(a) $1 ppm = 1 part out of 1 million parts.$ Mass percent of 15 ppm chloroform in H2O= $\frac{15}{{{10}^{6}}}\times 100$ $\approx 1.5 \times{10}^{-3}%$ $ (b)$100 grams of the sample is having 1.5 ×...
What do you mean by significant figures?
The meaningful numbers that are known with certainty are known as significant figures. Significant numbers imply that the tested value is unknown. For example, if the experiment yielded 15.6 mL, 15...
Match the following prefixes with their multiples:
What is the SI unit of mass? How is it defined?
Kilogram is the SI unit of mass (kg) Mass: “Mass is defined as the mass equivalent to the mass of the international kilogramme prototype.”
Pressure is determined as force per unit area of the surface. The SI unit of pressure, pascal is as shown below: 1Pa = 1N m–2 If mass of air at sea level is 1034 g cm–2, calculate the pressure in pascal
As per definition, pressure is force per unit area of the surface. $P = \frac{F}{A}$ =$ \frac{1034\;g\;\times \;9.8\;ms^{-2}}{cm^{2}}\times \frac{1\;kg}{1000\;g}\times \frac{(100)^{2}\;cm^{2}}{1...
If the density of methanol is 0.793 kg 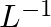 , what is its volume needed for making 2.5 L of its 0.25 M solution?
, what is its volume needed for making 2.5 L of its 0.25 M solution?
$Molar mass of CH_{3}OH$ = (1 * 12) + (4 * 1) + (1 * 16) =$32 g mol^{-1}$ = $0.032 kg mol^{-1}$ Molarity of the solution = $\frac{0.793\;kg\;L^{-1}}{0.032\;kg\;mol^{-1} }$ = 24.78 mol{L}^{-1}...
What is the concentration of sugar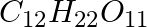 in mol
in mol 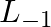 if its 20 g are dissolved in enough water to make a final volume up to 2L?
if its 20 g are dissolved in enough water to make a final volume up to 2L?
Molarity (M) is as given by, = $\frac{Number\;of\;moles\;of\;solute}{Volume\;of\;solution\;in\;Litres}$ =$\frac{\frac{Mass\;of\;sugar}{Molar\;mass\;of\;sugar}}{2\;L}$ =...
In three moles of ethane (C2H6), calculate the following: (i) Number of moles of carbon atoms. (ii) Number of moles of hydrogen atom (iii) Number of molecules of ethane
(a) 1 mole ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ contains two moles of C- atoms. ∴∴ No. of moles of C- atoms in 3 moles of ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ = 2 * 3 = 6 (b) 1 mole ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ contains six moles of H-...
Calculate the atomic mass (average) of chlorine using the following data:
Average atomic mass of Cl. = $[(\text{Fractional abundance of }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }_{{}}^{35}Cl)(\text{molar mass of }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }_{{}}^{35}Cl)+(\text{fractional abundance of }\!\!~\!\!\text{...
Determine the molecular formula of an oxide of iron, in which the mass percent of iron and oxygen are 69.9 and 30.1, respectively.
Mass percent of Fe = 69.9% Mass percent of O = 30.1% No. of moles of Fe present in oxide =$ \frac{69.90}{55.85}$ = 1.25 No. of moles of O present in oxide =$\frac{30.1}{16.0}$ =1.88 Ratio of Fe to...
How much copper can be obtained from 100 g of copper sulphate (CuSO4)?
1 mole of $CuSO_{4}$ contains 1 mole of Cu. Molar mass of $CuSO_{4}$ = (63.5) + (32.00) + 4(16.00) = 63.5 + 32.00 + 64.00 = 159.5 grams 159.5 grams of $CuSO_{4}$ contains 63.5 grams of Cu....
Calculate the concentration of nitric acid in moles per litre in a sample which has a density, 1.41 g mL–1 and the mass per cent of nitric acid in it being 69%
Mass percent of HNO3 in sample is 69 % Thus, 100 g of HNO3 contains 69 g of HNO3 by mass. Molar mass of HNO3 = { 1 + 14 + 3(16)} g.mol^{-1}g.mol−1 = 1 + 14 + 48 = 63g mol^{-1}=63gmol−1 Now,...
Calculate the mass of sodium acetate 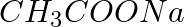 required to make 500 mL of 0.375 molar aqueous solution. Molar mass of sodium acetate is 82.0245 g mol–1.
required to make 500 mL of 0.375 molar aqueous solution. Molar mass of sodium acetate is 82.0245 g mol–1.
0.375 Maqueous solution of $CH_{3}COONa$ = 1000 mL of solution containing 0.375 moles of $CH_{3}COONa$ Therefore, no. of moles of $CH_{3}COONa$ in 500 mL = 0.1875 mole Molar mass of sodium acetate...
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when (i) 1 mole of carbon is burnt in air. (ii) 1 mole of carbon is burnt in 16 g of dioxygen. (iii) 2 moles of carbon are burnt in 16 g of dioxygen.
(i) 1 mole of carbon is burnt in air. $C+{{O}_{2}}\to C{{O}_{2}}$ 1 mole of carbon reacts with 1 mole of O2 to form one mole of CO2. Amount of $CO_{2}$ produced = 44 g (ii) 1 mole of carbon...
Determine the empirical formula of an oxide of iron, which has 69.9% iron and 30.1% dioxygen by mass.
Percentage of Fe by mass = 69.9% [As said previously] By mass, 30.1 percent of O2 is present. [As said previously] Relative moles of Fe in iron oxide: = (69.9)x(55.85}/55.8569.9 = 1.25 Relative...
Calculate the mass per cent of different elements present in sodium sulphate 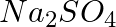
Now for Na2SO4. Molar mass of Na2SO4 = [(2 x 23.0) + (32.066) + 4(16.00)] =142.066 g Therefore, mass percent of the sodium element: = 32.379 = 32.4% Mass percent of the sulphur element: = 22.57...
Calculate the molar mass of the following: (i) 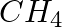 (ii)
(ii)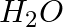 (iii)
(iii)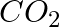
(i)Molecular weight of methane= (1 x Atomic weight of carbon) + (4 x Atomic weight of hydrogen) = [1(12.011 u) +4 (1.008u)] = 12.011u + 4.032 u = 16.043 u (ii)Molecular weight of water= (2 x...
Assertion (A): Among isomeric pentanes, 2, 2-dimethylpentane has the highest boiling point. Reason (R): Branching does not affect the boiling point. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (iii) is correct. Explanation: The lowest boiling point among isomeric pentanes is of 2,2-dimethylpentane, and further on branching, its boiling point decreases
Assertion (A): Nitration of benzene with nitric acid requires the use of concentrated sulphuric acid. Reason (R): The mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid produces the electrophile, NO2+. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (i) is correct Explanation: In nitration, benzene is treated with a nitrating mixture, which consists of conc. $HNO_3$ and $H_2SO_4$, and $H_2SO_4$ aids in the production of $NO_2 +$....
Assertion (A): Toluene on Friedel Crafts methylation gives o– and p–xylene. Reason (R): CH3-group bonded to benzene ring increases electron density at o– and p– position. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (i) is correct
Assertion (A): The compound cyclooctane has the following structural formula: It is cyclic and has conjugated 8π-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
Reason (R) : (4n + 2) π electrons rule does not hold good and the ring is not planar.
(i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) Both A and R are not correct.
(iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (i) is correct. Compounds with the following features are aromatic: planarity and complete delocalization of the electrons in the ring. The ring contains (4n+2) electrons, where n is an...
Match the reactions given in Column I with the reaction types in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is b (iv) is c
Match the following reactants in Column I with the corresponding reaction products in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is c (iii) is b (iv) is a
Match the hydrocarbons in Column I with the boiling points given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is c (iii) is a
Match the reagent from Column I which on reaction with CH3 —CH=CH2 gives some product given in Column II as per the codes given below :
(i) is d (ii) is a (iii) is e (iv) is c (v) is b
Suggest a route to prepare ethyl hydrogen sulphate (CH3–CH2–OSO2—OH) starting from ethanol (C2H5OH)
At about 140°C, ethanol is processed with sulphuric acid to produce hydrogen sulphate. The response is
Which of the following compounds are aromatic according to Huckel’s rule?
Huckel's rule states that it must meet the (4n+) rule. Aromatic compounds include B, C, D, and F.
The ring systems having the following characteristics are aromatic. (i) Planar ring containing conjugated π bonds. (ii) Complete delocalisation of the π−electrons in-ring system i.e. each atom in the ring has unhybridised p-orbital, and (iii) Presence of (4n+2)−electrons in the ring where n is an integer (n = 0, 1, 2,………..) [Huckel rule]. Using this information classifies the following compounds as aromatic/non-aromatic.
Aromatic compounds: A, E and F Non-Aromatic : B, C, D and G
An alkane C8H18 is obtained as the only product on subjecting a primary alkyl halide to Wurtz reaction. On monobromination, this alkane yields a single isomer of a tertiary bromide. Write the structure of alkane and the tertiary bromide.
Write hydrocarbon radicals that can be formed as intermediates during monochlorination of 2-methylpropane? Which of them is more stable? Give reasons.
In comparison to the 1° free radical, the 3° free radical is stabilised by 9 hyperconjugation structures, giving it greater stability.
Write the structures and names of products obtained in the reactions of sodium with a mixture of 1-iodo-2-methylpropane and 2-iodopropane.
When a combination of 1-iodo-2-methylpropane and 2-iodopropane is treated with salt, it produces three compounds as a result of intermolecular and intramolecular reactions:
The relative reactivity of 1°, 2°, 3° hydrogen’s towards chlorination is 1: 3.8: 5. Calculate the percentages of all mono-chlorinated products obtained from 2-methyl butane.
Number of hydrogen reactivity = number of mono-chlorinated compounds 1° H = 9 1 = 9 mono-chlorinated products 2° H = 2 3.8 = 7.6 mono-chlorinated products 3° H = 1 5 = 5 mono-chlorinated products...
Nucleophiles and electrophiles are reaction intermediates having electron-rich and electron-deficient centres’ respectively. Hence, they tend to attack electron-deficient and electron-rich centres respectively. Classify the following species as electrophiles and nucleophiles.
Nucleophiles I (vi), (vii), and (viii) Electrophiles are (ii), (iii), (iv), and (v).
Predict the major product (s) of the following reactions and explain their formation.
Step 1: Peroxide homolysis to produce free radicals Step 2: Bromine free radical formation ∙C6H5 + H-BR → C6H6 + Br Step 3: hydrogen bromide reacts with an alkyl radical.∙
Suggest a route for the preparation of nitrobenzene starting from acetylene?
I We can cycle acetylene using the intermolecular condensation technique and then treat it at high temperatures in a red hot iron tube. (ii) After being converted to benzene, the aliphatic molecule...
Why does the presence of a nitro group make the benzene ring less reactive in comparison to the unsubstituted benzene ring? Explain.
A nitrogen atom is linked to two extremely electronegative oxygen atoms in the Nitro group. This causes a net reduction in electron density around the nitrogen atom, giving nitrogen a positive charge.
Despite their – I effect, halogens are o- and p-directing in halo-arenes. Explain.
Halogens have a ns2p5 outer configuration, indicating that they may take one electron and are near to completing their octate; halogens have a significant affinity for attracting one electron,...
Arrange the following set of compounds in the order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile. Give reason.
How will you convert benzene into (i) p – nitrobromobenzene (ii) m – nitrobromobenzene
I Bromine undergoes electrophilic substitution with Br2 in the presence of anhydrous FeBr3 to generate bromobenzene. We get a p-nitrobromobenzene after treating it with conc. HNO3 and conc. H2SO4 at...
What will be the product obtained as a result of the following reaction and why?
Friedel Crafts alkylation with a Lewis acid is demonstrated in this process. The development of the carbocation will occur initially, followed by the production of a more stable secondary...
The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI, HBr and HCl with propane is the same and the bond energy of HCl, HBr and HI is 430.5 kJ mol-1, 363.7 kJ mol-1 and 296.8 kJ mol-1 respectively. What will be the order of reactivity of these halogen acids?
The ascending order of reactivity is HI >HBr>HCl. The rising order of halogen reactivity corresponds to the rise in bond energy.
Draw Newman and Sawhorse projections for the eclipsed and staggered conformations of ethane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?
Because there is less C – H bond pair repulsion and the atoms are at their furthest distance from one other, the staggered arrangement is more stable than an eclipse.
Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
In ethane, the single bond is a – bond, which is a coaxial overlap of orbitals that allows the C C bond to rotate on its axis. However, due to the torsional strain that the bond receives as a result...
Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia form trans alkenes. Will the butene thus formed on the reduction of the 2-butyne show the geometrical isomerism?
The negative charge that has generated on one carbon attacks the proton from NH3 and causes another sodium atom to lose its electron, causing the atom to create a second negative charge. The second...
Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain.
To produce a more stable saturated product, alkenes undergo an addition reaction. Hybridization shifts from sp2 to sp3 in this reaction. A substitution process maintains the resonance stability of...
The molecules having dipole moment are __________.(i) 2,2-Dimethylpropane (ii) trans-Pent-2-ene (iii) cis-Hex-3-ene (iv) 2, 2, 3, 3 – Tetramethylbutane.
Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers
Four structures are given in options (i) to (iv). Examine them and select the aromatic structures.
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
Which of the following is correct?
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
In an electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrobenzene, the presence of nitro group ________. (i) deactivates the ring by an inductive effect. (ii) activates the ring by an inductive effect. (iii) decreases the charge density at ortho and para position of the ring relative to meta position by resonance. (iv) increases the charge density at meta position relative to the ortho and para positions of the ring by resonance
Option (i) and (iii) are the answers.
For an electrophilic substitution reaction, the presence of a halogen atom in the benzene ring _______. (i) deactivates the ring by the inductive effect (ii) deactivates the ring by resonance (iii) increases the charge density at ortho and para position relative to meta position by resonance (iv) directs the incoming electrophile to meta position by increasing the charge density relative to ortho and para position.
The solutions are options (i) and (iii).
Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?;(i) 5 – (2′, 2′–Dimethylpropyl)-decane (ii) 4 – Butyl – 2,2– dimethylnonane (iii) 2,2– Dimethyl – 4– pentyloctane (iv) 5 – neo-Pentyldecane
Option (i) and (iv) are the answers.
Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?;(i) 5– Butyl – 4– isopropyldecane (ii) 5– Ethyl – 4– propyldecane (iii) 5– sec-Butyl – 4– iso-propyldecane (iv) 4–(1-methoxymethyl)– 5 – (1-methyl propyl)-decane
The solutions are options (iii) and (iv).
Which of the following alkenes on ozonolysis give a mixture of ketones only?
The solutions are options (iii) and (iv).
In the following questions, two or more options may be correct. Some oxidation reactions of methane are given below. Which of them is/are controlled oxidation reactions? (i) CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g)→ CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) (ii) CH4 (g) + O2 (g) → C (s) + 2H2O (l) (iii) CH4 (g) + O2 (g) →(Mo O2 3) HCHO + H2O (iv) 2CH4 (g) + O2 (g) → (Cu/523/100 atm) 2CH3OH
The solutions are options (iii) and (iv).
Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion:
Option (iii) is the answer.
Arrange the following alkyl halides in decreasing order of the rate of β– elimination reaction with alcoholic KOH.(i) A > B > C (ii) C > B > A (iii) B > C > A (iv) A > C > B
The solution is option (iv).
Arrange the following carbanions in order of their decreasing stability. (A) H3C – C ≡ C– (B) H – C ≡ C– (C) H3C-CH–2 (i) A > B > C (ii) B > A > C (iii) C > B > A (iv) C > A > B
The solution is option (ii).
Arrange the following hydrogen halides in order of their decreasing reactivity with propane. (i) HCl > HBr > HI (ii) HBr > HI > HCl (iii) HI > HBr > HCl (iv) HCl > HI > HBr
The solution is Option (iii)
Which of the following will not show geometrical isomerism?
Option (iv) is the answer.
The addition of HBr to 1-butene gives a mixture of products A, B and C;The mixture consists of (i) A and B as major and C as minor products (ii) B as major, A and C as minor products (iii) B as minor, A and C as major products (iv) A and B as minor and C as major products
Option I is the correct response.
The correct IUPAC name of the following alkane is ;(i) 3,6 – Diethyl – 2 – methyl octane (ii) 5 – Isopropyl – 3 – ethyloctane (iii) 3 – Ethyl – 5 – isopropyloctane (iv) 3 – Isopropyl – 6 – ethyloctane
Option I is the correct response.
The increasing order of reduction of alkyl halides with zinc and dilute HCl is (i) R–Cl < R–I < R–Br ii) R–Cl < R–Br < R–I (iii) R–I < R–Br < R–Cl (iv) R–Br < R–I < R–Cl
Option (ii) is the correct response.
Arrange the halogens F2 , Cl2 , Br2 , I2 , in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes. (i) I2 < Br2 < Cl2 < F2 (ii) Br2 < Cl2 < F2 < I2 (iii) F2 < Cl2 < Br2 < I2 (iv) Br2 < I2< Cl2 < F2
Option (i) is the solution
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n–butane (B) 2–methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2–dimethylpropane (i) A > B > C > D (ii) B > C > D > A (iii) D > C > B > A (iv) C > B > D > A
the answer is Option (iv)
Assertion (A): If BOD level of water in a reservoir is less than 5 ppm it is highly polluted. Reason (R): High biological oxygen demand means a low activity of bacteria in water. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (iii) is the answer.
Assertion (A): Excessive use of chlorinated synthetic pesticides causes soil and water pollution. Reason (R): Such pesticides are non-biodegradable. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct
Option (i) is the answer.
Assertion (A): Ozone is destroyed by solar radiation in the upper stratosphere. Reason (R): Thinning of the ozone layer allows excessive UV radiations to reach the surface of the earth. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (iv) is the answer.
Assertion (A): Carbon dioxide is one of the important greenhouse gases. Reason (R): It is largely produced by respiratory function of animals and plants. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (ii) is the answer.
Assertion (A): Photochemical smog is oxidising in nature. Reason (R): Photochemical smog contains NO2 and O3, which are formed during the sequence of reactions. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (i) is correct.
Assertion (A): The pH of acid rain is less than 5.6. Reason (R): Carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere dissolves in rain water and forms carbonic acid. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Option (ii) is correct.
Assertion (A): Greenhouse effect was observed in houses used to grow plants and these are made of green glass. Reason (R): Greenhouse name has been given because glasshouses are made of green glass. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct. (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
correct is Option (iii)
Match the pollutants given in Column I with their effects given in Column II.
(i) are a and d (ii) is c (iii) is a (iv) is b
Match the activity given in Column I with the type of pollution created by it given in Column II.
(i) is e (ii) is d (iii) is a (iv) is b (v) is c
Match the pollutant(s) in Column I with the effect(s) in Column II.
(i) is d (ii) is e (iii) is a (iv) is c (v) is b
Match the terms given in Column I with the compounds given in Column II.
(i) are c and d (ii) are e and d (iii) is b (iv) is a
A person was using water supplied by the Municipality. Due to the shortage of water, he started using underground water. He felt a laxative effect. What could be the cause?
The laxative effect is the loosening of faeces and increased bowel movement induced by laxative drugs. Laxatives in high dosages might induce diarrhoea. This might be due to an excessive amount of...
Ozone is a gas heavier than air. Why does the ozone layer not settle down near the earth?
The ozone layer is heavier than oxygen and is thermodynamically unstable, yet the interaction between ozone production and dissociation has a dynamic equilibrium. As a result, they avoid settling...
How is ozone produced in stratosphere?
The action of ultraviolet light on atmospheric oxygen forms the ozone layer in the stratosphere. UV rays cause molecular oxygen to divide or dissociate into two oxygen atoms. O 2 (g) → O (g) + O (g)...
From where does ozone come in the photochemical smog?
Nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds (VOC), ozone, and PAN (peroxyacetyl nitrate) are all components of photochemical smog. In the presence of sunshine, nitrogen oxide in the smog dissociates...
Oxidation of Sulphur dioxide into Sulphur trioxide in the absence of a catalyst is a slow process but this oxidation occurs easily in the atmosphere. Explain how does this happen. Give chemical reactions for the conversion of SO2 into SO3.
The uncatalyzed oxidation of sulphur dioxide to sulphur trioxide is sluggish, but it may be oxidised quickly in the presence of a catalyst in the environment. There are substances in the atmosphere...
A factory was started near a village. Suddenly villagers started feeling the presence of irritating vapours in the village and cases of headache, chest pain, cough, dryness of throat and breathing problems increased. Villagers blamed the emissions from the chimney of the factory for such problems. Explain what could have happened. Give chemical reactions for the support of your explanation.
This sort of breathing difficulty can be caused by toxic nitrogen and sulphur oxides in the environment. These oxides are produced in industry by the oxidation of fossil fuels such as coal. N2 (g) +...
Why does water cover with excessive algal growth become polluted?
Algae breakdown by bacteria continually generates a nasty odour, and algae contaminate and make water unpleasant. The quantity of dissolved oxygen in the water drops as well, which might cause...
What is the importance of measuring BOD of a water body?
The quantity of oxygen required by bacteria to breakdown organic materials is known as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). The higher the BOD of water, the more contaminated it is. The water with a...
What are the sources of dissolved oxygen in water?
Water absorbs oxygen from the atmosphere when it comes into direct contact with atmospheric air. During the day, green aquatic plants photosynthesise. Photosynthesis does not occur at night, but the...
What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants?
Biodegradable pollutants are ones that can be degraded by bacteria or other natural elements such as fruits, sewage, and so on. Bacteria have a difficult time decomposing non-biodegradable...
During an educational trip, a student of botany saw a beautiful lake in a village. She collected many plants from that area. She noticed that villagers were washing clothes around the lake and at some places waste material from houses was destroying its beauty. After a few years, she visited the same lake again. She was surprised to find that the lake was covered with algae, the stinking smell was coming out and its water had become unusable. Can you explain the reason for this condition of the lake?
The dumping of household garbage in the lake can give nutrients for algae and aquatic plants to develop fast. The breakdown of these, which is aided by bacteria, can also result in a bad odour. The...
What could be the harmful effects of improper management of industrial and domestic solid waste in a city?
Inadequate industrial and household waste management in a city can result in significant harm to both living and non-living objects. 1. If household trash is not properly disposed of, sewage pipes...
Based on chemical reactions involved, explain how chlorofluorocarbons cause thinning of the ozone layer in the stratosphere
The action of ultraviolet radiation causes chlorofluorocarbons to dissociate, releasing the free chlorine radicle. U V radiations + CF2Cl2 + Cl + CFC Now that this Chlorine radicle has formed, it is...
Dissolved oxygen in water is very important for aquatic life. What processes are responsible for the reduction of dissolved oxygen in water?
The process of eutrophication is when the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water decreases. It's a process in which nutrient-rich water bodies support a dense plant population, which then kills...
Ozone is a toxic gas and is a strong oxidizing agent even then its presence in the stratosphere is very important. Explain what would happen if ozone from this region is completely removed?
When ozone is removed from the atmosphere, UV radiation comes into direct contact with living organisms, causing harm such as skin cancer and a variety of other dangerous illnesses. The ozone in the...
Acid rain is known to contain some acids. Name these acids and where from they come in the rain?
Acid rain is caused by human activities that release sulphur and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. 2H2SO4 = 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) + 2H2O (l) (aq) 4HNO3 (aq) = 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g) + 2H2O (l). Acid rain...
Greenhouse effect leads to global warming. Which substances are responsible for the greenhouse effect?
Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, chlorofluorocarbon compounds (CFCs), and water vapour are all responsible for the greenhouse effect, which leads to global warming.
The consequences of global warming may be _________. (i) increase in average temperature of the earth (ii) melting of Himalayan Glaciers. (iii) increased biochemical oxygen demand. (iv) eutrophication.Solution:
The solutions are (i), (ii).
The acids present in acid rain are _________. (i) Peroxyacetylnitrate (ii) H2CO3 (iii) HNO3 (iv) H2SO4
The solutions are (ii), (iii), and (iv).
Phosphate containing fertilisers cause water pollution. Addition of such compounds in water bodies causes __________. (i) enhanced growth of algae. (ii) the decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water. (iii) deposition of calcium phosphate. (iv) increase in the fish population.
The solutions are option (i) and (ii)
Which of the following conditions shows the polluted environment. (i) a pH of rainwater is 5.6. (ii) amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is 0.03%. (iii) biochemical oxygen demand 10 ppm. (iv) eutrophication.
The solutions are option (iii) and (iv)
Which of the following practices will not come under green chemistry? (i) If possible, making use of soap made of vegetable oils instead of using synthetic detergents. (ii) Using H2O2 for bleaching purpose instead of using chlorine-based bleaching agents. (iii) Using a bicycle for travelling small distances instead of using petrol/diesel-based vehicles. (iv) Using plastic cans for neatly storing substances.
The solution is option (iV).
Which of the following statements is correct? (i) The ozone hole is a hole formed in the stratosphere from which ozone oozes out. (ii) The ozone hole is a hole formed in the troposphere from which ozone oozes out. (iii) The ozone hole is thinning of the ozone layer of the stratosphere at some places. (iv) Ozone hole means vanishing of ozone layer around the earth completely.
The solution is option (iii).
The pollutants which come directly in the air from sources are called primary pollutants. Primary pollutants are sometimes converted into secondary pollutants. Which of the following belongs to secondary air pollutants? (i) CO (ii) Hydrocarbon (iii) Peroxyacetyl nitrate (iv) NO
The solution is option (iii).
Dinitrogen and dioxygen are main constituents of air but these do not react with each other to form oxides of nitrogen because of _________. (i) the reaction is endothermic and requires very high temperature. (ii) the reaction can be initiated only in the presence of a catalyst. (iii) oxides of nitrogen are unstable. (iv) N2and O2 are unreactive.
The solution is option (i).
The gaseous envelope around the earth is known as the atmosphere. The lowest the layer of this is extended up to 10 km from sea level, this layer is _________. (i) Stratosphere (ii) Troposphere (iii) Mesosphere (iv) Hydrosphere
The solution is option (ii).
Which of the following statements about photochemical smog is wrong? (i) It has a high concentration of oxidising agents. (ii) It has a low concentration of the oxidising agent. (iii) It can be controlled by controlling the release of NO2 , hydrocarbons, ozone etc. (iv) Plantation of some plants like pinus helps in controlling photochemical smog.
The solution is option (ii).
Sewage containing organic waste should not be disposed of in water bodies because it causes major water pollution. Fishes in such polluted water die because of (i) Large number of mosquitoes. (ii) Increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen. (iii) The decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water. (iv) Clogging of gills by mud.
The solution is option (iii).
Which of the following statements is wrong? (i) Ozone is not responsible for the greenhouse effect. (ii) Ozone can oxidise sulphur dioxide present in the atmosphere to sulphur trioxide. (iii) The ozone hole is thinning of ozone layer present in the stratosphere. (iv) Ozone is produced in the upper stratosphere by the action of UV rays on oxygen.
The solution is option (i).
Biochemical Oxygen Demand, (BOD) is a measure of organic material present in water. BOD value less than 5 ppm indicates a water sample to be __________. (i) rich in dissolved oxygen. (ii) poor in dissolved oxygen. (iii) highly polluted. (iv) not suitable for aquatic life.
The solution is option (i).
Which of the following statements is not true about classical smog? (i) Its main components are produced by the action of sunlight on emissions of automobiles and factories. (ii) Produced in a cold and humid climate. (iii) It contains compounds of reducing nature. (iv) It contains smoke, fog and sulphur dioxide.
The solution is option (i).
Photochemical smog occurs in a warm, dry and sunny climate. One of the following is not amongst the components of photochemical smog, identify it. (i) NO2 (ii) O3 (iii) SO2 (iv) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
The solution is option (iii).
Which of the following gases is not a greenhouse gas? (i) CO (ii) O3 (iii) CH4 (iv) H2O vapour
Option (i) is the correct answer
Match the ions given in Column I with their nature-given in Column II.
(i) is a, b and d (ii) is b (iii) is b (iv) are c and d
Match Column I with Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is e (iii) is a (iv) is b (v) is d
Match the terms mentioned in Column I with the terms in Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is f (iii) is b (iv) is a (v) is d (vi) is e
Match the type of mixture of compounds in Column I with the technique of separation/purification given in Column II.
(i) is e (ii) is d (iii) is a (iv) is b (v) is c
Which of the two structures (A) and (B) given below is more stabilised by resonance? Explain. (A) CH3COOH (B) CH3COO-
Compound A's two resonant structures are not equal, but compound B, which has a negative charge on the oxygen atom, has two equivalent structures, making it more stable.
By mistake, an alcohol (boiling point 97°C) was mixed with a hydrocarbon (boiling point 68°C). Suggest a suitable method to separate the two compounds. Explain the reason for your choice.
Steam distillation can be used to separate the mixture. The boiling points of alcohol and hydrocarbon are almost same. Steam distillation is used to purify temperature-sensitive materials in...
Resonance structures of propenal are given below. Which of these resonating structures is more stable? Give a reason for your answer.
Because all of the atoms in structure I have a complete octet, while the carbon atom with a positive charge does not have a complete octet in structure II, structure I will be more stable.
Which of the following compounds will not exist as a resonance hybrid. Give the reason for your answer:
Conjugation is only feasible when an atom possesses any of the double bond's charge or alternate positions. Because of this, CH3OH will not exist as a resonance hybrid here.
Give three points of differences between the inductive effect and resonance effect.
1. In the inductive effect, the electron is only sent through the sigma bond, but in the resonance effect, the electron is transmitted through both the sigma and pi bonds. 2. It is feasible when the...
Identify the most stable species in the following set of ions giving reasons:
(i) Because the bromine atom destabilises the positive charge on a carbon atom, C+H3 will be more stable. Bromine possesses a lone pair of electrons and is an electron-withdrawing group. (ii) CCl3...
Draw the resonance structures of the following compounds.
Write structural formulae for compounds named as- (a) 1-Bromoheptane (b) 5-Bromoheptanoic acid
Name the compounds whose line formulae are given below:
(i)The compound's name is 3-ethyl-4-methyl-5-heptane-2-one. (ii) The chemical is called 1-nitro-cyclohexane-2-ene.
Three students, Manish, Ramesh and Rajni were determining the extra elements present in an organic compound given by their teacher. They prepared the Lassaigne’s extract (L.E.) independently by the fusion of the compound with sodium metal. Then they added solid FeSO4 and dilute sulphuric acid to a part of Lassaigne’s extract. Manish and Rajni obtained Prussian blue colour but Ramesh got a red colour. Ramesh repeated the test with the same Lassaigne’s extract but again got red colour only. They were surprised and went to their teacher and told him about their observation. A teacher asked them to think over the reason for this. Can you help them by giving the reason for this observation? Also, write the chemical equations to explain the formation of compounds of different colours
3NaCNS + FeSO4 + dilute sulphuric→ Fe(CNS)3 (Blood red colour) + 3Na+ Ramesh's organic molecule has both Nitrogen and Sulphur, resulting in the Blood-red colour of Fe(CNS)3, whereas Manish and...
Write structures of various carbocation that can be obtained from 2-methyl butane. Arrange these carbocations in order of increasing stability.
The following is the stability order: (III) > (II) > (I) > IV This is due to the fact that (III) is a tertiary carbocation, (II) is a secondary carbocation, and (I) and (IV) are primary...
The structure of triphenylmethylcation is given below. This is very stable and some of its salts can be stored for months. Explain the cause of the high stability of this cation.
Triphenylcarbocation is a tertiary carbocation with a positive charge on the carbon atom that is stabilised by resonance thanks to the three phenyl groups. The stability of the system improves as a...
Which of the following ions is more stable? Use resonance to explain your answer.
Inductive effect, hyperconjugation, resonance, and other factors influence the stability of carbocation. Because structure A has a carbocation that is both primary and allylic, whereas...
Draw the possible resonance structures for and predict which of the structures is more stable. Give the reason for your answer.
Structure C is more stable than structure A because all atoms' octets are complete in structure C, but in structure A, a C-atom with a positive charge does not have 8 electrons in its valence...
If a liquid compound decomposes at its boiling point, which method(s) can you choose for its purification. It is known that the compound is stable at low pressure, steam volatile and insoluble in water.
Because the liquid component decomposes near its boiling point, indicating that it is heat-sensitive, we purify it using "Steam distillation." For temperature-sensitive materials, this is done.
In DNA and RNA, the nitrogen atom is present in the ring system. Can the Kjeldahl method be used for the estimation of nitrogen present in these? Give reasons.
Because nitrogen cannot be transformed into ammonium sulphate at the conditions employed in the Kjeldahl technique, it cannot be used to estimate nitrogen levels in DNA and RNA. This test for DNA...
Which of the following selected chains is correct to name the given compound according to the IUPAC system.
a. The main(parent) chain should be the longest carbon chain feasible, including all carbons containing functional groups. With both functional groups in the main chain, the aforementioned option is...
Compounds with same molecular formula but differing in their structures are said to be structural isomers. What type of structural isomerism is shown by
The functional groups (thioether/sulphide) are the similar in both structures, but the atoms in the main chain are arranged differently. As a result, they can show chain isomerism.
Show the polarisation of carbon-magnesium bond in the following structure. CH3—CH2—CH2—CH2—Mg—X
CH3—CH2—CH2—δ-CH2—δ+Mg+ X- Because the electronegativity differential in the C-Mg bond is strongly polarised, carbon is more electronegative than magnesium. Because C is more electronegative, its...
Explain, how is the electronegativity of carbon atoms related to their state of hybridisation in an organic compound?
There are three forms of carbon hybridization in organic compounds: sp, sp2, and sp3. The electronegativity of carbon increases as the ‘s' character increases because ‘s' orbitals are closer to the...
What is the hybridisation of each carbon in H2C = C = CH2?
The terminal carbons are sp2 hybridised, forming three sigma bonds (two with H and one with C) and one pi bond (between carbons), whereas the middle carbon is sp hybridised (as it forms 2 sigma...
For testing halogens in an organic compound with AgNO3 solution, sodium extract (Lassaigne’s test) is acidified with dilute HNO3. What will happen if a student acidifies the extract with dilute H2 SO4 in place of dilute HNO3?
If dilute H2 SO4 is used, sodium sulphide and sodium cyanine are not destroyed, therefore the proper result will not be obtained if halides are present.
Identify the pairs of compounds that represent chain isomerism.
Chain isomerism is represented by the chemicals I and III, I and IV, II and III, II and IV, II and IV, V and VII, VI and VII. Chain isomerism refers to compounds that have the same chemical formula...
Identify the pairs of compounds that represent position isomerism.
Position isomerism is represented by the chemicals I and II, III and IV, V and VI. When the length of the parent chain and the functional group are the same but the position of the functional group...
Identify the pairs of compounds which are functional group isomers.
I and V, I and VI, I and VII, II and V, II and VI, II and VII, III and V, III and VI, III and VII, IV and V, IV and VI, IV and VII. Each ether in the listed seven compounds has an alcohol function...
Which of the above compounds form pairs of metamers?
Metamers V and VI form a pair. (Ethers' metamers) The chain length of compounds V and VI is the same, but the carbon arrangement around the oxygen atom differs.
Hyperconjugation involves delocalisation of ___________. (i) electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of an alkyl group directly attached to an atom of the unsaturated system. (ii) electrons of carbon-hydrogen σ bond of alkyl group directly attached to the positively charged carbon atom. (iii) π-electrons of carbon-carbon bond (iv) lone pair of electrons
The correct answers are (i) and (ii).
A nucleophile is a species that should have (i) a pair of electrons to donate (ii) positive charge (iii) negative charge (iv) electron-deficient species
The correct answers are I and (iii).
Which of the following pairs are not functional group isomers? (i) II and III (ii) II and IV (iii) I and IV (iv) I and II
The correct answers are (i) and (iii).
Which of the following pairs are position isomers? (i) I and II (ii) II and III (iii) II and IV (iv) III and IV
Correct Option is (ii)
Electrophiles are electron seeking species. Which of the following groups contain only electrophiles? (i) BF3, NH3, H2O (ii) AlCl3, SO3 , + NO2 (iii) NO2+ , CH3+ , CH3 –C+ = O (iv) C2H-5, C2H5, CH5+
The correct answers are (ii) and (iii).
In which of the following representations given below spatial arrangement of group/ atom different from that given in structure ‘A’?
Option (i), (iii) and (iv) are the answers.
Which of the following compounds contain all the carbon atoms in the same hybridisation state? (i) H—C ≡ C—C ≡ C—H (ii) CH3—C ≡ C—CH3 (iii) CH2 = C = CH2 (iv) CH2 = CH—CH = CH2
The correct answers are I and (iv).
The addition of HCl to alkene proceeds in two steps. The first step is the attack of H+ ion C=C to a portion which can be shown as
Option II is the correct answer.
A covalent bond can undergo fission in two different ways. The correct representation involving heterolytic fission of CH3—Br is
Option (ii) is the correct answer.
Electrophilic addition reactions proceed in two steps. The first step involves the addition of an electrophile. Name the type of intermediate formed in the first step of the following addition reaction. H3 C—HC = CH2 + H+ →? (i) 2° Carbanion (ii) 1° Carbocation (iii) 2° Carbocation (iv) 1° Carbanion
Option III is the correct answer.
Ionic species are stabilised by the dispersal of charge. Which of the following carboxylate ion is the most stable?
Option IV is the correct answer.
In which of the following compounds the carbon marked with an asterisk is expected to have the greatest positive charge? (i) *CH3—CH2—Cl (ii) *CH3—CH2—Mg+Cl– (iii) *CH3—CH2—Br (iv) *CH3—CH2—CH3
Option I is the correct answer.
Correct IUPAC name for is ___________.i) 2- ethyl-3-methylpentane (ii) 3,4- dimethylhexane (iii) 2-sec-butylbutane (iv) 2, 3-dimethylbutane
Option II is the correct answer.
What is the correct order of decreasing stability of the following cations?(i) II > I > III (ii) II > III > I (iii) III > I > II (iv) I > II > III
Option I is the correct answer.
The principle involved in paper chromatography is (i) Adsorption (ii) Partition (iii) Solubility (iv) Volatility
Option II is the correct answer.
During the hearing of a court case, the judge suspected that some changes in the documents had been carried out. He asked the forensic department to check the ink used at two different places. According to you which technique can give the best results? (i) Column chromatography (ii) Solvent extraction (iii) Distillation (iv) Thin-layer chromatography
Option IV is the correct answer.
The fragrance of flowers is due to the presence of some steam volatile organic compounds called essential oils. These are generally insoluble in water at room temperature but are miscible with water vapour in the vapour phase. A a suitable method for the extraction of these oils from the flowers is: (i) Distillation (ii) Crystallisation (iii) Distillation under reduced pressure (iv) Steam distillation
Option IV is the correct answer.
In which of the following, functional group isomerism is not possible? (i) Alcohols (ii) Aldehydes (iii) Alkyl halides (iv) Cyanides
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
Electronegativity of carbon atoms depends upon their state of hybridisation. In which of the following compounds, the carbon marked with an asterisk is most electronegative? (i) CH3 – CH2 – *CH2 –CH3 (ii) CH3 – *CH = CH – CH3 (iii) CH3 – CH2 – C ≡ *CH (iv) CH3 – CH2 – CH = *CH2
Option (iii) is the correct answer.
The IUPAC name for(i) 1-Chloro-2-nitro-4-methylbenzene (ii) 1-Chloro-4-methyl-2-nitrobenzene (iii) 2-Chloro-1-nitro-5-methylbenzene (iv) m-Nitro-p-chlorotoluene
Option II is the correct answer.
The IUPAC name for is ________.(i) 1-hydroxypentane-1,4-dione (ii) 1,4-dioxopentanol (iii) 1-carboxybutan-3-one (iv) 4-oxopentanoic acidSolution:
Option IV is the correct answer.
Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name? (i) 3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane (ii) 4,4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane (iii) 5-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane (iv) 4,4-Bis(methyl)-3-ethylheptane
Option I is the correct answer.
Assertion (A): Silicons are water-repelling in nature. Reason (R): Silicons are organosilicon polymers, which have (–R2SiO–) as repeating unit. (i) A and R both are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A and R both are not true. (iv) A is not true but R is true.
Correct Option is (ii)
Assertion (A): If aluminium atoms replace a few silicon atoms in three the dimensional network of silicon dioxide, the overall structure acquires a negative charge. Reason (R): Aluminium is trivalent while silicon is tetravalent. (i) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) Both A and R are not correct (iv) A is not correct but R is correct.
Correct Option is (i)
Match the species given in Column I with the hybridisation given in Column II.
(i) is b (ii) is c (iii) is b (iv) is a (v) is b (vi) is c
Match the species given in Column I with properties given in Column II.
(i) is c (ii) is d (iii) is a (iv) is e (v) is b
Match the species given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.
(i) is e (ii) is c (iii) is d (iv) is a,b
Complete the following chemical equations : Z + 3 LiAiH4 → X + 3 Lif + 3AIF3 3X + 3O2 → B2O3 + 3H2O
BF3 + 3LiAlH4 → B2H6 + 3LiF + 3AlF3 3B2H6 + 3O2 → B2O3 + 3H2O
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions : (i) A + 2HCL + 5H2O → 2NaCI + X X → HBO2 → Z
A is Borax, which produces Orthoboric acid when it combines with HCl in the presence of water (X). When Orthoboric acid is heated, Metaboric is formed, and when heated further, the chemical Z, i.e....
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions : (i) A + 2HCL + 5H2O → 2NaCI + X X → HBO2 → Z
A is Borax, which produces Orthoboric acid when it combines with HCl in the presence of water (X). When Orthoboric acid is heated, Metaboric is formed, and when heated further, the chemical Z, i.e....
Explain the following : (ix) BF3 does not hydrolyse. (x) Why does the element silicon, not form graphite-like structure whereas carbon does.
(ix) BF3 does not entirely hydrolyze. Instead, it forms boric acid and fluoroboric acid after partial hydrolysis. Because the HF is produced first, it interacts with H3BO3. As a result, BF3 does not...
Explain the following : (vii) Tl (NO3)3 acts as an oxidising agent. (viii) Carbon shows catenation property but lead does not.
(vii) The +3 oxidation state of Tl is less stable than the +1 oxidation state due to the weak shielding effect of the inner electronic orbitals. Because Tl's oxidation state is +3 in Tl(NO3)3, it...
Explain the following : (v) Pb4+ acts as an oxidising agent but Sn2+ acts as a reducing agent. (vi) Electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative as compared to fluorine.
(v); Due to the inert pair effect, the lower oxidation state, i.e. +2, is more stable than the higher one while travelling from top to bottom in the group. As a result of the inert pair effect, Pb...
Explain the following : (iii) Aluminium forms [AlF6]3- ion but boron does not form [BF6]3- ion. (iv) PbX2 is more stable than PbX4.
(iii) While aluminium has an empty d-orbital to accommodate the electrons from the fluorine atom, boron does not have an empty d-orbital. (iv); Pb is a part of the periodic table's group 14. (carbon...
Explain the following : (i) Gallium has a higher ionisation enthalpy than aluminium. (ii) Boron does not exist as B3+ ion
(i)The effective nuclear charge of Ga is somewhat greater than that of Al due to the poor shielding of valence electrons by the intervening 3d electrons. (ii) Boron's valence shell has three...
Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus shows amphoteric character. A piece of aluminium foil is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sodium hydroxide solution in a test tube and on bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound indicates the evolution of hydrogen gas. The same activity when performed with concentrated nitric acid, the reaction doesn’t proceed. Explain the reason.
Aluminium interacts with both acid and base to produce hydrogen gas, which pops and burns in the air. As a powerful oxidising agent, nitric acid produces a thin coating of aluminium oxide on the...
When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH]4]- only whereas AlCl3 in acidified aqueous solution forms [Al (H2O)6]3+ ion. Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
AlCl3 + 6H2O → [Al(H2O)6]3+ + 3Cl– The 6 H2O molecules bind to Al, donating 6 electron pairs to the Al3+ ion's 3s, 3p, and 3d orbitals. As a result, the Al atom hybridization in [Al(H2O)6]3+ species...
If a trivalent atom replaces a few silicon atoms in a three-dimensional network of silicon dioxide, what would be the type of charge on an overall structure?
One valence electron of each Si atom will become free if a few tetrahedral Si atoms in a three-dimensional network structure of SiO2 are replaced with an equal number of trivalent atoms. As a...
The +1 oxidation state in group 13 and +2 oxidation state in group 14 becomes more and more stable with increasing atomic number. Explain.
The likelihood of s orbital electrons to form bonds diminishes down the group from group 13 and 14 due to inadequate shielding of s orbital electrons by d and f orbitals. The inner pair effect is...
Explain the following : (i) CO2 is a gas whereas SiO2 is solid. (ii) Silicon forms SiF62- ion whereas the corresponding fluoro compound of carbon is not known.
I In comparison to carbon, silicon has a huge size. It does not provide a decent overlapping pattern. With oxygen atoms, it forms four single covalent bonds. Two Si atoms are connected to each...
Give reasons for the following: (i) CCl4 is immiscible in water, whereas SiCl4 is easily hydrolyzed. (ii) Carbon has a strong tendency for catenation compared to silicon.
I Because water is polar and CCl4 is non-polar, CCl4 is insoluble in water. There are no vacant orbitals on the carbon atom to absorb the electrons given by oxygen in water. Because Si possesses an...
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids? (ii) AlCl3
Because aluminium contains three electrons in its valence shell, AlCl3 forms a covalent connection with chlorine by creating three single chlorine bonds, making it an electron-deficient molecule and...
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids? (i) BCl3
Because it possesses 6 electrons in its outermost orbital and an empty p orbital, BCL3 is an electron-deficient compound. As a result, it functions as a Lewis acid, accepting a single pair of...
Draw the structure of boric acid showing hydrogen bonding. Which species is present in water? What is the hybridisation of boron in this species?
[B(OH)4]–species are formed when boric acid interacts with water. B(OH)3 + 2H2O → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+ Boron hybridization is sp3 in this species.
Explain the nature of boric acid as a Lewis acid in water.
Boric acid is a weak monobasic acid that accepts electrons from a hydroxyl ion to behave as a Lewis acid. B(OH)3 + 2H2O → [B(OH)4]– + H3O+ Boric acid accepts OH-, resulting in the production of the...
Draw the structures of BCl3.NH3 and AlCl3 (dimer).
Identify the correct resonance structures of carbon dioxide from the ones given below : (i) O – C ≡ O (ii) O = C = O (iii) –O ≡ C – O+ (iv) –O – C ≡ O+
The solutions are options (ii) and (iv).
Which of the following statements are correct. Answer based on Fig.11.1. (i) The two bridged hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane; (ii) Out of six B–H bonds two bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2-electron bonds. (iii) Out of six B-H bonds, four B-H bonds can be described in terms of 3 centres 2 electron bonds; (iv) The four-terminal B-H bonds are two centre-two electron regular bonds.
The solutions are I (ii), and (iv).
Which of the following statements are correct? (i) Fullerenes have dangling bonds (ii) Fullerenes are cage-like molecules (iii) Graphite is a thermodynamically most stable allotrope of carbon (iv) Graphite is slippery and hard and therefore used as a dry lubricant in Machines
The correct answers are II and (iii).
Me3SiCl is used during polymerisation of organic silicones because (i) the chain length of organic silicone polymers can be controlled by adding Me3SiCl (ii) Me3SiCl blocks the end terminal of a silicone polymer (iii) Me3SiCl improves the quality and yield of the polymer (iv) Me3SiCl acts as a catalyst during polymerisationSolution:
The correct answers are I and (ii).
The linear shape of CO2 is due to _________. (i) sp3 hybridisation of carbon (ii) sp hybridisation of carbon (iii) pπ– pπ bonding between carbon and oxygen (iv) sp2 hybridisation of carbonSolution:
The correct answers are II and (iii).
The reason for the small radius of Ga compared to Al is _______. (i) poor screening effect of d and f orbitals (ii) increase in nuclear charge (iii) presence of higher orbitals (iv) higher atomic number
The correct answers are I and (ii).
Cement, the important building material is a mixture of oxides of several elements. Besides calcium, iron and sulphur, oxides of elements of which of the group (s) are present in the mixture? (i) group 2 (ii) groups 2, 13 and 14 (iii) groups 2 and 13 (iv) groups 2 and 14
Option II is the correct response.
. Dry ice is (i) Solid NH3 (ii) Solid SO2 (iii) Solid CO2 (iv) Solid N2
Option III is the correct response.
The most commonly used reducing agent is (i) AlCl3 (ii) PbCl2 (iii) SnCl4 (iv) SnCl2
Option IV is the correct response.
Quartz is extensively used as a piezoelectric material, it contains ___________. (i) Pb (ii) Si (iii) Ti (iv) Sn
Option II is the correct response.
A compound X, of boron, reacts with NH3 on heating to give another compound Y which is called inorganic benzene. The compound X can be prepared by treating BF3 with Lithium aluminium hydride. The compounds X and Y are represented by the formulas. (i) B2H6, B3N3H6 (ii) B2O3, B3 N3 H6 (iii) BF3, B3N3 H6 (iv) B3N3H6, B2H6
Option I is the correct response.
In the structure of diborane (i) All hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane. (ii) 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane. (iii) 4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane. (iv) All the atoms are on the same plane.
Option II is the correct response.
Ionisation enthalpy (∆i H1 kJ mol–1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order. (i) B > Al > Ga > In > Tl (ii) B < Al < Ga < In < Tl (iii) B Ga Tl (iv) B > Al In < Tl
Option IV is the correct response
Silicon has a strong tendency to form polymers like silicones. The chain length of silicone, a polymer can be controlled by adding (i) MeSiCl3 (ii) Me2SiCl2 (iii) Me3SiCl (iv) Me4Si
Option III is the correct response.
Catenation i.e., linking of similar atoms dependson size and electronic configuration of atoms. The tendency of catenation in Group 14 elements follows the order: (i) C > Si > Ge > Sn (ii) C >> Si > Ge ≈ Sn (iii) Si > C > Sn > Ge (iv) Ge > Sn > Si > C
Option II is the correct response.
Boric acid is an acid because its molecule (i) contains replaceable H+ ion (ii) gives up a proton (iii) accepts OH– from water releasing a proton (iv) combines with a proton from the water molecule
Option III is the correct response.
