Given bend conditions are: \[y2\text{ }=\text{ }4x\text{ }\ldots \text{ }.\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\text{ }and\text{ }x2\text{ }+\text{ }y2\text{ }\text{ }6x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }0\text{...
solve the following:
Solution:
Find the angle of intersection of the curves y = 4 – x2 and y = x2.
The given bends are \[y\text{ }=\text{ }4\text{ }\text{ }x2\text{ }\ldots \text{ }.\text{ }\left( I \right)\text{ }and\text{ }y\text{ }=\text{ }x2\text{ }\ldots \text{ }\left( ii \right)\] Also, we...
solve the following:
Solution:
Solve the following:
Solution:
Find the co-ordinates of the point on the curve √x + √y = 4 at which tangent is equally inclined to the axes.
ACCORDING TO EQUATION OF CURVE, \[\surd x\text{ }+\text{ }\surd y\text{ }=\text{ }4\] Presently, let (x1, y1) be he required point on the bend SO , \[\surd x1\text{ }+\text{ }\surd y1\text{ }=\text{...
Solve the following:
Solution:
Solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
Prove that the curves xy = 4 and x2 + y2 = 8 touch each other.
Given bends are conditions of two circles, \[xy\text{ }=\text{ }4\text{ }\ldots \text{ }..\text{ }\left( I \right)\] and \[x2\text{ }+\text{ }y2\text{ }=\text{ }8\text{ }\ldots \text{ }.\text{...
Find the condition that the curves 2x = y2 and 2xy = k intersect orthogonally.
It's seen that the given bends are condition of two circles. \[2x\text{ }=\text{ }y2\text{ }\ldots \text{ }..\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\] and \[2xy\text{ }=\text{ }k\text{ }\ldots \text{ }..\text{...
Why is it important to have a clean surface in surface studies?
The surface of the adsorbent adsorbs the gases that are desirable in the process of adsorption. If an area already has other gases, it is saturated so it cannot adsorb the desired gases from the...
Why is chemisorption referred to as activated adsorption?
Chemisorption involves the formation of chemical bonds that require activating energy. That's why it's called activated adsorption.
x and y are the sides of two squares such that y = x – x2. Find the rate of change of the area of second square with respect to the area of first square.
How about we consider the space of the primary square \[A1\text{ }=\text{ }x2\] Furthermore, space of the subsequent square be \[A2\text{ }=\text{ }y2\] Presently, \[A1\text{ }=\text{ }x2\text{...
What type of solutions are formed on dissolving different concentrations of soap in the water?
The soap solution at low concentration acts as a standard electrolytic solution. But in the higher concentrations it behaves like a colloid and forms micelles.
What happens when gelatin is mixed with gold sol?
When the gelatin is mixed with gold sol, the gelatin forms a protective layer on the gold sol, thus preventing it from getting coagulated. So gold sol recovers by adding gelatin, which is a...
How does it become possible to cause artificial rain by spraying silver iodide on the clouds?
The Clouds hold charges as they are colloids. Silver iodide (AgI) electrolyte assists in the process of coagulation between colloidal water particles in a cloud. Thus, forming large raindrops that...
The volume of a cube increases at a constant rate. Prove that the increase in its surface area varies inversely as the length of the side.
We should expect x to be the length of the block. In this way, the volume of the solid shape \[V\text{ }=\text{ }x3\text{ }\ldots \text{ }.\text{ }\left( 1 \right)\] Considering that, \[dV/dt\text{...
A swimming pool is to be drained for cleaning. If L represents the number of litres of water in the pool t seconds after the pool has been plugged off to drain and L = 200 (10 – t)2. How fast is the water running out at the end of 5 seconds? What is the average rate at which the water flows out during the first 5 seconds?
Given, \[L\text{ }=\text{ }200\left( 10\text{ }\text{ }t \right)2\] where L addresses the quantity of liters of water in the pool. On separating both the sides w.r.t, t, we get \[dL/dt\text{...
A man, 2m tall, walks at the rate of m/s towards a street light which is m above the ground. At what rate is the tip of his shadow moving? At what rate is the length of the shadow changing when he is m from the base of the light?
Let AB is the stature of streetlamp post and CD is the tallness of the man with the end goal that \[AB\text{ }=\text{ }5\left( 1/3 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }16/3\text{ }m\text{ }and\text{ }CD\text{...
Which of the following phenomenon occurs when a chalk stick is dipped in ink?
(i) adsorption of coloured substance (ii) adsorption of solvent (iii) absorption and adsorption both of solvent (iv) absorption of solvent Correct Answers: (i) adsorption of coloured...
Find the approximate volume of metal in a hollow spherical shell whose internal and external radii are 3 cm and 3.0005 cm, respectively.
Given, The interior range $$ \[r\text{ }=\text{ }3\text{ }cm\] What's more, outside sweep \[R\text{ }=\text{ }r\text{ }+\text{ }r\text{ }=3.0005\text{ }cm\] \[r\text{ }=\text{ }3.0005\text{...
Which class of the manufactured cleansers is utilized in toothpaste?
Solution: Anionic cleansers are utilized in toothpaste to clean teeth and structure reasonable froth. Eg: sodium or ammonium lauryl sulfate
If a relation R on the set ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-df9a10089e417e1bc74e4a43afb3835b_l3.png)
be defined by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{R}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7d4fbd5bf6f1080340e0ad730c73e592_l3.png)
, then R is (A) reflexive (B) transitive (C) symmetric (D) none of these
The correct option is (D) none of these Given R on the set \[\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3 \right\}\]be defined by \[R\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( 1,\text{ }2 \right) \right\}\] Therefore, its...
The maximum number of equivalence relations on the set ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6b1b0a84bfc5cc886f5c4fd5e453f9a3_l3.png)
are (A) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-64318110f3a374fb786ef713c0b0c575_l3.png)
(B) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[2\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b1e8e3db630df9050b1fec3c4066d5e6_l3.png)
(C) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[3\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-df8bcc09db12acd0f6bda88b4b8135fb_l3.png)
(D) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[5\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7dc8465919d0838925dbc6c99670258c_l3.png)
The correct option is (D) \[5\] Given, set \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right\}\] Now, the number of equivalence relations as follows...
Consider the non-empty set consisting of children in a family and a relation R defined as aRb if a is brother of b. Then R is (A) symmetric but not transitive (B) transitive but not symmetric (C) neither symmetric nor transitive (D) both symmetric and transitive
The correct option is (B) transitive but not symmetric Given aRb ⇒ a is brother of b. This does not mean b is also a brother of a as b can be a sister of a. Therefore, R is not symmetric. aRb ⇒ a is...
Let T be the set of all triangles in the Euclidean plane, and let a relation R on T be defined as aRb if a is congruent to b ∀ a, b ∈ T. Then R is (A) reflexive but not transitive (B) transitive but not symmetric (C) equivalence (D) none of these
The correct option is (C) equivalence Given aRb, if a is congruent to b, ∀ a, b ∈ T. Then, we have aRa ⇒ a is congruent to a; which is always true. So, R is reflexive. Let aRb ⇒ a ~ b b ~ a bRa So,...
Let * be binary operation defined on R by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{1}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ab},\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2961f64055cadc8b7cae88fe60a1b709_l3.png)
. Then the operation * is (i) commutative but not associative (ii) associative but not commutative (iii) neither commutative nor associative (iv) both commutative and associative
(i) Given that * is a binary operation defined on R by \[\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{1}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ab},\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in...
Let * be the binary operation defined on Q. Find which of the following binary operations are commutative ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{b}\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~+\text{ }{{\mathbf{b}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q} \\ \left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ab}\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }{{\left( \mathbf{a}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{b} \right)}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q} \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0a1f3a790697fd211e1ec8a051a8dcce_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{b}\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~+\text{ }{{\mathbf{b}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q} \\ \left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ab}\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{a}\text{ }*\text{ }\mathbf{b}\text{ }=\text{ }{{\left( \mathbf{a}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{b} \right)}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Q} \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0a1f3a790697fd211e1ec8a051a8dcce_l3.png)
Given that * is a binary operation defined on Q. (i) \[a\text{ }*\text{ }b\text{ }=\text{ }a\text{ }\text{ }b,\forall a,\text{ }b\in Q\] and \[b\text{ }*\text{ }a\text{ }=\text{ }b\text{ }\text{...
Functions f , g : R → R are defined, respectively, by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}~\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~+\text{ }\mathbf{3x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{1},~\mathbf{g}~\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{2x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2dd0a70d016c1b6709d883a89deaa7c8_l3.png)
, find (i) f o g (ii) g o f (iii) f o f (iv) g o g
Given, \[\mathbf{f}~\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~+\text{ }\mathbf{3x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{1},~\mathbf{g}~\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{...
. Let ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\ldots \text{ }\mathbf{9} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4bba703b875f44961cf66438db00c2aa_l3.png)
and R be the relation in A ×A defined by (a, b) R (c, d) if a + d = b + c for (a, b), (c, d) in ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[A\text{ }\times A\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b2d867ff818b6c236e399d822f63f0a7_l3.png)
. Prove that R is an equivalence relation and also obtain the equivalent class ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right) \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3affb3b24e311584fc304dd1f72979fc_l3.png)
.
Given, \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\ldots \text{ }\mathbf{9} \right\}\]and (a, b) R (c, d) if a + d = b + c for \[\left( a,\text{ }b...
The compound that causes general upper activity on the focal sensory system has a place with the class of (a) analgesics (b) sedatives (c) opiate analgesics (d) antihistamines
Solution: (b) The compound that causes general stimulant activity on the focal sensory system has a place with the class of sedatives.
Each of the following defines a relation on N: (i) x is greater than y, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-53bce6e1c6a20d27eb7981b3f2a0d9cc_l3.png)
(ii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{y}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{10},\text{ }\mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ac2a04bdc6b7e6a9e6cf59fc647f9a46_l3.png)
(iii) x y is square of an integer ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-53bce6e1c6a20d27eb7981b3f2a0d9cc_l3.png)
(iv) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{4y}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{10}\text{ }\mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-066b5246906e9f67cf4ce6457424ca50_l3.png)
. Determine which of the above relations are reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
(i) Given, x is greater than y; \[\mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N}\] If \[\left( x,\text{ }x \right)\in R\], then \[x\text{ }>\text{ }x\], which is not true for any \[x\in N\]. Thus, R...
Let ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec86688849079e7c6493bd34b7abb7a3_l3.png)
. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective: (i) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{x}/\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-60d315a329816d5d7d74e09a6424ff3b_l3.png)
(ii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\left| \mathbf{x} \right|\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7a2feecb05cc88418ae74c021378e4f5_l3.png)
(iii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{h}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{x}\left| \mathbf{x} \right|\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e4e9b95c341051db94c9983ee99d99dc_l3.png)
(iv) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{k}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-531f812814bd08b1132646e938b5d74e_l3.png)
Given, \[A\text{ }=\text{ }\left[ 1,\text{ }1 \right]\] (i) \[f:\text{ }\left[ -1,\text{ }1 \right]\text{ }\to \text{ }\left[ -1,\text{ }1 \right],\text{ }f\text{ }\left( x \right)\text{ }=\text{...
Let ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{R}\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{3} \right\},\text{ }\mathbf{B}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{R}\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1} \right\}.\text{ }\mathbf{Let}\text{ }\mathbf{f}\text{ }:\text{ }\mathbf{A}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{B}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4826e8120534bd03f6ed6670ce6482c3_l3.png)
be defined by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{2}/\text{ }\mathbf{x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{3}\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{A}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3be59825d072da5199347321d3e97a56_l3.png)
. Then show that f is bijective.
According to the question, \[A\text{ }=\text{ }R\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ 3 \right\},\text{ }B\text{ }=\text{ }R\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ 1 \right\}\] And, f : A → B be defined by \[f\text{ }\left( x...
Give an example of a map (i) which is one-one but not onto (ii) which is not one-one but onto (iii) which is neither one-one nor onto.
(i) Let f: N → N, be a mapping defined by \[f\text{ }\left( x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }{{x}^{2}}\] For \[f\text{ }({{x}_{1}})\text{ }=\text{ }f\text{ }({{x}_{2}})\] Then, \[{{x}_{1}}^{2}~=\text{...
The most valuable order of medications for restorative scientific experts is (a) based on synthetic design (b) based on drug activity (c) based on sub-atomic targets (d) based on pharmacological impact
Solution: (c) The most valuable grouping of medications for therapeutic physicists. It is based on sub-atomic targets. Target particles are typically biomolecules like carbs, lipids, proteins and...
Given ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1d0332e8f8738588de84e4d9d4c7882a_l3.png)
, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{B}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{5},\text{ }\mathbf{6},\text{ }\mathbf{7} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5d67b0b282f80ff369f931d204458d4d_l3.png)
. Construct an example of each of the following: (a) an injective mapping from A to B (b) a mapping from A to B which is not injective (c) a mapping from B to A.
Given, \[\mathbf{A}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right\}\],\[\mathbf{B}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{5},\text{ }\mathbf{6},\text{...
Let R be relation defined on the set of natural number N as follows: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{R}\text{ }=\text{ }\{\left( \mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y} \right):\text{ }\mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{N},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N},\text{ }\mathbf{2x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{y}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{41}\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-88df5ebd7ad6cdd01200d5d66cf2b418_l3.png)
. Find the domain and range of the relation R. Also verify whether R is reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
Given function: \[\mathbf{R}\text{ }=\text{ }\{\left( \mathbf{x},\text{ }\mathbf{y} \right):\text{ }\mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{N},\text{ }\mathbf{y}\in \mathbf{N},\text{ }\mathbf{2x}\text{ }+\text{...
Find the approximate value of (1.999)5.
\[\left( 1.999 \right)5\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 2\text{ }\text{ }0.001 \right)5\] Let \[x\text{ }=\text{ }2\text{ }and\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }-\text{ }0.001\] Likewise, let \[y\text{ }=\text{ }x5\]...
Find the approximate value of (1.999)5.
question suggests, angle is \[\pi /3.\]
Find an angle q, 0 < q < /2, which increases twice as fast as its sine.
As per the inquiry, we have In this manner, the necessary point is \[\pi /3.\]
The value of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{sin}\text{ }(\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( \mathbf{0}.\mathbf{75} \right))\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-68c7d427817e899bb8b5a68d5aed6574_l3.png)
is equal to (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{75}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-446d3f09e70b6cad0293b7ed4c3da967_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0be31f8506cd6a9fb18570daae72de29_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{96}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f0483be7dacb7fe556620b46cb0154b5_l3.png)
(d) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{sin}\text{ }\mathbf{1}.\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0b77460703a89e6fbd25aab1d917b285_l3.png)
The correct option is (c) \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{96}\] We have, \[sin\text{ }(2\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}\left( 0.75 \right))\]
If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cos}\text{ }(\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{2}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{x})\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{0}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1cb547e2a81fe2ddca2b94ec20b7efdb_l3.png)
, then x is equal to (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-698ecc2591e4187b3b31451e4a8412ac_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}/\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5995ed954b2b025ca426324f5a89a8fe_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-fd0385a423a02a2235879aff6bfece5b_l3.png)
(d) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-64318110f3a374fb786ef713c0b0c575_l3.png)
The correct option is (b) \[\mathbf{2}/\mathbf{5}\] Given, \[cos\text{ }(si{{n}^{-1}}~2/5\text{ }+\text{ }co{{s}^{-1}}~x)\text{ }=\text{ }0\] So, this can be rewritten as \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
The domain of the function by f(x) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\sqrt{\left( \mathbf{x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right)}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dfbf35cc7cb2d872feaf569485ef4904_l3.png)
is (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-fcfcb28dd59583bc3e7a020a8cf5f451_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ -\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b21f7411312e08e9e9c76b1a5369f211_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4951cedbbb831e919142a21d14151c6a_l3.png)
(d) none of these
The correct option is (a) \[\left[ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2} \right]\] We know that, \[si{{n}^{-1}}~x\] is defined for \[x\in \left[ -1,\text{ }1 \right]\] So, f(x) =...
The domain of the function ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cos}-\mathbf{1}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2x}-\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-99b8e6286b585837ce48c8b01132334e_l3.png)
is (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4951cedbbb831e919142a21d14151c6a_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ -\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b21f7411312e08e9e9c76b1a5369f211_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ -\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b21f7411312e08e9e9c76b1a5369f211_l3.png)
(d) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi } \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4f3b7c31075d2dae94fe9c4f60b1821a_l3.png)
The correct option is (a) \[\left[ \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right]\] Since, \[cos-1\text{ }x\] is defined for \[x\in \left[ -1,\text{ }1 \right]\] So, f(x) = \[\mathbf{cos}-\mathbf{1}\text{...
The value of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{cos}\text{ }\mathbf{33\pi }/\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-aea705b6330621ecb7f543a1fea098c8_l3.png)
is (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3\pi }/\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c2d1bda05bc0967141df29b8057cf78a_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[-\mathbf{7\pi }/\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c3e656e247ec5c6b18a8ecf530d059fe_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{10}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-47aaedd99c7dba30799394a11a516fb5_l3.png)
(d) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[-\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{10}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4b6678b39bfd2e446cdbc2e73b32692d_l3.png)
The correct option is (d) \[-\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{10}\]
Two men A and B start with velocities v at the same time from the junction of two roads inclined at 45° to each other. If they travel by different roads, find the rate at which they are being separated.
How about we believe P to be any point where the two streets are leaned at a point of \[45o.\] Presently, two men An and B are moving along the streets PA and PB separately with same speed 'V'....
A kite is moving horizontally at a height of 151.5 meters. If the speed of kite is 10 m/s, how fast is the string being let out; when the kite is 250 m away from the boy who is flying the kite? The height of boy is 1.5 m.
Speed of the kite(V) \[=\text{ }10\text{ }m/s\] Leave FD alone the tallness of the kite and AB be the stature of the kite and AB be the tallness of the kid. Presently, let AF \[=\text{ }x\text{ }m\]...
If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{x}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f24489a3235ab60a7d1ead918fee879b_l3.png)
, then x equals (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-fd0385a423a02a2235879aff6bfece5b_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[-\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-96158281230e100426cf2f540c6264ad_l3.png)
(d) ½
The correct option is (b) \[\mathbf{1}\] Given, \[\mathbf{3}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{x}\text{...
Which of the following is the principal value branch of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cose}{{\mathbf{c}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{x}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6d1eb220a0e4116384d174374ab9174c_l3.png)
? (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( -\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-04e628daf78abc2132895875d18d553a_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi } \right]\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1095ec138b1c83380bf46ca1d2d9c985_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ -\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5354ebba5b1885dfedd7d083862690a1_l3.png)
(d) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ -\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right]\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{0} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6730dd1a41f4218ce47d3ee43e4842e8_l3.png)
The correct option is (d) \[\left[ -\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right]\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{0} \right\}\] According to the principal branch of...
If the area of a circle increases at a uniform rate, then prove that perimeter varies inversely as the radius.
We realize that the space of circle, \[A\text{ }=\text{ }\pi r2\] , where r = span of the circle Furthermore, \[edge\text{ }=\text{ }2\pi r\] As indicated by the inquiry, we have Subsequently, it's...
A spherical ball of salt is dissolving in water in such a manner that the rate of decrease of the volume at any instant is proportional to the surface. Prove that the radius is decreasing at a constant rate.
Given, a round ball of salt Then, at that point, the volume of ball \[V\text{ }=\text{ }4/3\text{ }\pi r3\] where r = sweep of the ball Presently, as per the inquiry we have \[dV/dt\propto S\] ,...
Consider the circuit arrangement in which the input and output characteristics of NPN transistor in CE configuration
Select the values of RB and RC for a transistor whose VBE = 0.7 V, so that the transistor is operating at point Q as shown in the characteristics shown in the figure (b). Given that the input...
Assuming the ideal diode. Explain the waveform.
Answer: When signal 20sinωt provides an input voltage less than 5 volt (because after 5V, the diode will receive a positive voltage at its P-junction), the diode will be in reverse bias, and the...
Draw the output signals C1 and C2 in the given combination of gates in the figure.
In the circuit shown in the figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Answer: As $ {{V}_{BE}}=0 $, the potential drop across $ {{R}_{B}} $ is 10 Volts. $ {{I}_{B}}=\frac{10}{400\times {{10}^{3}}}=25\mu A $ Now, as $ {{V}_{CE}}=0 $, The potenial drop across $...
If each diode in the figure has a forward bias resistance of 25Ω and infinite resistance in reverse bias, what will be the values of the current I1, I2, I3 and I4?
Answer: Because the diode in that branch is reverse biased, I3 is zero. I3 = 0 We know that the resistance in AB = 150 ohms and the resistance in EF = 150 ohms and AB is parallel to EF Therefore,...
A Zener of power rating 1 W is to be used as a voltage regulator. If Zener has a breakdown of 5V and it has to regulate voltage which fluctuated between 3V and 7V, what should be the value of Rs for safe operation in the figure?
Answer: According to the question, Power = 1W and Zener breakdown voltage = 5V We are given that the minimum voltage = 3V and the maximum voltage = 7V $ {{I}_{\max }}=\frac{P}{{{V}_{z}}}=\frac{1}{5}...
Write the truth table for the circuit shown in the figure. Name the gate that the circuit resembles.
Answer: The given circuit is AND and the truth table is: A B X = A.B 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1
Explain why elemental semiconductor cannot be used to make visible LEDs.
Answer: The bandgap in an elemental conductor is such that the emissions are infrared rather than visible. Elemental semiconductors cannot be used to make visible LEDs. This is because the energy...
How would you set up a circuit to obtain NOT gate using a transistor?
Answer: a) There is only one input and only one output b) By making use of the Boolean expression c) Realization of NOT gate d) Making use of the truth table The NOT gate is a single-input,...
Two car garages have a common gate which needs to open automatically when a car enters either of the garages or cars enter both. Devise a circuit that resembles this situation using diodes for this situation.
Answer: When an automobile approaches the gate, one or both gates are open. As a result, the OR gate produces the required result. The following is a truth table for the same: A B Y = A + B 0 0 0 0...
If the resistance R1 is increased, how will the readings of the ammeter and voltmeter change?
Answer: From the circuit diagram, we have IbR1 + Vbe = Vbb Expression for the base current gives us Ib = Vbb – Vbe/R1 It can be seen that Ib is inversely proportional to R1 The reading of the...
Three photodiodes D1, D2 and D3 are made of semiconductors having band gaps of 2.5eV, 2eV and 3eV, respectively. Which ones will be able to detect light of wavelength 6000 Ao?
Answer: According to the question, the wavelength is: λ = 6000 Ao = 6000 × 10-10m Expression for the energy of the light photon is as follows: E = hc/ λ Upon substituting the values of h, c and...
(i) Name the type of a diode whose characteristics are shown in the figure (a) and in the figure (b)
(ii) What does the point P in the figure (a) represent? (iii) What does the points P and Q in the figure (b) represent? Answer: (i) Figure a) depicts the Zener diode's characteristics, whereas...
In a CE transistor amplifier there is a current and voltage gain associated with the circuit. In other words, there is a power gain. Considering power a measure of energy, does the circuit violate conservation of energy?
Answer: The DC supply is connected to the CE transistor amplifier to provide energy to the signal. As a result, the CE configuration amplifier has a significant power gain. The extra power necessary...
The amplifiers X, Y and Z are connected in series. If the voltage gains of X, Y and Z are 10, 20 and 30, respectively and the input signal is 1 mV peak value, then what is the output signal voltage (peak value)
(i) if dc supply voltage is 10V? (ii) if dc supply voltage is 5V? Answer: According to the question, we can write Voltage gain in X = vx = 10 Voltage gain in Y = vy = 20 Voltage gain in Z = vz = 30...
Draw the output waveform across the resistor in the figure.
The waveform formed across the resistance diode conducts when the diode is forward biassed in the given circuit, hence the output will be only when the input +1V is between t1 and t2. As a result,...
Can the potential barrier across a p-n junction be measured by simply connecting a voltmeter across the junction?
Answer: We can't use a voltmeter to detect the potential barrier across a p-n junction because the voltmeter's resistance must be very high relative to the junction resistance, which is almost...
Sn, C, and Si, Ge are all group XIV elements. Yet, Sn is a conductor, C is an insulator while Si and Ge are semiconductors. Why?
Answer: If there is no energy gap between the conduction and valence bands in an atom's energy band diagram, the material will conduct current. This energy gap narrows when the material transitions...
Why are elemental dopants for Silicon or Germanium usually chosen from group XIII or group XV?
Answer: Because the size of the dopant must be compatible with the semiconductor and they must form covalent bonds. The elemental dopants for silicon or germanium are usually chosen from groups XIII...
Which of the following is the principal value branch of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cos}-\mathbf{1}\text{ }\mathbf{x}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d8e6ba03fbd43d222c09e6d7ff5e6405_l3.png)
? (a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ -\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5354ebba5b1885dfedd7d083862690a1_l3.png)
(b) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi } \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-304afae725f16f5826abffbd7d0e3505_l3.png)
(c) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{0}.\text{ }\mathbf{\pi } \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-96074c13411cdba9487f8ef3abfc6ff9_l3.png)
(d) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left[ \mathbf{0},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi } \right]\text{ }\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1095ec138b1c83380bf46ca1d2d9c985_l3.png)
The correct answer is (c) \[\left[ \mathbf{0}.\text{ }\mathbf{\pi } \right]\] According to the principal value branch \[co{{s}^{-1}}~x\] is \[\left[ 0,\text{ }\pi \right]\].
If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{1}}},\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{2}}},\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{3}}},\text{ }\ldots .,\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{n}}}~\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f0761db9221d8c4a34fb1a319790ab96_l3.png)
is an arithmetic progression with common difference d, then evaluate the following expression.
Given \[{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{1}}},\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{2}}},\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{3}}},\text{ }\ldots .,\text{ }{{\mathbf{a}}_{\mathbf{n}}}~\] is an arithmetic progression with...
The breakdown in a reverse-biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to
(a) large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small (b) large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large (c) strong electric...
To reduce the ripples in a rectifier circuit with capacitor filter
(a) RL should be increased (b) input frequency should be decreased (c) input frequency should be increased (d) capacitors with high capacitance should be used Answer: The correct options are: (a) RL...
Show that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~(\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{4})\text{ }=\text{ }\left( \mathbf{4}\text{ }\text{ }\surd \mathbf{7} \right)/\text{ }\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dccff6f472609b4472e4046132f40b0b_l3.png)
and justify why the other value ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{4}\text{ }+\text{ }\surd \mathbf{7} \right)/\text{ }\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c7d7e4f6ad4b104e1c211168af33a9_l3.png)
is ignored.
We have, \[ta{{n}^{-1}}\left( 1/2\text{ }si{{n}^{-1}}~3/4 \right)\] Let, \[~{\scriptscriptstyle 1\!/\!{ }_2}\text{ }si{{n}^{-1}}~{\scriptscriptstyle 3\!/\!{ }_4}\text{ }=\text{ }\theta \] or,...
Find the value of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{239}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1c868672679244103bf531dc883f771b_l3.png)
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 4\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~1/5\text{ }\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~1/239 \\ =\text{ }2\text{ }(ta{{n}^{-1}}~1/5)\text{ }\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~1/239 \\ \end{array}\] \[=\text{ }2\text{...
What happens during regulation action of a Zener diode?
(a) The current in and voltage across the Zenor remains fixed (b) The current through the series Resistance (Rs ) changes (c) The Zener resistance is constant (d) The resistance offered by the Zener...
Prove that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{4}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{2}/\mathbf{9}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\surd \mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-17821387054a6129ddeeec9c8d470549_l3.png)
Taking the LHS, \[ta{{n}^{-1}}~1/4\text{ }+\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~2/9\] = RHS – Hence Proved
In the depletion region of a diode
(a) there are no mobile charges (b) equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral (c) recombination of holes and electrons has taken place (d) immobile charged ions exist...
In an NPN transistor circuit, the collector current is 10mA. If 95 per cent of the electrons emitted reaches the collector, which of the following statements are true?
(a) The emitter current will be 8 mA (b) The emitter current will be 10.53 mA (c) The base current will be 0.53 mA (d) The base current will be 2 mA Answer: The correct options are: (b) The emitter...
Show that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{5}/\mathbf{13}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{63}/\mathbf{16}\text{ }\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9f862e2ddc16f49b0d8cb191b1265cde_l3.png)
Solution: Here, \[si{{n}^{-1}}~5/13\text{ }=\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~5/12\] And, \[co{{s}^{-1}}~3/5\text{ }=\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~4/3\] Taking the L.H.S, we have Thus, L.H.S = R.H.S – Hence Proved...
In the figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) At Vi = 0.4V, transistor is in active state (b) At Vi = 1V, it can be used as an amplifier (c) At Vi = 0. .5V, it can be used as a switch turned off (d) At Vi = 2.5V, it can be used as a switch...
Prove that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{8}/\mathbf{17}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{77}/\mathbf{85}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4a29de9d312057185353faf3423c5473_l3.png)
Taking the L.H.S, = \[\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{8}/\mathbf{17}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{si}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{5}\] = tan-1 8/15 + tan-1 3/4 – Hence...
. Find the simplified form of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left[ \mathbf{3}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{cos}\text{ }\mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{4}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{sin}\text{ }\mathbf{x} \right],\text{ }\mathbf{x}\in \left[ -\mathbf{3\pi }/\mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{4} \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d850eeacf1c4cdcc74e478df322d0565_l3.png)
.
We have, \[\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left[ \mathbf{3}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{cos}\text{ }\mathbf{x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{4}/\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{sin}\text{ }\mathbf{x}...
Prove that
Taking L.H.S, = R.H.S – Hence Proved
Solve the equation ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cos}\text{ }(\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}~}}\mathbf{x})\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{sin}\text{ }(\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}~}}\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{4})\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6cd380c08ad8ec5642d29a05211ae34a_l3.png)
.
Given equation, \[\mathbf{cos}\text{ }(\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}~}}\mathbf{x})\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{sin}\text{ }(\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}~}}\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{4})\]...
Show that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cos}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{7} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{sin}\text{ }(\mathbf{4}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{3}).\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c138d201ed7e18941451df2a61b7d942_l3.png)
Taking L.H.S, we have Thus, L.H.S = R.H.S – Hence proved
If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( \mathbf{cos}\text{ }\mathbf{\theta } \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left( \mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{cosec}\text{ }\mathbf{\theta } \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d2c7880428f4dda9d218ce3ce1285562_l3.png)
,then show that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{\theta }\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8f04b641eff03fb75d5c846a8eb665ad_l3.png)
.
Given, \[\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( \mathbf{cos}\text{ }\mathbf{\theta } \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left( \mathbf{2}\text{...
Find the value of the expression ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{sin}\text{ }(\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{3})\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{cos}\text{ }(\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{2}\surd \mathbf{2})\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5540e2f416552b974588e8588acb6daf_l3.png)
.
Given expression, \[\mathbf{sin}\text{ }(\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{1}/\mathbf{3})\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{cos}\text{...
Find the real solution of the equation : 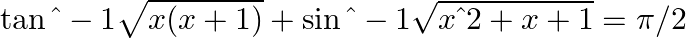
Given equation, Hence, the real solutions of the given trigonometric equation are \[0\] and \[-1\].
Show that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( -\mathbf{3} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( -\mathbf{4}/\mathbf{3} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1bf1fa38e67e8dd0a1d86ec247fb01c5_l3.png)
Taking L.H.S = \[2\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}\left( -3 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }-2\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~3\text{ }(\because ta{{n}^{-1}}~\left( -x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }ta{{n}^{-1}}~x)\text{ }\in...
Find the value of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}~}}\left( \mathbf{tan}\text{ }\mathbf{2\pi }/\mathbf{3} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d9347e59b88d99bd217f83bd865f0408_l3.png)
.
We know that, \[ta{{n}^{-1}}~tan\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }x,\text{ }x\in \left( -\pi /2,\text{ }\pi /2 \right)\]
Find the value of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left( -\mathbf{1}/\surd \mathbf{3} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( \mathbf{1}/\surd \mathbf{3} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( \mathbf{sin}\text{ }\left( -\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{2} \right) \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-648eb67f374bfb1b0ea85a535aa93285_l3.png)
According to the question, \[\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left( -\mathbf{1}/\surd \mathbf{3} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( \mathbf{1}/\surd...
Prove that ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cot}\text{ }(\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{4}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{-2}\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{t}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\mathbf{3})\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{7}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-158939f2ec8b756711a45b4e1f072354_l3.png)
According to the question, L.H.S = R.H.S – Hence Proved
Evaluate ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{cos}[\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}\left( -\surd \mathbf{3}/\mathbf{2} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{\pi }/\mathbf{6}]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-129f4b73ad8a452af907b31ca9d311f8_l3.png)
Consider an NPN transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector-base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) Electrons crossover from emitter to collector (b) Holes move from base to collector (c) Electrons move from emitter to base (d) Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the...
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor
(a) electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band (b) electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band (c) holes in the...
Truth table for the given circuit in the figure is
(a) A B E 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 (b) A B E 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 (c) A B E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 (d) A B E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 Answer: The correct option is (c) A B E 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1...
In the circuit shown in the figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is
(a) 1.3 V (b) 2.3 V (c) 0 (d) 0.5 V Answer: The correct option is (b) 2.3 V Explanation: Let V represent the potential difference between A and B, then we can write: V - 0.3 = (5 +5) x 103 x (0.2 x...
The output of the given circuit in the figure
(a) would be zero at all times (b) would be like a half-wave rectifier with positive cycles in output (c) would be like a half-wave rectifier with negative cycles in output (d) would be like that of...
Find the value of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{ta}{{\mathbf{n}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left[ \mathbf{tan}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{5\pi }/\mathbf{6} \right) \right]\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{co}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-\mathbf{1}}}~\left[ \mathbf{cos}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{13\pi }/\mathbf{6} \right) \right]\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5cebef4c3e42c84da0e476a637feb0b1_l3.png)
We know that, \[ta{{n}^{-1}}~tan\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }x,\text{ }x\in \left( -\pi /2,\text{ }\pi /2 \right)\] And, here \[ta{{n}^{-1}}~tan\text{ }\left( 5\pi /6 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }5\pi...
Hole is
(a) an anti-particle of the electron (b) a vacancy created when an electron leaves a covalent bond (c) absence of free electrons (d) an artificially created particle Answer: The correct option is...
A 220 V A.C. supply is connected between points A and B in the figure. What will be the potential difference V across the capacitor?
(a) 220V (b) 110V (c) 0V (d) 220 √2 V Answer: The correct option is (d) 220 √2 V Explanation: V(max) will be the potential difference across the capacitor. It is given by: ${{V}_{\max...
In the figure, assuming the diodes to be ideal,
(a) D1 is forward biased and D2 is reverse biased and hence current flows from A to B (b) D2 is forward biased and D1 is reverse biased and hence no current flows from B to A and vice versa (c) D1...
In the figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction
(a) 1 and 3 both correspond to forward bias of junction (b) 3 corresponds to forward bias of junction and 1 corresponds to reverse bias of junction (c) 1 corresponds to forward bias and 3...
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because
(a) number density of free current carriers increases (b) relaxation time increases (c) both number density of carriers and relaxation time increase (d) number density of current carriers...
Let n be a fixed positive integer. Define a relation R in Z as follows: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Z}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ad8e1c13fb20f78579c0c903ffbb8c13_l3.png)
, aRb if and only if a – b is divisible by n. Show that R is an equivalance relation.
Given \[\forall \mathbf{a},\text{ }\mathbf{b}\in \mathbf{Z}\], aRb if and only if a – b is divisible by n. Now, for \[aRa\Rightarrow \left( a\text{ }\text{ }a \right)\]is divisible by n, which is...
Let ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{R}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dd6ed4993146108e6223c8db2541e3f7_l3.png)
be the function defined by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{1}/\left( \mathbf{2}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{cos}\text{ }\mathbf{x} \right)\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-84cddfb14d8332eb9da79af0df936940_l3.png)
. Then, find the range of f.
According to the question, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} f\left( x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }1/\left( 2\text{ }\text{ }cos\text{ }x \right)\forall x\in R \\ Let\text{ }y\text{ }=\text{ }1/\left( 2\text{...
If functions ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{A}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{B}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a65b4f87417f32d09792148a75d456c6_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}:\text{ }\mathbf{B}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{A}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1fe8f0a4ce8e1b942287832dc9c329ac_l3.png)
satisfy ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }\mathbf{o}\text{ }\mathbf{f}\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}_{\mathbf{A}}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2822f57295d364ff6b54fcd63ddbadb5_l3.png)
, then show that f is one-one and g is onto.
Given, \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{A}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{B}\]and \[\mathbf{g}:\text{ }\mathbf{B}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{A}\] satisfy \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }\mathbf{o}\text{...
Let ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{X}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-00a236a7e355a7d670dcb8476df3ab87_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{Y}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-213326489477be96ad3cd80e2d540705_l3.png)
. Find whether the following subsets of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{X}\text{ }\times \text{ }\mathbf{Y}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f014b536a97f4ce864b7dfedf28891d9_l3.png)
are functions from X to Y or not. (i) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6691f233314673e77e22007af106b401_l3.png)
(ii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5042e575b4ccda6cf2e48eaa227a27b8_l3.png)
(iii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{h}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\mathbf{4} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8b578f4fddc68e8e0e586ca65111a21a_l3.png)
(iv) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{k}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\mathbf{4} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-345e65558e5e27c048ec049113afadcd_l3.png)
.
Solution: From the question, \[\mathbf{X}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right\}\]and \[\mathbf{Y}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{5}...
. Let the function ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{R}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dd6ed4993146108e6223c8db2541e3f7_l3.png)
be defined by f (x) = cos x, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93681e8b3dafd096e20967b3836271fa_l3.png)
. Show that f is neither one-one nor onto.
We have, \[f:\text{ }R\text{ }\to \text{ }R\], \[f\left( x \right)\text{ }=\text{ }cos\text{ }x\] Now, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} f\text{ }({{x}_{1}})\text{ }=\text{ }f\text{ }({{x}_{2}}) \\...
Let C be the set of complex numbers. Prove that the mapping ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{C}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b91d0e5e712c414bc7e31733b22d22a9_l3.png)
given by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[f\left( \mathbf{z} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\left| \mathbf{z} \right|\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f825948db38f9f56374d6b1effa2f56c_l3.png)
, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\forall \mathbf{z}\in \mathbf{C}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a74567bb0e077aca3e2b1f592c075bd3_l3.png)
, is neither one-one nor onto.
According to the question, \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{C}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{R}\] such that \[f\left( \mathbf{z} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\left| \mathbf{z} \right|\], \[\forall \mathbf{z}\in...
If the mappings f and g are given by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-58479171ac85089e2b7c869f6a70f385_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{5},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6bae4d20c2ddb3f71bbf7e1016b46c25_l3.png)
, write ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }\mathbf{o}\text{ }\mathbf{g}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-079b2a9780de7bb51c6a828ea8162b7e_l3.png)
.
From the question, \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{1}...
Are the following set of ordered pairs functions? If so, examine whether the mapping is injective or surjective. (i) {(x, y): x is a person, y is the mother of x}. (ii){(a, b): a is a person, b is an ancestor of a}.
(i) from the question, {(x, y): x is a person, y is the mother of x} So we can say that each person ‘x’ has only one biological mother. Therefore, the above set of ordered pairs make a function. If...
Is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{5} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{7} \right) \right\}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d072d1f94a4403000866fa1969963f5e_l3.png)
a function? If g is described by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{\alpha x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{\beta }\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e132af380935f39045049cfed6bc479e_l3.png)
, then what value should be assigned to ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{\alpha }\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2290b3b6ebb8da39f941931b782a55ee_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{\beta }\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-24941173bdd7b0c67a5c814c4779615f_l3.png)
From the question, \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \left( \mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{1} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3} \right),\text{ }\left( \mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{5}...
If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}:\text{ }\mathbf{R}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dd6ed4993146108e6223c8db2541e3f7_l3.png)
is defined by ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\text{ }\mathbf{3x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-995851d8d7836e7b40ef98cf0bd42f1a_l3.png)
, write f (f (x)).
Given, \[\mathbf{f}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{x} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\text{ }\mathbf{3x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{2}\] Then, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} f\text{ }\left(...
If A = {a, b, c, d} and the function f = {(a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)}, write ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}{{~}^{\mathbf{1}}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-767f1094114853260386f6d809284ad0_l3.png)
.
According to the question, A = {a, b, c, d} and f = {(a, b), (b, d), (c, a), (d, c)} So, \[\mathbf{f}{{~}^{\mathbf{1}}}\] = {(b, a), (d, b), (a, c), (c, d)}
. Let f: R → R be the function defined by f (x) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-022296614ad7968c0c3b37dedea5273e_l3.png)
, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93681e8b3dafd096e20967b3836271fa_l3.png)
. write ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{f}{{~}^{\mathbf{1}}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-767f1094114853260386f6d809284ad0_l3.png)
.
According to the question the function, f (x) = \[\mathbf{2x}\text{ }\text{ }\mathbf{3}\], \[\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{R}\] Let us consider \[y\text{ }=\text{ }2x\text{ }\text{ }3\] \[x\text{...
Let f, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}:\text{ }\mathbf{R}\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2a6e4f932765ad5e387a51e3c62eeb38_l3.png)
be defined by f(x) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-16fd72fb9940c8b247bd1589bb6b4d2a_l3.png)
and g (x) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\text{ }\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e52890f89dba1d3f978c6f41597f9bd7_l3.png)
, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{R}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93681e8b3dafd096e20967b3836271fa_l3.png)
, respectively. Then, find ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{g}\text{ }\mathbf{o}\text{ }\mathbf{f}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-446f4667cf4569e1d8763649734e7995_l3.png)
.
According to the question, f(x) = \[\mathbf{2x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{1}\]and g (x) = \[{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}}~\text{ }\mathbf{2}\], \[\forall \mathbf{x}\in \mathbf{R}\] Thus, \[g\text{...
. Let D be the domain of the real valued function f defined by f(x) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\sqrt{(\mathbf{25}\text{ }\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}})}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-653a123eb2d1b6788fe0e3cb5438b845_l3.png)
. Then, write D
According to the question, f(x) = \[\sqrt{(\mathbf{25}\text{ }\text{ }{{\mathbf{x}}^{\mathbf{2}}})}\] The function is defined if \[25\text{ }\text{ }{{x}^{2}}~\ge \text{ }0\] So, \[{{x}^{2}}~\le...
Let A = {a, b, c} and the relation R be defined on A as follows: R = {(a, a), (b, c), (a, b)}. Then, write minimum number of ordered pairs to be added in R to make R reflexive and transitive.
According to the given question the relation, R = {(a, a), (b, c), (a, b)} Therefore, to make R as reflexive we should add (b, b) and (c, c) to R. Also, to make R as transitive we should add (a, c)...
Out of o-nitrophenol and o-cresol which is more acidic?
In ortho-nitrophenol, there is an electron-withdrawing group NO2 in the ortho position, which increases the acidic strength and makes it more acidic. There is an electron releasing group in o-cresol...
Write the structures of the isomers of alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O. Which of these exhibits optical activity?
Because Butan-2-ol possesses a chiral carbon atom, it is the only one that displays optical activity.
Arrange water, ethanol and phenol in increasing order of acidity and give a reason for your answer.
Ethanol water phenol ethanol ethanol ethanol ethanol ethanol ethanol ethanol ethanol Because it forms the phenoxide ion after deprotonation and is stabilized by resonance, phenol is more acidic....
The Bohr model for the H-atom relies on the Coulomb’s law of electrostatics. Coulomb’s law has not directly been verified for very short distances of the order of angstroms. Supposing Coulomb’s law between two opposite charge 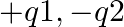 is modified to
is modified to 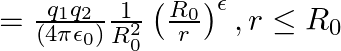 Calculate in such a case, the ground state energy of an
Calculate in such a case, the ground state energy of an  atom, if
atom, if 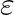
Case 1: When $\varepsilon=0.1, \mathrm{R_O}=1 \mathrm{~A}$ $\mathrm R_1=8 \times 10^{-11}$ $\mathrm{M}=0.08 \mathrm{~nm}$ Velocity at ground level is given as $\mathrm v_1=1.44 \times 10^{6}...
In the Auger process, an atom makes a transition to a lower state without emitting a photon. The excess energy is transferred to an outer electron which may be ejected by the atom. (This is called an Auger electron). Assuming the nucleus to be massive, calculate the kinetic energy of an 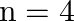 Auger electron emitted by Chromium by absorbing the energy from an
Auger electron emitted by Chromium by absorbing the energy from an 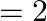 to
to 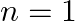 transition.
transition.
The energy in the nth state can be calculated as, $-\operatorname{Rch} Z^{2} / n^{2}=-13.6 z^{2} / n^{2} e V$ Where $R=$ Rydberg constant and $\mathrm{Z}=24$ Energy released is given as $\left(13.6...
If a proton had a radius R and the charge was uniformly distributed, calculate using Bohr theory, the ground state energy of a H-atom when
(i) R = 0.1Å,
and (ii) R = 10 Å.
(i) Consider the nucleus of a H atom as a point charge electron circling about it at a speed of $v$ and a radius of $r_A$ The Coulombian force acts as a centrifugal force, causing the nucleus to...
Deuterium was discovered in 1932 by Harold Urey by measuring the small change in wavelength for a particular transition in 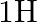 and
and 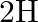 . This is because the wavelength of transition depends to a certain extent on the nuclear mass. If nuclear motion is taken into account then the electrons and nucleus revolve around their common centre of mass. Such a system is equivalent to a single particle with a reduced mass
. This is because the wavelength of transition depends to a certain extent on the nuclear mass. If nuclear motion is taken into account then the electrons and nucleus revolve around their common centre of mass. Such a system is equivalent to a single particle with a reduced mass 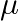 , revolving around the nucleus at a distance equal to the electron-nucleus separation. Here
, revolving around the nucleus at a distance equal to the electron-nucleus separation. Here 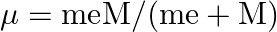 where
where 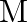 is the nuclear mass and
is the nuclear mass and 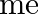 is the electronic mass. Estimate the percentage difference in wavelength for the 1 st line of the Lyman series in
is the electronic mass. Estimate the percentage difference in wavelength for the 1 st line of the Lyman series in 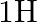 and
and 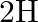 . (Mass of
. (Mass of 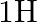 nucleus is
nucleus is 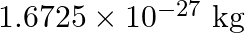 , Mass of
, Mass of 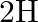 nucleus is
nucleus is 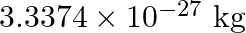 , Mass of electron
, Mass of electron 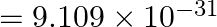 kg.)
kg.)
The energy of an electron in the nth state is given by the expression, $E_ n=-\mu Z^{2} \mathrm{e}^{4} / 8 \varepsilon_ 0^{2} h^{2}\left(1 / n^{2}\right)$ For hydrogen atom we have, $\mu...
What is the minimum energy that must be given to an 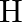 atom in ground state so that it can emit an Hy line in Balmer series? If the angular momentum of the system is conserved, what would be the angular momentum of such Hy photon?
atom in ground state so that it can emit an Hy line in Balmer series? If the angular momentum of the system is conserved, what would be the angular momentum of such Hy photon?
Energy required for the transition from $n=1$ to $n=5$ can be calculated as, $E=E _5-E_ 1=\left(-13.6 / 5^{2}\right)-\left(-13.6 / 1^{2}\right)=13.06 \mathrm{eV}$ Angular momentum is given as change...
Using the Bohr model, calculate the electric current created by the electron when the H-atom is in the ground state.
Let the velocity of the electron be $v$ Number of revolutions per unit time is given as $\mathrm{f}=2 \mathrm{ma}_{0} / \mathrm{V}$ The electric current is given as $I=Q$ When change $Q$ flows in...
Positronium is just like an H-atom with the proton replaced by the positively charged anti-particle of the electron (called the positron which is as massive as the electron). What would be the ground state energy of positronium?
The positronium has the lowest energy of -6.8 electron volts. The greatest energy level of positronium is -1.7 electron volt, which is the next highest energy level after n = 1.
Would the Bohr formula for the H-atom remain unchanged if proton had a charge (+4/3)e and electron a charge 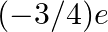 , where
, where  ? Give reasons for your answer.
? Give reasons for your answer.
The product of both charges will remain the same since the position of the proton and electron will not change.
When an electron falls from a higher energy to a lower energy level, the difference in the energies appears in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Why cannot it be emitted as other forms of energy?
Because the charged particle accelerates, the difference in energies shows in the form of electromagnetic radiation as an electron descends from a higher to a lower energy level.
Imagine removing one electron from 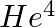 and
and 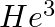 . Their energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close. Explain why.
. Their energy levels, as worked out on the basis of Bohr model will be very close. Explain why.
According to the Bohr model, the energies of $He^4$ and $He^3$ will be fairly near because each have one electron, much like the hydrogen atom, and the nucleus is four times heavier than the...
The mass of H atom is less than sum of the masses of a proton and electron. Why is this?
Protons and neutrons (and other particles) are held together by something called the strong nuclear force (strong interaction). This force diminishes the system's overall energy, which is dissipated...
The simple Bohr model is not applicable to 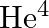 atom because
atom because
(a) 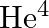 is an inert gas
is an inert gas
(b) 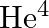 has neutrons in the nucleus
has neutrons in the nucleus
(c) 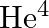 has one more electron
has one more electron
(d) electrons are not subject to central forces
The correct options are: (c) $\mathrm{He}^{4}$ has one more electron (d) electrons are not subject to central forces
Let 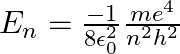 be the energy of the nth level of H-atom. If all the H-atoms are in the ground state and radiation of frequency
be the energy of the nth level of H-atom. If all the H-atoms are in the ground state and radiation of frequency 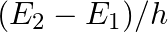 falls on it
falls on it
(a) it will not be absorbed at all
(b) some of the atoms will move to the first excited state
(c) all atoms will be excited to the 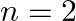 state
state
(d) no atoms will make a transition to the 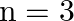 state
state
The correct options are: (b) some of the atoms will move to the first excited state (d) no atoms will make a transition to the $n=3$ state
The Balmer series for the H-atom can be observed
(a) if we measure the frequencies of light emitted when an excited atom falls to the ground state
(b) if we measure the frequencies of light emitted due to transitions between excited states and the first excited state
(c) in any transition in a  -atom
-atom
(d) as a sequence of frequencies with the higher frequencies getting closely packed
The correct options are: (b) if we measure the frequencies of light emitted due to transitions between excited states and the first excited state (d) as a sequence of frequencies with the higher...
The Bohr model for the spectra of an H-atom
(a) will not be applicable to hydrogen in the molecular from
(b) will not be applicable as it is for a He-atom
(c) is valid only at room temperature
(d) predicts continuous as well as discrete spectral lines
The correct options are: (a) will not be applicable to hydrogen in the molecular from (b) will not be applicable as it is for a $\mathrm{He}$-atom
A set of atoms in an excited state decays.
(a) in general to any of the states with lower energy
(b) into a lower state only when excited by an external electric field
(c) all together simultaneously into a lower state
(d) to emit photons only when they collide
The correct option is: (a) in general to any of the states with lower energy
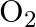 molecule consists of two oxygen atoms. In the molecule, nuclear force between the nuclei of the two atoms
molecule consists of two oxygen atoms. In the molecule, nuclear force between the nuclei of the two atoms
(a) is not important because nuclear forces are short-ranged
(b) is as important as an electrostatic force for binding the two atoms
(c) cancels the repulsive electrostatic force between the nuclei
(d) is not important because the oxygen nucleus have an equal number of neutrons and protons
The correct option is: (a) is not important because nuclear forces are short-ranged
For the ground state, the electron in the H-atom has an angular momentum  , according to the simple Bohr model. Angular momentum is a vector and hence there will be infinitely many orbits with the vector pointing in all possible directions. In actuality, this is not true,
, according to the simple Bohr model. Angular momentum is a vector and hence there will be infinitely many orbits with the vector pointing in all possible directions. In actuality, this is not true,
(a) because Bohr model gives incorrect values of angular momentum
(b) because only one of these would have a minimum energy
(c) angular momentum must be in the direction of spin of electron
(d) because electrons go around only in horizontal orbits
The correct option is: (a) because Bohr model gives incorrect values of angular momentum
Taking the Bohr radius as 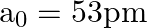 , the radius of
, the radius of 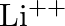 ion in its ground state, on the basis of Bohr’s model, will be about
ion in its ground state, on the basis of Bohr’s model, will be about
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 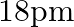
(d) 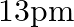
The correct option is: (c) $18 \mathrm{pm}$
The activity 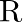 of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline$t(\mathrm{~h})$ & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\ \hline R(MBq) & 100 & $35.36$ & $12.51$ & $4.42$ & $1.56$ \\ \hline \end{tabular}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2cff4d33a1ea1a3274f405d5eee59de6_l3.png)
(i) Plot the graph of R versus 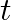 and calculate half-life from the graph.
and calculate half-life from the graph.
(ii) Plot the graph of 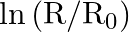 versus
versus 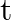 and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline$t(\mathrm{~h})$ & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\ \hline R(MBq) & 100 & $35.36$ & $12.51$ & $4.42$ & $1.56$ \\ \hline \end{tabular}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2cff4d33a1ea1a3274f405d5eee59de6_l3.png)
(i) Graph between $\mathrm{R}$ versus $\mathrm{t}$ will be an exponential curve. From the graph at slightly more than $\mathrm{t}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~h}$ the $\mathrm{R}$ should be $50 \%$ so at...
A nuclide 1 is said to be the mirror isobar of nuclide 2 if 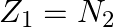 and
and 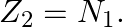
(a) What nuclide is a mirror isobar of 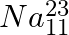 ?
?
(b) Which nuclide out of the two mirror isobars have greater binding energy and why?
a) We are given that a nuclide 1 is to be the mirror isobar of nuclide 2 if, $\mathrm Z_1=\mathrm N_2$ and $\mathrm Z_2=\mathrm N_1$ As a result, mirror isobar is $Z _2=12-N_ 1$ and $N_...
Why do stable nuclei never have more protons than neutrons?
Because protons are charged particles that resist one other, stable nuclei never have more protons than neutrons. Because of the strong repulsion, extra neutrons only produce attractive forces,...
Which one of the following cannot emit radiation and why? Excited nucleus, excited electron.
Because the energy of the electronic energy level is in the eV range rather than the MeV range, an excited electron cannot release radiation.
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
According to Rutherford and Soddy law, the radioactive decay is given as –dN/dt = λN.
The variation of the decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in the figure. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) The decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B (b) The decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A...
Fusion processes, like combining two deuterons to form a He nucleus are impossible at ordinary temperatures and pressure. The reasons for this can be traced to the fact:
(a) nuclear forces have short-range
(b) nuclei are positively charged
(c) the original nuclei must be completely ionized before fusion can take place
(d) the original nuclei must first break up before combining with each other
The correct options are: (a) nuclear forces have short-range (b) nuclei are positively charged
Heavy stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons. This is because of the fact that
(a) neutrons are heavier than protons
(b) electrostatic force between protons are repulsive
(c) neutrons decay into protons through beta decay
(d) nuclear forces between neutrons are weaker than that between protons
The correct option is: (b) electrostatic force between protons are repulsive
In a reaction, catalyst changes ____________.
(i) physically (ii) qualitatively (iii) chemically (iv) quantitatively Correct Answers: (i) physically (ii) qualitatively Explanation: In a reaction, catalyst changes physically and...
Which phenomenon occurs when an electric field is applied to a colloidal solution and electrophoresis is prevented?
(i) Reverse osmosis takes place. (ii) Electro osmosis takes place. (iii) Dispersion medium begins to move. (iv) Dispersion medium becomes stationary. Correct Answers: (ii) Electro osmosis...
What happens when a lyophilic sol is added to a lyophobic sol?
(i) Lyophobic sol is protected. (ii) Lyophilic sol is protected. (iii) Film of lyophilic sol is formed over lyophobic sol. (iv) Film of lyophobic sol is formed over lyophilic sol. Correct...
Which of the following colloids cannot be coagulated easily?
(i) Lyophobic colloids. (ii) Irreversible colloids. (iii) Reversible colloids. (iv) Lyophilic colloids. Correct Answers: (iii) Reversible colloids. (iv) Lyophilic colloids. Explanation:...
Which of the following substances will precipitate the negatively charged emulsions?
(i) KCl (ii) glucose (iii) urea (iv) NaCl Correct Answers: (i) KCl (iv) NaCl Explanation: KCl and NaCl are the substances that can precipitate the negatively charged...
An emulsion cannot be broken by __________ and ___________.
(i) heating (ii) adding more amount of dispersion medium (iii) freezing (iv) adding emulsifying agent Correct Answers: (ii) adding more amount of dispersion medium (iv) adding emulsifying...
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Mixing two oppositely charged sols neutralises their charges and stabilises the colloid. (ii) Presence of equal and similar charges on colloidal particles provides stability to the colloids....
H2 gas is adsorbed on activated charcoal to a very little extent in comparison to easily liquefiable gases due to ____________.
(i) very strong van der Waal’s interaction. (ii) very weak van der Waals forces. (iii) very low critical temperature. (iv) very high critical temperature. Correct Answers: (ii) very weak van...
Freundlich adsorption isotherm is given by the expression x/m = kp1/n which of the following conclusions can be drawn from this expression
(i) When1/n= 0, the adsorption is independent of pressure. (ii) When 1/n = 0, the adsorption is directly proportional to pressure. (iii)When n = 0,x/m vs p graph is a line parallel to x-axis. (iv)...
Which of the following statements are correct about solid catalyst?
(i) Same reactants may give different product by using different catalysts. (ii) Catalyst does not change ∆H of reaction. (iii) Catalyst is required in large quantities to catalyse reactions. (iv)...
Which of the following option are correct?
(i) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution is possible at all temperatures. (ii) Micelle formation by soap in aqueous solution occurs above a particular concentration. (iii) On dilution of...
Which of the following phenomenon applies to the process shown in Figure?
(i) Absorption (ii) Adsorption (iii) Coagulation (iv) Emulsification Correct Answer: (ii) Adsorption Explanation: Adsorption is the process that can be applied to this...
The gravitational force between an H-atom and another particle of mass m will be given by Newton’s law: 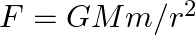 , where r is in km and
, where r is in km and
(a) M = mproton + m electron
(b) M = mproton  melectron
melectron 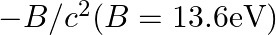
(c) M is not related to the mass of the hydrogen atom
(d) M = mproton +melectron 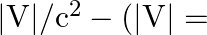 magnitude of the potential energy of electron in the
magnitude of the potential energy of electron in the  -atom)
-atom)
The correct option is: (b) M = mproton $+$ melectron $-B / c^{2}(B=13.6 \mathrm{eV})$
Which of the following process is not responsible for the presence of electric charge on the sol particles?
(i) Electron capture by sol particles. (ii) Adsorption of ionic species from solution. (iii) Formation of Helmholtz electrical double layer. (iv) Absorption of ionic species from solution. ...
Which of the following curves is in accordance with Freundlich adsorption isotherm?
Correct Answer: Option (iii) Explanation: According to the Freundlich adsorption isotherm, the option (iii) represents the proper graph.
Which of the following process is responsible for the formation of the delta at a place where rivers meet the sea?
(i) Emulsification (ii) Colloid formation (iii) Coagulation (iv) Peptisation Correct Answer: (iii) Coagulation Explanation: The Coagulation is responsible for the formation of the delta at a...
Arrange the following diagrams in the correct sequence of steps involved in the mechanism of catalysis, in accordance with modern adsorption theory.
(i) a → b → c → d → e (ii) a → c → b → d → e (iii) a → c → b → e → d (iv) a → b → c → e → d Correct Answer: (ii) a → c → b → d → e Explanation: According to the modern adsorption theory, the...
The values of colligative properties of the colloidal solution are of small order in comparison to those shown by true solutions of same concentration because of colloidal particles __________________.
(i) exhibit an enormous surface area. (ii) remain suspended in the dispersion medium. (iii) form lyophilic colloids. (iv) are comparatively less in number Correct Answer: (iv) are...
A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is classified as ____________.
(i) solid sol (ii) gel (iii) emulsion (iv) sol Correct Answer: (iv) sol Explanation: A colloidal system having a solid substance as a dispersed phase and a liquid as a dispersion medium is...
Which of the following electrolytes will have maximum coagulating value for AgI/Ag+ sol?
(i) Na2S (ii) Na3PO4 (iii) Na2SO4 (iv) NaCl Correct Answer: (ii) Na3PO4 Explanation: Na3PO4 is the electrolyte that has maximum coagulating value for AgI/Ag+ sol.
Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by ___________.
(i) coagulation (ii) electrolysis (iii) diffusion (iv) peptisation Correct Answer: (iv) peptisation Explanation: Freshly prepared precipitate sometimes gets converted to colloidal solution by...
The method by which lyophobic sol can be protected.
(i) By the addition of oppositely charged sol. (ii) By the addition of an electrolyte. (iii) By the addition of lyophilic sol. (iv) By boiling. Correct Answer: (iii) By the addition of...
Which of the following will show the Tyndall effect?
(i) An aqueous solution of soap below critical micelle concentration. (ii) An aqueous solution of soap above critical micelle concentration. (iii) An aqueous solution of sodium chloride. (iv) An...
At high concentration of soap in water, soap behaves as ____________.
(i) molecular colloid (ii) associated colloid (iii) macromolecular colloid (iv) lyophilic colloid Correct Answer: (ii) associated colloid Explanation: At high concentration of soap in water,...
In which of the following reactions heterogeneous catalysis is involved?
(a) 2SO2(g) + O2(g)→ [NO(g)] 2SO3(g) (b) 2SO2(g) → [Pt(s)] 2SO3(g) (c) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → [Fe(s)] 2NH3(g) (d) CH3COOCH3(l) + H2O (l) → [HCl(l)] CH3COOH (aq) + CH3OH (aq) Correct Answer: (a)...
Based on data given below to predict which of the following gases shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?
Gas Critical temo./K CO2304 SO2630 CH4190 H233 (i) CO2 (ii) SO2 (iii) CH4 (iv) H2 Correct Answer: (iv) H2 Explanation: H2 is the gas that shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of...
Which of the following an example of absorption?
(i) Water on silica gel (ii) Water on calcium chloride (iii) Hydrogen on finely divided nickel (iv) Oxygen on the metal surface Correct Answer: (ii) Water on calcium chloride Explanation:...
In physisorption adsorbent does not show specificity for any particular gas because ______________.
(i) involved van der Waals forces are universal. (ii) gases involved behave like ideal gases. (iii) enthalpy of adsorption is low. (iv) it is a reversible process. Correct Answer: (i)...
Physical adsorption of a gaseous species may change to chemical adsorption with ______________.
(i) decrease in temperature (ii) increase in temperature (iii) increase in surface area of the adsorbent (iv) the decrease in surface area of the adsorbent Correct Answer: (ii) increase in...
Which of the following is not a favourable condition for physical adsorption?
(i) high pressure (ii) negative ∆H (iii) the higher critical temperature of adsorbate (iv) high temperature Correct Answer: (iv) high temperature Explanation: The high temperature is not a...
Which one of the following is not applicable to the phenomenon of adsorption?
(i) ∆H > 0 (ii) ∆G < 0 (iii) ∆S < 0 (iv) ∆H < 0 Correct Answer: (i) ∆H > 0 Explanation: ∆H > 0 is not applicable to the phenomenon of adsorption.
The extent of adsorption of adsorbate from the solution phase increases with ________.
(i) increase in the amount of adsorbate in solution. (ii) the decrease in surface area of the adsorbent. (iii) increase in temperature of the solution. (iv) the decrease in the amount of adsorbate...
Extent of physisorption of a gas increases with ___________.
(i) increase in temperature. (ii) the decrease in temperature. (iii) the decrease in surface area of the adsorbent. (iv) the decrease in strength of van der Waals forces. Correct Answer: (ii)...
The term ‘sorption’ stands for ____________.
(i) absorption (ii) adsorption (iii) both absorption and adsorption (iv) desorption Correct Answer: (iii) both absorption and adsorption Explanation: SORPTION - Both absorption and...
Which of the following interface cannot be obtained?
(i) liquid-liquid (ii) solid-liquid (iii) liquid-gas (iv) gas-gas Correct Answer:(iv) gas-gas Explanation: The gas-gas interface cannot be obtained.
At the equilibrium position in the process of adsorption ___________.
(i) ∆H > 0 (ii) ∆H = T∆S (iii) ∆H > T∆S (iv) ∆H < T∆S Correct Answer: (ii) ∆H = T∆S Explanation: At the equilibrium position in the process of adsorption, ∆H =...
Which of the following process does not occur at the interface of phases?
(i) crystallisation (ii) heterogeneous catalysis (iii) homogeneous catalysis (iv) corrosion Correct Answer: (iii) homogeneous catalysis Explanation: The homogeneous catalysis do not occur in...
Why in the redox titration of KMnO4 vs oxalic acid, we heat oxalic acid solution before starting the titration?
We heat the oxalic acid solution because without heat it is a slow process as much more energy than the activation power needed to react. Therefore to increase energy, the temperature should be...
Why can’t molecularity of any reaction be equal to zero?
Zero molecularity means that there is no reactant, therefore the reaction will not be possible. So if there is a reaction then its molecularity will be greater than the zero.
Why molecularity is applicable only for elementary reactions and order is applicable for elementary as well as complex reactions?
Molecularity works only in the elementary reaction as it is a single reaction and the rate depends on the concentration of each molecule. And in the case of complex reactions there are many...
Why can we not determine the order of a reaction by taking into consideration the balanced chemical equation?
Order of a reaction is involved in a reaction. In complex reactions, rate and order of the reaction depend on the slow reaction, so in such cases, the order does not depend entirely on the balanced...
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction. Explain with the help of one example.
The thermodynamic feasibility of reaction alone cannot determine the rate of reaction because in order for a reaction to occur it is important that the molecules have a greater potential than the...
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decrease during the reaction?
The reaction rate decreases because the reactants will continue to be converted into products. The reaction rate always depends on the concentration of the reactants.
Why is the probability of reaction with molecularity higher than three very rare?
For a response to have more than three molecules, the correct position is not possible which makes this reaction unusual. Thus the probability of colliding more than three molecules at the same time...
Oxygen is available in plenty in the air yet fuels do not burn by themselves at room temperature. Explain.
Oxygen is found in the air but fuels do not burn themselves at room temperature because reactants must have a small amount of energy to form the products which is known as activation energy.
Why does the rate of a reaction increase with a rise in temperature?
The reaction rate increases with increasing temperature because at higher temperatures the friction of the colliding particles across the energy barrier will be larger. So the rate is also faster.
The reaction between H2(g) and O2(g) is highly feasible yet allowing the gases to stand at room temperature in the same vessel does not lead to the formation of water. Explain.
According to Maxwell Boltzmann's energy distribution curve, where the temperature T + 10 degree Celsius then the collision of molecular energy efficiency increases which leads to product formation....
