mass of the Earth is known as $M_{E}=6 \times 10^{24} \mathrm{~kg}$ Radius of the Earth is given as $R_{E}=6.4 \times...
What is the SI unit of potential difference?
Answer: The SI unit of potential difference is volts. It is a potential difference that resists a resistance of one ohm through a current of one ampere.
How much work is done when one-coulomb charge moves against a potential difference of 1 volt?
Answer: Given the information in question: Potential difference = 1V Charge to be moved = 1C To find, Work done We know that the work done is given as: Work done = Potential difference × Charge...
What is meant by saying that the electric potential at a point is 1 volt?
Answer: In order to move one unit of positive charge from infinity to a specific point, the electric potential at that point must be one volt, which means that one joule of work must be done.
A body weighs 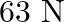 on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it due to the earth at a height equal to half the radius of the earth?
on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it due to the earth at a height equal to half the radius of the earth?
Weight of the man is given as $W=63 \mathrm{~N}$ Acceleration due to gravity at height 'h' from the Earth's surface is: g'=g1+hRe2...
a) What do the letters p.d stand for? b) Which device is used to measure p.d?
Answer: a).) p.d. stand for potential difference b) voltmeter is a device which used to measure potential difference
How will you ‘weigh the sun’, that is estimate its mass? The mean orbital radius of the earth around the sun is 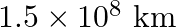 .
.
Earth's orbit has a radius of $r=1.5 \times 10^{11} \mathrm{~m}$ Time taken by the Earth for one complete revolution can be $\mathrm{T}=1$ year $=365.25$ days i.e. $T=(365.25 \times 24 \times 60...
Choose the correct answer from among the given ones: the direction of the gravitational intensity at an arbitrary point  is indicated by the arrow (i)
is indicated by the arrow (i)  , (ii) e, (iii) f, (iv)
, (ii) e, (iii) f, (iv)  .
.
(ii) e Reason: From the previous response, we can deduce that, The gravitational intensity at P is directed downwards along 'e' using the logic/explanation
Which of the following statements correctly defines a volt? a) A volt is a joule per ampere b) A volt is a joule per coulomb
Answer: The joule/coulomb is also known as volt. The SI unit of electric potential is the volt. The potential difference between two points of a current-carrying wire of 1 ampere is represented by...
By what other name is the unit joule/coulomb called?
Answer: The joule/coulomb is also known as volt. The SI unit of electric potential is the volt. The potential difference between two points of a current-carrying wire of 1 ampere is represented by...
Which of the following symptoms is likely to afflict an astronaut in space
(a) headache,
(b) orientational problem.
(a). Astronauts may get headaches as a result of the increased blood supply to their faces. (b). Because space has multiple orientations, an astronaut may experience orientational issues.
Which of the following symptoms is likely to afflict an astronaut in space
(a) swollen feet,
(b) swollen face
(a) Because blood flow to the feet is not increased in zero gravity, the astronaut's feet do not swell. (b) There is more blood supply to the astronaut's face. As a result, the astronaut's face will...
A comet orbits the Sun in a highly elliptical orbit.
(a) potential energy
(b) total energy throughout its orbit? Neglect any mass loss of the comet when it comes very close to the Sun.
(a) Potential energy changes along the path. (b) Total energy will remain constant throughout the orbit.
A comet orbits a sun in a highly elliptical orbit. Does the comet have a constant
(a) linear speed,
(b) angular speed,
(c) angular momentum,
(d) kinetic energy,
(e) potential energy,
(f) total energy throughout its orbit? Neglect any mass loss of the comet when it comes very close to the sun.
A comet in an elliptical orbit around the Sun has constant angular momentum and total energy owing to the Law of Conservation of Energy at all locations, but other variables change. The torque...
Does the escape speed of a body from the earth depend on
(a) the direction of projection,
(b) the height of the location from where the body is launched?
The escape speed can be given by the relation, $v=\sqrt{\frac{2 G M}{R}}=\sqrt{2 g R}$ (a) The escape speed does not depend on the direction of projection of a body. (b) Because the escape velocity...
Choose the correct alternative:
(a) If the zero of potential energy is at infinity, the total energy of an orbiting satellite is negative of its kinetic/potential energy.
(b) The energy required to launch an orbiting satellite out of earth’s gravitational influence is more/less than the energy required to project a stationary object at the same height (as the satellite) out of earth’s influence.
(a) The total energy of an orbiting satellite is negative of its kinetic energy if the zero potential energy is at infinity. (b) The energy required to launch an orbiting satellite out of Earth's...
Let us assume that our galaxy consists of  stars each of one solar mass. How long will a star at a distance of
stars each of one solar mass. How long will a star at a distance of 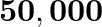 ly from the galactic centre take to complete one revolution? Take the diameter of the Milky Way to be
ly from the galactic centre take to complete one revolution? Take the diameter of the Milky Way to be 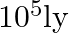 .
.
Mass of our galaxy is given as $M=2.5 \times 10^{11}$ solar mass 1 Solar mass as we know is, Mass of Sun $=2 \times 10^{30} \mathrm{~kg}$ Mass of our galaxy as we know is $M=2.5 \times 10^{11}...
lo, one of the satellites of Jupiter, has an orbital period of 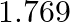 days and the radius of the orbit is
days and the radius of the orbit is 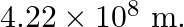 Show that the mass of J upiter is about one-thousandth that of the sun.
Show that the mass of J upiter is about one-thousandth that of the sun.
Orbital period of $I0$, is given as $T_{10}=1.769$ days $=1.769 \times 24 \times 60 \times 60 \mathrm{~s}$ Orbital radius of $I0$, is given as $R_{10}=4.22 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~m}$ Mass of jupiter...
Suppose there existed a planet that went around the Sun twice as fast as the earth. What would be its orbital size as compared to that of the earth?
Time taken by the earth for one complete revolution is represented by $\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{E}}$ having value $1$ Year Radius of Earth's orbit is represented by $\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{E}}$ having value...
Choose the correct alternative:
(a) Acceleration due to gravity is independent of the mass of the earth/mass of the body.
(b) The formula 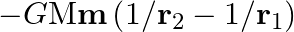 is more/less accurate than the formula
is more/less accurate than the formula 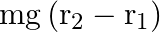 for the difference of potential energy between two points
for the difference of potential energy between two points  and
and  distance away from the centre of the earth.
distance away from the centre of the earth.
(a) Acceleration due to gravity is given by the formula: $g=G{{M}_{e}} /{{ {R}_{e}}^{2}}$ is Hence, it is independent of mass of body, but is dependent on mass of earth. (b) Gravitational...
Choose the correct alternative:
(a) Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing altitude.
(b) Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing depth (assume the earth to be a sphere of uniform density).
(a) According to the formula g′=g(1-R2h), acceleration decreases. where h is the height and R is the earth's radius (b) According to the formula g′=g(1−Rd),, acceleration decreases. where d is the...
Answer the following: If you compare the gravitational force on the earth due to the sun to that due to the moon, you would find that the Sun’s pull is greater than the moon’s pull. (you can check this yourself using the data available in the succeeding exercises). However, the tidal effect of the moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of the sun. Why?
Tidal effects are inversely proportional to the cube of distance, whereas gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of distance. The moon will have a stronger influence on the...
The front face of a circular wire carrying current behaves like a north pole. The direction of current in this face of the circular wire is: a) clockwise b) downwards c) anticlockwise d) upwards
Answer: The correct option is c) anticlockwise The front face of the circular wire (or coil) is the South pole if the current flows clockwise around it (S-pole). The current flow in the circular...
The magnetic field lines in the middle of the current-carrying solenoid are: a) circles b) spirals c) parallel to the axis of the tube d) perpendicular to the axis of the tube
Answer: The correct option is c) parallel to the axis of the tube Explanation: The magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying solenoid are parallel to the tube's axis.
A soft iron bar is inserted inside a current-carrying solenoid. The magnetic field inside the solenoid: a) will decrease b) will increase c) will become zero d) will remain the same
Answer: The correct option is b) will increase Explanation: To boost the magnetic field within a current-carrying solenoid, insert a soft iron bar. The iron bar gains magnetic properties when...
The magnetic effect of current was discovered by: a) Maxwell b) Fleming c) Oersted d) Faraday
Answer: The correct option is c) Oersted Explanation: Hans Christian Oersted discovered the magnetic effect of electricity in 1820. He showed the effect by observing the deflection of a long...
The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is: a) soft iron b) brass c) aluminum d) steel
Answer: The correct option is a) soft iron Explanation: When creating the core of an electromagnet, soft iron is preferred over hard iron because the core is employed in a solenoid to generate the...
If the direction of electric current in a solenoid when viewed from a particular end is anticlockwise, then this end of solenoid will be: a) west pole b) south pole c) north pole d) east pole
Answer: The correct option is c) north pole Explanation: Using the clock face rule, we found that if the flow of electric current in a solenoid is anticlockwise, that end is the north pole. Both a...
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be: a) north pole b) east pole c) south pole d) west pole
Answer: The correct option is c) south pole Explanation: An electromagnet is a current-carrying coil that might be regarded to be inductive. To determine which end of the electromagnet will behave...
The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using: a) Fleming’s right-hand rule b) Fleming’s left-hand rule c) Clock face rule d) Left-hand thumb rule
Answer: The correct option is c) Clock face rule Explanation: Option c is the best choice. This rule is more straightforward than other rules because it only requires that you glance at the coil...
Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wore? a) the field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire b) the field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire c) the field consists of radial lines originating from the wire d) the field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire
Answer: The correct option is d) the field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire Explanation: In magnetism and electricity, a straight wire or conductor forms concentric magnetic...
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current: a) is zero b) decreases as we move towards its ends c) increases as we move towards its ends d) is the same at all points
Answer: option d) A long straight solenoid's magnetic field is constant. The magnetic field in the solenoid is constant since the lines are parallel.
The strength of the magnetic field between the poles of an electromagnet would be unchanged if: a) current in the electromagnet winding were doubled b) direction of current in electromagnet were reversed c) distance between the poles of electromagnet were doubled d) material of the core of electromagnet were changed
Answer: The correct option is b) direction of current in electromagnet were reversed. Answer: The electromagnetic winding's current direction is reversed only on one side of the pole. The magnetic...
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is: a) the process of charging a body b) the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil d) the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor
Answer: The correct option is c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil Explanation: According to Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction, a...
A horizontal wire carries a current as shown in figure below between magnetic poles N and S: Is the direction of the force on the wire due to the magnet: a) in the direction of the current b) vertically downwards c) opposite to the current direction d) vertically upwards
Answer: The correct answer is d) vertically upwards Explanation: Using Fleming's left-hand rule, the wire's force acts vertically upward. The index finger indicates the direction of the magnetic...
A magnetic field exerts no force on: a) an electric charge moving perpendicular to its direction b) an unmagnetized iron bar c) a stationary electric charge d) a magnet
Answer: The correct option is c) a stationary electric charge Explanation: The magnetic field is the area around a magnet where the magnetic force is delivered. The magnetic field lines can be...
