(a) Na and K (b) K and C (c) Na and S (d) K and P Solution: Option (a) is the answer. Phenolphthalein is a synthetic indicator that remains colourless in acidic and neutral environments but turns...
(c) State three reasons (of which at least one must be chemical) for believing that sodium is a metal. (d) State three reasons (of which at least one must be chemical) for believing that sulphur is a non-metal. (e) Which non-metal has been placed in the reactivity series of metals?
Solution: (c) Sodium exists in solid form. It is a conductor of electricity and a source of basic oxides. As a result, sodium is classified as a metal. (d) Sulphur is a hard, brittle substance. It...
(a) State any three differences between the physical properties of metals and non-metals. (b) Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Solution: (a) Differences in physical properties between metals and non-metals 1. Metals are malleable, whereas nonmetallic materials are not. 2. Non-metals are non-ductile, whereas metals are...
(c) Name one metal more reactive and another less reactive than hydrogen.
(d) Name one metal that displaces copper from copper sulphate solution and one which does not. (e) Name one metal that displaces silver from silver nitrate solution and one which does not....
(a) What is meant by the reactivity series of metals? Arrange the following metals in increasing order of their reactivities towards water: Zinc, Iron, Magnesium, Sodium. (b) Hydrogen is not a metal but still, it has been assigned a place in the reactivity series of metals. Why?
Solution: (a) A reactivity series is a vertical column of items arranged in decreasing order of their reactivities. Increasing order of reactivity : Iron< Zinc< Magnesium< Sodium (b)...
(e) How do non-metals react with oxygen? Explain with an example. Give an equation of the reaction involved. What is the nature of the product formed? How will you demonstrate it?
(e) Acidic or neutral oxides are formed when non-metals react with oxygen. Carbon dioxide is produced when carbon is burned in the air. C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) The resulting product is acidic....
(c) Name a non-metal having lustre (shining surface). (d) Name a non-metal which is extremely hard.
(c) Iodine has a lustrous sheen to it. Iodine is a chemical element with atomic number 53 and the symbol I. (d) Carbon allotrope diamonds are extremely hard. Carbon is a chemical element with the...
c) Explain how sun is considered to be the ultimate source of fossil fuels.
d) Which fossil fuels were formed by the buried remains of small plants and animals? e) Which fossil fuel was formed by the buried remains of large land plants? Answer – c) The sun is regarded...
a) What are fossil fuels? Give three examples of fossil fuels.
b) Describe how fossil fuels were formed. Answer – a) Fossil fuels are natural fuels that are created deep beneath the earth's surface from prehistoric species' remains. Fossil fuels include coal,...
Why is the leakage of LPG detected easily although it is odourless? State the steps to be taken in case its leakage is detected in the kitchen.
Answer: LPG is an odourless material that can nonetheless be detected by its odour due to the addition of mercaptan to the LPG. The actions to take in the event of an LPG leak in the kitchen are as...
Why is LPG considered a better fuel than coal?
Answer: LPG is a better fuel than coal because when coal is burned, dangerous gases are released, however when LPG is burned, no harmful gases are generated..
Why is LPG considered a good fuel?
Answer: Because of its calorific value and lack of hazardous gas production, LPG is considered a good fuel. LPG also has a high calorific value.
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Answer: LPG is utilised as a source of energy for heating food since it has a high calorific value and produces smokeless flames.
What are the various steps which can be taken to control pollution caused by burning fossil fuels?
Answer: Increasing the efficiency of the combustion process and developing strategies to decrease the discharge of toxic gases and ashes into nature are two steps that can be taken to control...
What are the various steps which can be taken to control pollution caused by burning fossil fuels?
Answer: Increasing the efficiency of the combustion process and, developing strategies to decrease the discharge of toxic gases and ashes into nature are two steps that can be taken to control...
Write a short note on the pollution caused by burning fossil fuels.
Answer: When fossil fuels are burned, acidic gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide are released. Acid rain is caused by these chemicals, which harm trees, buildings, and plants while...
What are the disadvantages of burning fossil fuels?
Answer: The following are some of the disadvantages of burning fossil fuels: a) Acidic gases are produced when fossil fuels are burned. b) The amount of smoke produced is higher, as is the amount of...
Explain the principle of working of a thermal power plant. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
Answer: Heat is generated in thermal power plants by burning coal, which is then used to boil water and create steam. When high-temperature, high-pressure steam is introduced to turbines, it causes...
What is meant by conventional sources of energy? Write the names of two conventional sources of energy.
Answer: Traditional sources of energy are the traditional sources of energy that a great number of people are familiar with. Wood and coal are examples of traditional energy sources.
Explain why natural gas is considered to be a good fuel.
Answer: Natural gas is regarded as an excellent fuel since it has a high calorific value and burns with a smokeless flame, producing no hazardous fumes.
Complete the following sentence:
Domestic gas cylinders like Indane contain mainly …… Answer: Butane
State one important use of CNG these days.
Answer: CNG these days is being used as a fuel in transport vehicles which results in lesser air pollution.
State two important uses of natural gas.
Answer: The two most important uses of natural gas are as follows: It is utilised as a fuel in thermal power plants and transportation vehicles.
Name the component which is found in natural gas as well as in biogas.
Answer: Butane is the component which is found in natural gas as well as in biogas.
What is the main constituent of:
a) petroleum gas? b) natural gas? Answer: a) The main constituent of petroleum gas is butane b) The main constituent of natural gas is methane
Write the full form of: a) LPG b) CNG
Answer: a) Full form of LPG is Liquefied Petroleum Gas b) Full form of CNG is Compressed Natural Gas
Which gaseous fuel is being used increasingly in transport vehicles like cars and buses these days?
Answer: Compressed Natural Gas is used in transport vehicles such as cars and buses.
What is the composition of liquefied petroleum gas?
Answer: Liquefied petroleum gas is composed of butane with smaller amounts of propane and ethane.
Name any four fractions obtained from petroleum which are used as fuels.
Answer: Petroleum gas, diesel, kerosene, and petrol are the fractions derived from petroleum that are used as fuels.
What are the various fuels which are used to generate electricity in a thermal power plant?
Answer: Coal, gas, and oil are the different fuels utilised in the generation of electricity in a thermal power station.
Name any one hydrocarbon fraction obtained during the fractional distillation of petroleum which is used as a domestic fuel.
Answer: Kerosene is a hydrocarbon fraction derived by fractional distillation of petroleum and used as a household fuel.
Give one example of a good domestic fuel.
Answer: Liquified Petroleum Gas is an example of a good domestic fuel.
Name the product of petroleum that is used to drive heavy vehicles.
Answer: The product of petroleum that is used to drive heavy vehicles is Diesel.
Which of the following is not a fossil fuel?
a) coal b) petroleum gas c) biogas d) natural gas Answer: c) biogas Biogas is a renewable source while rest are non-renewable
One of the following is not a characteristics of a good fuel. This is:
a) high calorific value b) no emission of smoke c) smooth burning d) high ignition temperature Answer: d) high ignition temperature High ignition temperature leads to system instability and...
There are four fuels which all contain only carbon and hydrogen. The fuel having highest calorific value will be one which has:
a) more of carbon but less of hydrogen b) less of carbon but more of hydrogen c) equal proportions of carbon and hydrogen d) less of carbon as well as less of hydrogen Answer: b) less of...
The fuel having the lowest calorific value is:
a) coal b) wood c) charcoal d) kerosene Answer: b) wood
Which of the following fuels has the highest calorific value?
a) natural gas b) methane gas c) hydrogen gas d) biogas Answer: c) hydrogen gas
A newly planted sapling usually grows and mature into a tree in more than:
a) 50 years b) 25 years c) 45 years d) 15 years Answer: d) 15 years
The fuel having a calorific value of 55kJ/g is likely to be:
a) biogas b) methane gas c) hydrogen gas d) natural gas Answer: b) methane gas
A good fuel is one which possesses:
a) high calorific value and low ignition temperature b) high calorific value and high ignition temperature c) high calorific value and moderate ignition temperature d) low calorific value and...
Which of the following is not a renewable source of energy?
a) wind b) flowing water c) fossil fuels d) fuel wood Answer: c) fossil fuels Fossil fuels once exhausted can not be replenished.
A non-renewable source of energy is:
a) wood b) alcohol c) hydrogen gas d) natural gas Answer: d) Natural gas Natural Gas once exhausted can not be replenished.
An example of a renewable source of energy is:
a) petrol b) natural gas c) biogas d) kerosene Answer: c) biogas Only biogas is replenishable.
The calorific value and ignition temperature of fuel A are 55kJ/g and 80 degree Celsius respectively. These values for fuel B are 80kJ/g and 10 degree Celsius respectively. On burning, the fuel A produces CO2 and H2O while the fuel B produces CO2, CO, and SO2. Give three points of relative advantages and disadvantages of these two fuels.
Answer: Fuel-A i) It has a low calorific value of 55kJ/g, which is a drawback. ii) The ignition temperature is 80°C, which is moderate and advantageous. iii) No hazardous gases are created, which is...
a) What is a fuel? Give five examples of fuels.
b) What are the characteristics of an ideal fuel or good fuel? Answer: a) A fuel is a material that is burned to generate heat energy. The five types of fuels are wood, LPG, coal, kerosene, and...
Coal is said to be formed from the wood of trees. Why then is coal considered to be a non-renewable source of energy whereas wood is a renewable source of energy?
Answer: Because coal takes longer to accumulate than growing trees, it is regarded a non-renewable source of energy. Whereas wood is considered a renewable source of energy. As a result, utilising...
a) Classify the following into renewable and non-renewable sources of energy:
Coal, wind, tides, petroleum, wood , natural gas b) What is the basis of above classification? Answer: Wind, tides, and wood are examples of renewable energy sources. Coal, petroleum, and natural...
Name two sources of energy which you consider to be non-renewable. Give reason for your choice.
Answer: Petroleum and coal are the only non-renewable sources of energy. This is due to the fact that they cannot be reclaimed once they have been fully utilised.
Name two sources of energy that you think are renewable. Give reason for your choice.
Answer: Air and water are renewable energy sources since they are abundant in nature and may be used repeatedly.
Why are fossil fuels classified as non-renewable source of energy?
Answer: Fossil fuels are classified as non-renewable source of energy since once these are used completely these cannot be replenished.
What is the difference between a renewable and a non-renewable source of energy? Explain with examples.
Answer: The difference between a renewable and a non-renewable energy source is that a renewable energy source is abundant in nature, but a non-renewable energy source is finite. Overuse of...
What is meant by a renewable source of energy? Give two examples of renewable sources of energy.
Answer: A renewable energy source is described as a source of energy that is abundant in nature and may be used for an indefinite amount of time; it never runs out. Solar and wind energy are two...
What is meant by a non-renewable source of energy? Give two examples of non-renewable sources of energy.
Answer: A non-renewable energy source is described as one that will deplete rapidly if used for an extended length of time. These energy sources are only found in small amounts in nature. Coal and...
State any four characteristics of a good source of energy.
Answer: The following four properties will characterise a good source of energy: a) It's simple to store and move. b) The energy is simple to handle and secure. d) There is a lot of energy...
What is a source of energy? What are the two main categories of the sources of energy?
Answer: A source of energy is one from which a sufficient amount of energy can be obtained over an extended period of time. The two primary categories of energy sources are as follows: a) Renewable...
Fill in the blanks with a suitable word:
The amount of heat produced by burning a unit mass of a fuel completely is known as its ………. value. Answer: Calorific value.
“The ignition temperature of a fuel is 80 degree Celsius”. What does this mean?
Answer: When a fuel's ignition temperature is 80 degrees Celsius, it signifies that the fuel's lowest temperature for catching fire and burning is 80 degrees Celsius.
Define ignition temperature of a fuel.
Answer: A fuel's ignition temperature is defined as The minimal temperature at which it must be heated in order to catch fire and begin burning.
Define ignition temperature of a fuel.
Answer: A fuel's ignition temperature is defined as the minimal temperature at which it must be heated in order to catch fire and begin burning.
Which of the following produces more heat per unit mass on burning?
Coal or LPG Answer: Because LPG has a larger calorific value than coal, it will create more heat per unit mass when burned.
“The calorific value of cooking gas is 50kJ/g”. What does it mean?
Answer: Cooking gas has a calorific value of 50kJ/g, which indicates that if 1 gramme of LPG is totally burned,...
Define calorific value of a fuel.
Answer: The quantity of heat produced by totally burning 1 gramme of fuel is referred to as the calorific value of the fuel.
Name a non-renewable source of energy other than fossil fuels.
Answer: Other than fossil fuels, nuclear fuels such as uranium are a non-renewable source of energy.
The main constituent of petroleum gas is:
a) methane b) ethane c) butane d) propane Answer: The correct answer is c) butane
The natural gas consists of mainly of:
a) methane b) ethane c) propane d) butane Answer: The correct answer is a) methane
Which of the following is not produced by the burning of fossil fuels?
a) nitrogen oxides b) sulphur oxides c) sodium oxides d) carbon oxides Answer: The correct answer is c) sodium oxides
The product of petroleum used to drive heavy vehicles like trucks is:
a) petrol b) kerosene c) petrol d) CNG Answer: The correct answer is c) petrol
The aviation fuel which is used in the engines of jet aeroplanes is:
a) diesel b) kerosene c) petrol d) CNG Answer: The correct answer is b) kerosene
The ultimate source of energy stored in fossil fuels is:
a) moon b) earth c) sun d) sea Answer: The correct answer is c) sun
Which of the following is not a fossil source of energy?
a) kerosene oil b) cow-dung cakes c) CNG d) coal Answer: The correct answer is b) cow-dung cake
The fuel which is not used at thermal plants is:
a) coal b) uranium c) natural gas d) fuel oil Answer: The correct answer is b) uranium
LPG consists mainly of:
a) butane b) ethane c) butanone d) methane Answer: The correct answer is a) butane
Coke is more valuable when used:
a) as a fuel for industrial boilers b) as an oxidizing agent c) as a reducing agent d) as a fuel in domestic ovens Answer: The correct answer is c) as a reducing agent
Coal cannot be converted into one of the following forms of energy. This is:
a) coal gas b) electricity c) oil d) charcoal Answer: The correct answer is d) charcoal
One of the following does not contribute to acid rain. That is:
a) nitrogen monoxide b) sulphur dioxide c) carbon monoxide d) carbon dioxide Answer: The correct answer is c) carbon monoxide
A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on:
a) a sunny day b) a cloudy day c) a hot day d) a windy day Answer: The correct option is b) a cloudy day
At a hydro power plant:
a) kinetic energy possessed by stored water is converted into electrical energy b) electricity is extracted from water c) water is converted into steam to turn turbines and produce electricity d)...
The part of box-type solar cooker which is responsible for producing greenhouse effect is:
a) plane mirror reflector b) black coating inside the box c) glass sheet cover d) utensils placed in the cooker box Answer: The correct option is c) glass sheet cover
Solar cells are made of:
a) conductors b) insulators c) semiconductors d) superconductors Answer: The correct option is c) semiconductors
The value of solar constant is:
a) 1.4kWh b) 1.4kW/m c) 1.4kW/m2 d) 1.4kW/m3 Answer: The correct option is c) 1.4kW/m2
The radiations present in sunlight which make a solar cooker work are:
a) visible light rays b) ultraviolet rays c) cosmic rays d) infrared rays Answer: The correct option is d) infrared rays
In order to make an efficient solar cooker, the cover of cooker box should be made of:
a) transparent plastic sheet b) shining aluminum sheet c) butter paper sheet d) transparent glass sheet Answer: The correct option is d) transparent glass sheet
The minimum speed of wind necessary for the satisfactory working of a wind generator to produce electricity is about:
a) 15km/h b) 25km/h c) 35km/h d) 45km/h Answer: The correct option is a) 15km/h
If the solar constant is 1.4 kW/m2 then solar energy received by 1 m2 area in one hour is: (a) 5040 J (b) 504.0 kJ (c) 5040 kJ (d) 5.04 kJ
The correct option is c) 5040kJ Given that $\begin{array}{l}\text { Solar constant }=1.4 \mathrm{~kW} / \mathrm{m}^{2}=1.4 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{s} / \mathrm{m}^{2} \quad\left(\text { converted }...
A solar cooker may not cook food if:
a) the solar cooker is not placed in the shade b) the glass sheet cover of solar cooker is not closed c) a convex mirror reflector is not used d) the food containers of insulating material are not...
Which of the following is not an example of a biomass energy source?
a) wood b) biogas c) atomic energy d) cow-dung Answer: The correct option is c) atomic energy
most of the sources of energy that we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the sun’s energy?
a) wind energy b) geothermal energy c) fossil fuels d) ethane Answer: The correct option is b) geothermal energy
The constituent of biogas which makes it an excellent fuel is:
a) butane b) methane c) propane d) ethane Answer: The correct option is b) methane
The major component of biogas is:
a) hydrogen b) butane c) hydrogen sulphide d) methane Answer: The correct option is d) methane
Which of the following is more environmentally friendly?
a) burning of diesel b) burning of coal c) burning of charcoal d) burning of wood Answer: The correct option is c) burning of charcoal
Which of the following is not renewable energy technology?
a) solar cells b) windmills c) nuclear power d) tidal power Answer: The correct option is c) nuclear power
The rise of sea-water during high tide is caused by the gravitational pull of the:
a) sun b) earth c) moon d) mars Answer: The correct option is c) moon
One of the following is not required in the formation of biogas plant. This is:
a) cow-dung b) water c) oxygen d) anaerobic bacteria Answer: The correct option is c) oxygen
The fuel which is not obtained from biomass is:
a) firewood b) cow-dung cakes c) coke d) charcoal Answer: The correct option is c) coke
The non-renewable source of energy among the following is:
a) hydroelectricity b) sewage gas c) natural gas d) gobar gas Answer: The correct option is c) natural gas\
Geothermal energy is produced by the:
a) fission of radioactive materials b) burning of coal inside the coal mines c) combustion of natural gas deep inside the earth d) fusion of radioactive substance Answer: The correct option is a)...
The harnessing of which of the following leads to the destruction of large eco-systems?
a) thermal power b) tidal power c) hydro power d) geothermal power Answer: The correct option is c) hydro power
Which of the following is not a consequence of establishing hydroelectric power plants?
a) displacement of people b) production of methane c) occurrence of floods d) ecological disturbance Answer: The correct option is c) occurrence of floods
Which of the following is used as a moderator in the reactor of a nuclear power station?
a) liquid sodium b) boron c) graphite d) carbon dioxide Answer: The correct option is c) graphite
The control rods used in the reactor of a nuclear power plant are made of:
a) steel b) graphite c) uranium d) boron Answer: The correct option is d) boron
The ‘coolants’ which can be used in the reactor of a nuclear power station are:
a) liquid mercury and nitrogen dioxide b) liquid sodium and carbon dioxide c) liquid ammonia and carbon monoxide d) liquid boron and uranium oxide Answer: The correct option is b) liquid sodium and...
In a nuclear power plant, coolant is a substance:
a) which cools the hot, spent steam to condense it back to water b) which transfers heat from reactor to water in heat exchanger c) which is boiled to make steam to turn the turbine d) which cools...
Which of the following is ultimately not derived from the sun’s energy?
a) wind energy b) nuclear energy c) biomass energy d) ocean thermal energy Answer: The correct option is b) nuclear energy
One atomic mass unit is equivalent to an energy of:
a) 931 eV b) 9.31 MeV c) 1 MeV d) 931 MeV Answer: The correct option is d) 931 MeV
The energy in the reactor of a nuclear power station is produced by the process of:
a) nuclear diffusion b) nuclear fission c) nuclear fusion d) nuclear fermentation Answer: The correct option is b) nuclear fission
One eV of nuclear energy is equivalent to:
a) 1.6 × 10-14 J b) 1.6 × 10-12 J c) 1.6 × 10-19 J d) 1.6 × 10-13 J Answer: The correct option is c) 1.6 × 10-19 J
Which of the following can be produced during the nuclear fission as well as nuclear fusion reactions?
a) protons b) deuterons c) electrons d) neutrons Answer: The correct option is d) neutrons
Nuclear fission reactions are not a source of energy for one of the following. This is:
a) atom bomb b) power plants c) sun d) pacemaker Answer: The correct option is c) sun
The energy produced by converting 1 gram mass of a nuclear fuel into energy completely is:
a) 9 × 1016 J b) 9 × 1014 J c) 9 × 1015 J d) 9 × 1013 J Answer: The correct option is d) 9 × 1013 J
The source of energy of the sun is:
a) conversion of hydrogen gas into helium b) conversion of carbon fuel into carbon dioxide c) burning of hydrogen gas present in the sun d) disintegration of uranium into barium and krypton Answer:...
An uncontrolled nuclear chain reaction forms the basis of:
a) nuclear power plant b) hydrogen bomb c) thermal power station d) atom bomb Answer: The correct answer is d) atom bomb
One MeV of nuclear energy is equivalent to:
a) 1.6 × 10-13 J b) 1.6 × 10-19 J c) 1.6 × 10-16 J d) 1.6 × 10-15 J Answer: The correct option is a) 1.6 × 10-13 J Explanation: When an electron with a charge of 1.6 × 10-19 J Coulomb is accelerated...
One type of energy which has not been controlled so far is
a) ocean thermal energy b) nuclear fusion energy c) geothermal energy d) nuclear fission energy Answer: The correct option is b) nuclear fusion energy
The disposal of wastes produced in a nuclear power plant poses a big problem because it is:
a) too heavy b) highly inflammable c) extremely foul smelling d) highly radioactive Answer: The correct option is d) highly radioactive
The heat energy released during nuclear fission and fusion is due to the:
a) conversion of stored chemicals into energy b) conversion of momentum into energy c) conversion of mass into energy d) conversion of magnetism into energy Answer: The correct option is c)...
Which of the following can undergo nuclear fusion reaction?
a) uranium b) deuterium c) barium d) krypton Answer: The correct option is b) deuterium Deuterium is formed by the fusion of two Hydrogen atoms.
108 The major cause of environmental pollution is the use of:
a) hydrogen as fuel b) biomass energy c) ocean energy d) fossil fuels Answer: The correct option is d) fossil fuels. Burning of fossil fuels results in the release of many harmful...
The world’s known coal reserves are expected to last for about:
a) 200 years b) 400 years c) 500 years d) 100 years Answer: The correct option is a) 200 years
The fossil fuel whose known reserves in the earth are expected to last for the minimum period is:
a) coal b) uranium c) petroleum d) natural gas Answer: The correct answer is c) petroleum because petroleum is a non renewable resource and it can't be replenished once exhausted...
An energy efficient device for producing light is:
a) DLF b) CFL c) FCL d) LPG Answer: The correct option b)...
(a) Define non-metals. Give five examples of non-metals. (b) Name a non-metal which conducts electricity.
Solution: (a) Non-metals are materials that conduct electricity poorly and are neither malleable nor ductile. Carbon, sulphur, phosphorus, silicon, and oxygen are some examples. (b) Carbon is a good...
Light of frequency 7.21 x 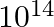 Hz is incident in a metal surface. Electrons with a maximum speed of 6.0 x
Hz is incident in a metal surface. Electrons with a maximum speed of 6.0 x 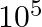 m/s are ejected from the surface. What is the threshold frequency for photoemission of electrons?
m/s are ejected from the surface. What is the threshold frequency for photoemission of electrons?
Frequency of the incident photon is given as $\mathbf{v}=488 \mathrm{~nm}=488 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$Maximum speed of the electrons is given as $\mathbf{v}=6.0 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{~m} /...
The work function for a certain metal is 4.2 eV. Will this metal give photoelectric emission for incident radiation of wavelength 330 nm?
Work function of the metal is given as $\Phi_{o}=4.2 \mathrm{eV}$Charge on an electron, $\mathrm{e}=1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}$Planck's constant, $\mathrm{h}=\mathbf{6} .626 \times 10^{-34}...
A 100W sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The lamp is located at the centre of a large sphere that absorbs all the sodium light which is incident on it. The wavelength of the sodium light is 589 nm. (a) What is the energy per photon associated with the sodium light? (b) At what rate are the photons delivered to the sphere?
Power of the sodium lamp is given as $\mathbf{P}=\mathbf{1 0 0 W}$Wavelength of the emitted sodium light is given as $\lambda=589 \mathrm{~nm}$$$=589 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$$Planck's constant,...
A uniform magnetic field of 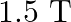 exists in a cylindrical region of a radius of
exists in a cylindrical region of a radius of 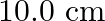 , its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying a current of
, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying a current of 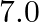 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if, the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of
A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if, the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 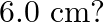
When the wire is lowered by $6 \mathrm{~cm}$, then Then, $x=\sqrt{(10)^{2}-\left(6^{2}\right)}=\sqrt{64}=8 \mathrm{~cm}$ $2 \mathrm{x}=\mathrm{I}_{2}=16 \mathrm{~cm}$ $F_{2}=BII_{2}$=$1.5 \times 7...
Answer the following question:
An electron travelling west to east enters a chamber having a uniform electrostatic field in the north to south direction. Specify the direction in which a uniform magnetic field should be set up to prevent the electron from deflecting from its straight-line path.
Because of the electric field, the negatively charged electron tends to go towards the north. The electron will not be deflected if an equal magnetic force acts in the other direction. We derive the...
A toroid has a core (non-ferromagnetic) of inner radius 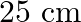 and outer radius
and outer radius 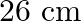 , around which 3500 turns of a wire are wound. If the current in the wire is
, around which 3500 turns of a wire are wound. If the current in the wire is 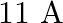 , what is the magnetic field in the empty space surrounded by the toroid.
, what is the magnetic field in the empty space surrounded by the toroid.
The magnetic field in the empty space surrounded by the toroid is zero as it is non-ferromagnetic.
The wavelength of light from the spectral emission line of sodium is 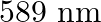 . Find the kinetic energy at which (a) an electron, and (b) a neutron, would have the same de Broglie wavelength.
. Find the kinetic energy at which (a) an electron, and (b) a neutron, would have the same de Broglie wavelength.
Wavelength of light of a sodium line is given as $\lambda=589 \mathrm{~nm}=589 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$ Mass of an electron, $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{e}}=9.1 \times 10^{-31} \mathrm{Kg}$ Mass of a...
What is the De Broglie wavelength of an electron with a kinetic energy of 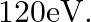
de Broglie wavelength of an electron having a momentum $p$, is given by the relation: $\lambda=\frac{h}{p}$ $=\frac{6.6 \times 10^{-34}}{5.91 \times 10^{-24}}=1.116 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{~m}=0.112...
What is the: (a) Momentum, (b) Speed of an electron with a kinetic energy of 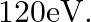
Kinetic energy of the electron is given as $\mathbf{E}_{\mathrm{K}}=\mathbf{1 2 0} \mathrm{eV}$ Planck's constant, $\mathbf{h}=\mathbf{6 . 6} \times \mathbf{1 0}^{-34} \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~s}$ Mass...
Calculate the (a) momentum, and (b) the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons accelerated through a potential difference of 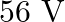 .
.
Potential difference is given in the question as $\mathbf{V}=\mathbf{5 6 V}$ Planck's constant, $\mathbf{h}=6.6 \times 10^{-34} \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~s}$ Mass of an electron, $\mathbf{m}=\mathbf{9 ....
Light of wavelength 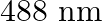 is produced by an argon laser which is used in the photoelectric effect. When light from this spectral line is incident on the emitter, the stopping (cut-off) potential of photoelectrons is
is produced by an argon laser which is used in the photoelectric effect. When light from this spectral line is incident on the emitter, the stopping (cut-off) potential of photoelectrons is 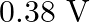 . Find the work function of the material from which the emitter is made.
. Find the work function of the material from which the emitter is made.
Wavelength of light produced by the argon laser is given as $\lambda=488 \mathrm{~nm}=488 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$ Stopping potential of the photoelectrons is given as...
Light of frequency 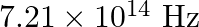 is incident in a metal surface. Electrons with a maximum speed of
is incident in a metal surface. Electrons with a maximum speed of 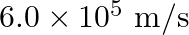 are ejected from the surface. What is the threshold frequency for photoemission of electrons?
are ejected from the surface. What is the threshold frequency for photoemission of electrons?
Frequency of the incident photon is provided as $v=488 \mathrm{~nm}=488 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$ Maximum speed of the electrons is $\mathbf{v}=\mathbf{6 . 0} \times \mathbf{1 0}^{5} \mathrm{~m} /...
The work function for a certain metal is  Will this metal give photoelectric emission for incident radiation of wavelength 330 nm?
Will this metal give photoelectric emission for incident radiation of wavelength 330 nm?
Work function of the metal is given as $\Phi_{o}=4.2 \mathrm{eV}$ Charge on an electron is $\mathbf{e}=\mathbf{1 . 6} \times \mathbf{1 0}^{-19} \mathbf{C}$ Planck's constant, $\mathbf{h}=\mathbf{6 ....
The threshold frequency for a certain metal is 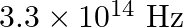 . If the light of frequency
. If the light of frequency 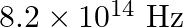 is incident on the metal, predict the cut-off voltage for the photoelectric emission.
is incident on the metal, predict the cut-off voltage for the photoelectric emission.
Threshold frequency of the metal given to us is $\mathbf{v}_{\mathbf{0}}=\mathbf{3 . 3} \times \mathbf{1 0}^{\mathbf{1 4}} \mathrm{Hz}$. Frequency of light incident on the metal is given as...
A 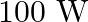 sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The lamp is located at the centre of a large sphere that absorbs all the sodium light which is incident on it. The wavelength
sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The lamp is located at the centre of a large sphere that absorbs all the sodium light which is incident on it. The wavelength
of the sodium light is 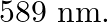 (a) What is the energy per photon associated with the sodium light? (b) At what rate are the photons delivered to the sphere?
(a) What is the energy per photon associated with the sodium light? (b) At what rate are the photons delivered to the sphere?
Power of the sodium lamp is given as $\mathbf{P}=\mathbf{1 0 0 W}$ Wavelength of the emitted sodium light is given as $\lambda=589 \mathrm{~nm}$ $=589 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}$ Planck's constant,...
In an experiment on the photoelectric effect, the slope of the cut-off voltage versus frequency of incident light is found to be 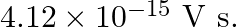 Calculate the value of Planck’s constant.
Calculate the value of Planck’s constant.
The slope of cut-off voltage (V) versus frequency (v) is given as, $\frac{V}{v}=4.12 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{Vs}$ $\mathrm{V}$ and frequency is related by the equation: $\mathrm{Hv}=\mathrm{eV}$...
The energy flux of sunlight reaching the surface of the earth is 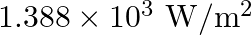 . How many photons are incident on the Earth per second/square meter? Assume an average wavelength of
. How many photons are incident on the Earth per second/square meter? Assume an average wavelength of 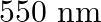
Energy flux of sunlight reaching the surface of the earth: $\phi=1.388 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m}^{2}$ Hence, power of sunlight per square metre, $\mathbf{P}=\mathbf{1 . 3 8 8} \times...
Two ores A and B were taken. On heating ore A gives CO2 whereas, ore B gives SO2. What steps will you take to convert them into metals?
Identification: Ore A - Carbonate ore Steps to convert carbonate ore into metal: 1. Calcination - Metal oxide is obtained by heating the ore in the presence of oxygen. Reaction Involved: ACO3→ AO+...
An element A burns with golden flame in the air. It reacts with another element B, atomic number 17 to give a product C. An aqueous solution of product C on electrolysis gives a compound D and liberates hydrogen. Identify A, B, C and D. Also write down the equations for the reactions involved.
Identification: A - Sodium B - Chlorine C - Sodium Chloride D - Sodium hydroxide Reactions Involved: 2Na +CL2 →2NaCl 2NaCl+ 2H2O→ 2NaOH+ Cl2+H2
Of the three metals X, Y and Z. X reacts with cold water, Y with hot water and Z with steam only. Identify X, Y and Z and also arrange them in order of increasing reactivity.
Identification: X - Sodium Y - Magnesium Z – Iron Reactions Involved: Na + H₂O → 2NaOH + H₂ Mg + H₂O → Mg(OH)₂ + H₂ Fe + H₂O → Fe₂O₃+ H₂ Arrangement of the metals in order of...
(i) Given below are the steps for extraction of copper from its ore. Write the reaction involved.
(a) Roasting of copper (1) sulphide (b) Reduction of copper (1) oxide with copper (1) sulphide. (c) Electrolytic refining (ii) Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of...
Explain the following
(a) Reactivity of Al decreases if it is dipped in HNO3 (b) Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of Na or Mg (c) NaCl is not a conductor of electricity in the solid-state whereas it does conduct...
Give the steps involved in the extraction of metals of low and medium reactivity from their respective sulphide ores.
The steps involved in the extraction of metals of low and medium reactivity from their respective sulphide ores are heating the ores in the presence of oxygen to produce the oxides of the metal....
A non-metal A which is the largest constituent of air, when heated with H2 in 1:3 ratio in the presence of a catalyst (Fe) gives a gas B. On heating with O2 it gives an oxide C. If this oxide is passed into water in the presence of air, it gives an acid D which acts as a strong oxidising agent.
(a) Identify A, B, C and D (b) To which group of periodic table does this non-metal belong? Answers: (a) A - Nitrogen Explanation: Nitrogen is the non-metal which is the largest constituent of...
A solution of CuSO4 was kept in an iron pot. After a few days, the iron pot was found to have a number of holes in it. Explain the reason in terms of reactivity. Write the equation of the reaction involved.
FeSO4 is produced when iron displaces the copper which makes the reactivity of iron higher than that of copper. And this nature of iron is responsible for the holes in the pot. Reaction Involved:...
An element forms an oxide A2O3 which is acidic in nature. Identify A as metal or non-metal.
Identification of the element A is a non-metal as they their oxides are usually acidic.
An alkali metal A gives a compound B (molecular mass = 40) on reacting with water. The compound B gives a soluble compound C on treatment with aluminium oxide. Identify A, B and C and give the reaction involved.
A - Sodium B - Sodium Hydroxide C - Sodium Aluminate Reaction Involved: Al2O3 +2NaOH →2NaAlO2+H2O
A metal M does not liberate hydrogen from acids but reacts with oxygen to give a black colour product. Identify M and black colored product and also explain the reaction of M with oxygen.
Identification: Metal M - Copper Black colored product - copper oxide Reaction Involved: 2Cu+ O2 →2CuO
Give the reaction involved during the extraction of zinc from its ore by (a) roasting of zinc ore (b) calcination of zinc ore
Reactions involved during the extraction of zinc from its ore by, (a) Roasting of zinc ore: 2ZnS + 3O2→2ZnO + 2SO2. (b) Calcination of zinc ore: ZnCo3→ZnO+CO
An element A reacts with water to form a compound B which is used in whitewashing. The compound B on heating forms an oxide C which on treatment with water gives back B. Identify A, B and C and give the reactions involved.
A - Calcium B - Calcium Hydroxide C - Calcium Oxide Reactions Involved: Ca+2H2O →Ca(OH)2+ H2 Ca(OH)2 →CaO+H2O CaO+H2O→ Ca(OH)2
Name one metal and one non-metal that exist in a liquid state at room temperature. Also, name two metals having a melting point less than 310 K (37°C)
Mercury and Bromine exists in a liquid state at room temperature; Caesium and Gallium has a melting point less than 310 K (37°C).
Give two examples each: The metals that are good conductors and poor conductors of heat, respectively.
Examples of good conductors are Iron and Copper. Examples of bad conductors are Lead and Mercury.
A non-metal A is an important constituent of our food and forms two oxides B and C. Oxide B is toxic whereas C causes global warming
(a) Identify A, B and C (b) To which Group of Periodic Table does A belong? Answers: (a) A - Carbon B - Carbon monoxide C - Carbon-dioxide (b) Group...
What happens when
(a) ZnCO3 is heated in the absence of oxygen? (b) a mixture of Cu2O and Cu2S is heated? Answers: (a) Carbon-di-oxide are liberated Reaction: ZnCo3 →ZnO + CO2 (b) Pure Copper is obtained...
Give the formulae of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of the following pairs of elements.
(a) Mg and N2 (b) Li and O2 (c) Al and Cl2 (d) K and O2 Answers: (a) Magnesium Nitride (Mg3N2) (b) Lithium Oxide( Li2O) (c) Aluminium Chloride( AlCl3) (d) Potassium Oxide (...
A metal that exists as a liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide in the presence of air. Identify the metal and its ore and give the reaction involved.
Mercury is the metal that exists as a liquid at room temperature is obtained by heating its sulphide in the presence of air. Cinnabar is the ore of mercury. Reaction: 2HgS + 3O2→ 2HgO +...
A metal A, which is used in thermite process, when heated with oxygen gives an oxide B, which is amphoteric in nature. Identify A and B. Write down the reactions of oxide B with HCl and NaOH.
Metal A - Aluminium (Al) Metal B – Aluminium Oxide (Al2O3 ) With HCl, the following reaction occurs: Al2O3+ 6HCl →2AlCl3+3H2O With NaOH, the following reaction occurs: Al2O3+2NaOH...
What are the constituents of solder alloy? Which property of solder makes it suitable for welding electrical wires?
Constituents of solder - Lead and aluminium. The low melting point of this alloy makes it fit for the welding of electrical wires.
The following reaction takes place when the aluminium powder is heated with MnO2
3 MnO2 (s) + 4 Al (s) → 3 Mn (l) + 2 Al2O3 (l) + Heat (a) Is aluminium getting reduced? (b) Is MnO2 getting oxidised? Answer: Aluminium gets oxidized when oxygen is combined and MnO2 gets...
A non-metal X exists in two different forms Y and Z. Y is the hardest natural substance, whereas Z is a good conductor of electricity. Identify X, Y and Z.
Identification: X – Carbon Y – Diamond Z – Graphite
When a metal X is treated with cold water, it gives a basic salt Y with molecular formula XOH (Molecular mass = 40) and liberates a gas Z which easily catches fire. Identify X, Y and Z and also write the reaction involved.
Identification: X - Sodium (Na) Y - Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) Z - Hydrogen gas Reaction Involved: 2Na+2H2O → 2NaOH+H2
Compound X and aluminium are used to join railway tracks. (a) Identify the compound X (b) Name the reaction (c) Write down its reaction.
(a) Compound X - Fe2O3 (b) Aluminothermy (c) Fe2O3(s) + 2Al(s)→ Al2O3 (s) + 2Fe(s)
Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated, but when metals (except Mn and Mg), treated with HNO3, hydrogen is not liberated, why?
HNO3 which is a strong oxidizing agent, oxidises the liberated Hydrogen into the water and converts itself into nitrogen oxide.
Although metals form basic oxides, which of the following metals form an amphoteric oxide?
(a) Na (b) Ca (c) Al (d) Cu Answer: (c) Al Reason: Aluminum oxide exhibits both acidic and basic performance which is why it is an amphoteric oxide.
Why should the metal sulphides and carbonates be converted to metal oxides in the process of extraction of metal from them?
Usually, metals can be obtained easily in oxide form than in its sulphide or carbonate form and because of this reason metal sulphides and carbonated must be converted to metal oxides in the metal...
During the extraction of metals, electrolytic refining is used to obtain pure metals. (a) Which material will be used as anode and cathode for refining of silver metal by this process? (b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte also. (c) In this electrolytic cell, where do we get pure silver after passing electric current?
(a) Anode - Impure metal; Cathode - Pure metal (b) Electrolyte - Silver Sulphate/Silver Nitrate (c) Cathode
Iqbal treated a lustrous, divalent element M with sodium hydroxide. He observed the formation of bubbles in a reaction mixture. He made the same observations when this element was treated with hydrochloric acid. Suggest how he can identify the produced gas. Write chemical equations for both the reactions.
The lighted matchstick must be brought close to the gas to identify the produced gas. When the stick burns a pop sound is observed which will help for the identification of the gas. Chemical...
Which one of the following figures correctly describes the process of electrolytic refining?
Answer: (b) Explanation: The figure in option (b) properly shows the correct process of the electrolytic refining.
Electrical wires have a coating of an insulating material. The material, generally used is
(a) Sulphur (b) Graphite (c) PVC (d) All can be used Answer: (c) PVC Reason: Insulators are materials that do not allow electrical energy to flow. Therefore, insulators are used to cover electrical...
Which of the following can undergo a chemical reaction?
(a) MgSO4 + Fe (b) ZnSO4 + Fe (c) MgSO4 + Pb (d) CuSO4 + Fe Answer: (d) CuSO4 + Fe Reason: The reactivity of Iron is more than copper which is why it transmits copper in response...
Generally, non-metals are not conductors of electricity. Which of the following is a good conductor of electricity?
(a) Diamond (b) Graphite (c) Sulphur (d) Fullerene Answer: (b) Graphite Reason: Normally non-metals do not transmit heat and electricity, however, graphite is different. Graphite (an allotropic form...
Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
(a) Carbon (b) Bromine (c) Phosphorus (d) Sulphur Answer: (b) Bromine Reason: Physically most of the non-metallic material around us exists as gases, solid brittle. For example, hydrogen, oxygen...
The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are X — 2, 8; Y — 2, 8, 7 and Z — 2, 8, 2. Which of the following is correct?
(a) X is a metal (b) Y is a metal (c) Z is a non-metal (d) Y is a non-metal and Z is a metal Answer: (d) Y is a non-metal and Z is a metal Reason: Based on the electronic configuration of the...
Reaction between X and Y, forms compound Z. X loses electron and Y gains electron. Which of the following properties is not shown by Z?
(a) Has a high melting point (b) Has a low melting point (c) Conducts electricity in molten state (d) Occurs as solid Answer: (b) Has a low melting point Reason: X is a metal that is electropositive...
Which among the following alloys contain mercury as one of its constituents?
(a) Stainless steel (b) Alnico (c) Solder (d) Zinc amalgam Answer: (d) Zinc amalgam Reason: Zinc amalgam is a mixture of mercury (10%) containing zinc (90%). It contains mercury as one of its...
Which among the following statements is incorrect for magnesium metal?
(a) It burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame (b) It reacts with cold water to form magnesium oxide and evolves hydrogen gas (c) It reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and evolves...
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of a metal with a metal or nonmetal. Which among the following alloys contain non-metal as one of its constituents?
(a) Brass (b) Bronze (c) Amalgam (d) Steel Answer: (d) Steel Reason: Iron in its purest form is very soft and rusts. Therefore, it is combined with another metal to change its properties. Iron mixed...
An element A is soft and can be cut with a knife. This is very reactive to air and cannot be kept open in the air. It reacts vigorously with water. Identify the element from the following
(a) Mg (b) Na (c) P (d) Ca Answer: (b) Na Reason: Sodium is an element that is soft and can be cut with a knife, reactive to air and cannot be kept open in the air and also reacts vigorously with...
During electrolytic refining of zinc, it gets
(a) deposited on cathode (b) deposited on anode (c) deposited on the cathode as well as anode (d) remains in the solution Answer: (a) deposited on cathode Reason: During the process of refining of...
An electrolytic cell consists of
(i) positively charged cathode (ii) negatively charged anode (iii) positively charged anode (iv) negatively charged cathode (a) (i) and (ii) (b) (iii) and (iv) (c) (i) and (iii) (d) (ii) ad (iv)...
An alloy is
(a) an element (b) a compound (c) a homogeneous mixture (d) a heterogeneous mixture Answer: (c) a homogeneous mixture Reason: An alloy is a homogeneous mixture
2 mL each of concentrated HCl, HNO3 and a mixture of concentrated HCl and concentrated HNO3 in the ratio of 3: 1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A and B but the metal got dissolved in test tube C respectively. The metal could be
(a) Al (b) Au (c) Cu (d) Pt Answer: (b) Au Reason: Gold is an insoluble metal in soluble acids and only soluble in aqua region. Therefore, the metal on the C test plate should be gold (Au). The...
Identify the compound X on the basis of the reactions given below. Also, write the name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.
Compound X - Sodium hydroxide A – Sodium Zincate Reaction: 2NaOH+ Zn→ Na₂ZnO₂ + H2(g) B – Sodium Chloride Reaction: NaOH + HCl →NaCl + H2O C – Sodium Acetate Reaction: NaOH + CH3 COOH→ CH3COONa +...
A sulphate salt of Group 2 element of the Periodic Table is a white, soft substance, which can be molded into different shapes by making its dough. When this compound is left in the open for some time, it becomes a solid mass and cannot be used for molding purposes. Identify the sulphate salt, and why does it show such behavior? Give the reaction involved.
Plaster of Paris is calcium sulphate which is white in colour and has soft texture. 2. Gypsum is a hard compound which is used for molding purposes and is formed when Plaster of Paris is left open...
A dry pellet of a common base B, when kept in the open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also a by-product of the chloralkali process. Identify B. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with an acidic oxide? Write a balanced chemical equation for one such solution.
Identification: B – Sodium Hydroxide(NaOH) Neutralization process occurs when sodium hydroxide reacts with acidic oxide. 2NaOH+ CO2 →Na2CO3+ H2O
A metal carbonate X on reacting with acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution Y gives the carbonate back. On the other hand, a gas G that is obtained at the anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, and it gives a compound Z, used for disinfecting drinking water. Identity X, Y, G and Z.
Identification: X - Calcium Y - Lime water G - Chlorine gas Z - Bleaching powder
For making a cake, baking powder is taken. If at home, your mother uses baking soda instead of baking powder in cake,
how will it affect the taste of the cake and why?how can baking soda be converted into baking powder?what is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda Answers: The cake will be bitter as...
In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen gas, as shown in Figure 2.3, what would happen if the following changes are made?
1. In place of zinc granules, the same amount of zinc dust is taken in the test tube 2. Instead of dilute sulphuric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken 3. In place of zinc, copper turnings are...
When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, a gas is evolved, which is utilised in the hydrogenation of oil. Name the gas evolved. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, hydrogen gas is evolved. Reaction: ...
What are strong and weak acids? In the following list of acids, separate strong acids from weak acids. Hydrochloric acid, citric acid, acetic acid, nitric acid, formic acid, sulphuric acid.
Acids that can be completely ionized is called strong acids. Acids that can be partially ionized is called weak acid. 1. Hydrochloric acid is a Strong Acid 2. Citric acid is a Weak Acid 3. Acetic...
Fill in the missing data in the following table
Name of the SaltFormulaBaseAcidAmmonium chlorideNH4ClNH4OH–Copper sulphate––H2 SO4Sodium chlorideNaClNaOH–Magnesium nitrateMg (NO3 ) 2–HNO3Potassium sulphateK2 SO4––Calcium nitrateCa(NO3 ) 2Ca(OH)2–...
In one of the industrial processes used for the manufacture of sodium hydroxide, a gas X is formed as a by-product. The gas X reacts with lime water to give a compound Y which is used as a bleaching agent in the chemical industry. Identify X and Y, giving the chemical equation of the reactions involved.
Identification: X = Chlorine Y = Bleaching powder Reaction Involved: Ca(OH)2 (s) + Cl2 (g) → CaOCl2 (s) + H2O — Calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder)
Salt A commonly used in bakery products on heating gets converted into another salt B which itself is used for removal of hardness of water, and a gas C is evolved. The gas C, when passed through lime water, turns it milky. Identify A, B and C.
Identification: Salt A - Baking soda Salt B - Sodium carbonate Gas C - CO2
How would you distinguish between baking powder and washing soda by heating?
When we heat baking powder, CO2 is released and when this gas is introduced into lime water the solution will turn milky. This reaction will not occur if you heat a washing soda.
A student prepared solutions of (i) an acid and (ii) a base in two separate beakers. She forgot to label the solutions, and litmus paper is not available in the laboratory. Since both the solutions are colourless, how will she distinguish between the two?
The student can use phenopthalein indicator to identify which solution is acid and base.
What happens when nitric acid is added to eggshell?
When the egg shell is dissolved in nitric acid, the calcium carbonate present in the eggshell reacts with the nitric acid and produces calcium nitrate and carbon-di-oxide gas.
Name the acid present in ant sting and give its chemical formula. Also, give the common method to get relief from the discomfort caused by the ant sting.
Methanoic acid is the acid present in ant sting and its chemical formula is HCOOH. Rubbing the affected place with baking soda can cause relief from the discomfort of ant sting.
What will be the action of the following substances on litmus paper? Dry HCl gas, Moistened NH3 gas, Lemon juice, Carbonated soft drink, Curd, Soap solution.
1. Dry HCl gas- No effect 2. Moistened NH3 gas- litmus paper turns to blue colour 3. Lemon juice- litmus paper turns to red colour 4. Carbonated soft drink- litmus paper turns to blue colour 5....
