(i) What is the order of the reaction? (ii) What is the slope of the curve? (iii) What are the units of the rate constant? Answers: (i) Zero-order reaction is the order of reaction. (ii)...
For a zero-order reaction will the molecularity be equal to zero? Explain.
The molecularity of any reaction is the number of reactions involved in the basic reaction. Zero molecularity means that there is no reactant so reaction does not occur. Thus molecularity cannot be...
If A = {x : x ∈ W, x < 2}, B = {x : x ∈ N, 1 < x < 5}, C = {3, 5} find(i) A × (B ∩ C)(ii) A × (B ∪ C)
Given, A = {x: x ∈ W, x < 2}, B = {x : x ∈N, 1 < x < 5} C = {3, 5}; W is the set of whole numbers A = {x: x ∈ W, x < 2} = {0, 1} B = {x : x ∈N, 1 < x < 5} = {2, 3, 4} (i) (B∩C) =...
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z-direction is given by 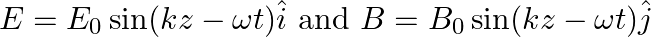
a) evaluate 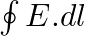 over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in the figure
over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in the figure
b) evaluate 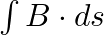 over the surface bounded by loop 1234
over the surface bounded by loop 1234
Solution: (a) $\oint_{\vec{E}} \cdot \overrightarrow{d l}=E_{0} h\left[\sin \left(k z_{2}-\omega t\right)-\sin \left(k z_{1}-\omega t\right)\right]$ (b) $\int \vec{B}.{\overrightarrow{d s}} =...
For a certain reaction large fraction of molecules has energy more than the threshold energy, yet the rate of reaction is very slow. Why?
The two most important responses that occur according to the collision theory are that the energy is greater than the activation energy and the correct position of the reactant molecules during a...
For a reaction A + B → Products, the rate law is — Rate = k [A][B]3/2 Can the reaction be an elementary reaction? Explain.
In an elementary reaction both the molecularity and order must be same. So, the given reaction is not an elementary reaction as the order of the given reaction is different.
A long straight cable of length  is placed symmetrically along the z-axis and has radius
is placed symmetrically along the z-axis and has radius 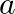 . The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current
. The cable consists of a thin wire and a co-axial conducting tube. An alternating current 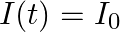 sin
sin 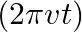 flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance
flows down the central thin wire and returns along the co-axial conducting tube. The induced electric field at a distance 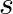 from the wire inside the cable is
from the wire inside the cable is 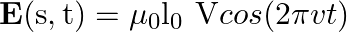 . In
. In 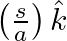 ,
,
a) calculate the displacement current density inside the cable
b) integrate the displacement current density across the cross-section of the cable to find the total displacement current I
a) The displacement current density is given as $\vec{J}_{d}=\frac{2 \pi I_{0}}{\lambda^{2}} \ln \frac{a}{s} \sin 2 \pi v t \hat{k}$ b) Total displacement current will be, $I^{d}=\int J_{d} 2 \pi s...
Show that the following system of linear inequalities has no solution x + 2y ≤ 3, 3x + 4y ≥ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 1
SOLUTION: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} x\text{ }+\text{ }2y\text{ }\le \text{ }3 \\ {} \\ \end{array}\] \[Line:\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }2y\text{ }=\text{ }3\] x 3 1 y 0 1 Also, (0, 0) satisfies...
Derive an expression to calculate the time required for completion of the zero-order reaction.
Let us take a reaction, R → P t=0 R = Reactant P = Product Rate = k[R]0 t=t –dR/dt = k , dR =-kdt Integrate on both the sides, ʃDr = -k ʃdt [R] = -kt + I If, t = 0 [R]= [R0] Then, I= R0 [R] = [R0]–...
In a reaction, if the concentration of reactant A is tripled, the rate of reaction becomes twenty-seven times. What is the order of the reaction?
Let us take the rate of a reaction, Rate = k[A]α Multiplying the rate into twenty seven, 27 ˟ Rate = k[A]α Dividing the equations, α = 3 Hence, Order of the reaction = 3
For which type of reactions, order and molecularity have the same value?
The type of reaction that have the same value of order and molecularity is the elementary reaction. This type of reaction happens in only one step.
How can you determine the rate law of the following reaction? 2NO (g) + O2 (g) → 2NO2 (g)
Rate law of a reaction can be determined by the formula, Rate = k[NO]2[O2]1 The rate law can be measured by the reaction rate as the initial concentration activity by keeping the concentration of...
Write the rate equation for the reaction 2A + B → C if the order of the reaction is zero.
Rate Equation of the reaction: k[A]0[B]0 The concentration capacity of the reactants will be equal to zero. In the zero-order reaction, the rate constant and rate of the reaction is the same....
State a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is a kinetically first-order reaction.
Condition: A situation in which the order of a chemical reaction can be converted under it by taking a solvent or reactant at an exorbitant rate because its concentration does not change much. Let...
What happens to the intensity of light from a bulb if the distance from the bulb is doubled? As a laser beam travels across the length of a room, its intensity essentially remains constant. What geometrical characteristics of the LASER beam is responsible for the constant intensity which is missing in the case of light from the bulb?
When the distance between two points is doubled, the intensity of light is reduced by one-fourth. Geometrical characteristics of the LASER are: a) unidirectional b) monochromatic c) coherent...
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
i) 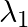 is used in satellite communication
is used in satellite communication
ii) 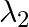 is used to kill germs in water purifies
is used to kill germs in water purifies
iii) 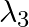 is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines
iv) 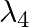 is used to improve visibility in runaways during fog and mist conditions
is used to improve visibility in runaways during fog and mist conditions
a) identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong
b) arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude
c) write one more application of each
a) i) $\lambda_{1}$ is a microwave, used in satellite communication. ii) $\lambda_{2}$ is UV rays, used in a water purifier for killing germs. iii) $\lambda_{3}$ is X-rays, used in improving the...
Consider a light beam incident from air to a glass slab at Brewster’s angle as shown in the figure.A polaroid is placed in the path of the emergent ray at point P and rotated about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to the plane of the polaroid (a) For a particular orientation, there shall be darkness as observed through the polaroid (b) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall be independent of the rotation (c) The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid (d) The intensity of light as seen through the polaroid shall go through a minimum for four orientations of the polaroid
The correct answer is c) The intensity of light as seen through the Polaroid shall go through a minimum but not zero for two orientations of the polaroid
Consider sunlight incident on a slit of width 104 A. The image seen through the slit shall (a) be a fine sharp slit white in colour at the centre (b) a bright slit white at the centre diffusing to zero intensities at the edges (c) a bright slit white at the centre diffusing to regions of different colours (d) only be a diffused slit white in colour
The correct answer is (a) be a fine sharp slit white in colour at the centre
In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the source is white light. One of the holes is covered by a red filter and another by a blue filter. In this case (a) there shall be alternate interference patterns of red and blue (b) there shall be an interference pattern for red distinct from that for blue (c) there shall be no interference fringes (d) there shall be an interference pattern for red mixing with one for blue
The correct answer is c) there shall be no interference fringes
Two sources S1 and S2 of intensity I 1 and I 2 are placed in front of a screen in the figure (a). The pattern of intensity distribution seen in the central portion is given by the figure (b). In this case which of the following statements are true;(a) S1 and S2 have the same intensities (b) S1 and S2 have a constant phase difference (c) S1 and S2 have the same phase (d) S1 and S2 have the same wavelength.
The correct answer is a) S1 and S2 have the same intensities b) S1 and S2 have a constant phase difference c) S1 and S2 have the same phase
In any unimolecular reaction ______________.
(i) only one reacting species is involved in the rate-determining step. (ii) the order and the molecularity of the slowest step are equal to one. (iii) the molecularity of the reaction is one and...
Consider sunlight incident on a pinhole of width 103A. The image of the pinhole seen on a screen shall be (a) a sharp white ring (b) different from a geometrical image (c) a diffused central spot, white in colour (d) diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot
The correct answer is b) different from a geometrical image d) diffused coloured region around a sharp central white spot
For a complex reaction ______________.
(i) order of an overall reaction is the same as molecularity of the slowest step. (ii) order of an overall reaction is less than the molecularity of the slowest step. (iii) order of an overall...
Solve for x, the inequalities in
Solution: Hence, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 1\text{ }\le \text{ }y\text{ }<\text{ }2 \\ \Rightarrow ~1\text{ }\le \text{ }\left| x-\text{ }\text{ }2 \right|\text{ }<\text{ }2 \\ \end{array}\]...
At high pressure, the following reaction is zero order. 2NH3(g) →1130 K Platinum catalyst N2(g) + 3H2(g)
Which of the following options are correct for this reaction? (i) Rate of reaction = Rate constant (ii) Rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of ammonia. (iii) Rate of decomposition of...
Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased (a) the size decreases (b) the intensity increases (c) the size increases (d) the intensity decreases
The correct answer is a) the size decreases b) the intensity increases
During decomposition of an activated complex.
(i) energy is always released (ii) energy is always absorbed (iii) energy does not change (iv) reactants may be formed Correct Answers: (i) energy is always released (iv) reactants may be...
For light diverging from a point source (a) the wavefront is spherical (b) the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared (c) the wavefront is parabolic (d) the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance
The correct answer is a) the wavefront is spherical b) the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared
According to Maxwell Boltzmann distribution of energy, __________.
(i) the fraction of molecules with most probable kinetic energy decreases at higher temperatures. (ii) the fraction of molecules with most probable kinetic energy increases at higher temperatures....
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
For longitudinal sound waves, Huygen's concept holds true.
In the graph showing Maxwell Boltzman distribution of energy, ___________.
(i) the area under the curve must not change with an increase in temperature. (ii) the area under the curve increases with increase in temperature. (iii) the area under the curve decreases with...
Which of the following statements are in accordance with the Arrhenius equation?
(i) Rate of a reaction increases with increase in temperature. (ii) Rate of a reaction increases with a decrease in activation energy. (iii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with an increase in...
Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
Wavefront and ray orientations are perpendicular to each other. L1 is the source of parallel rays that produce I2 at the focal length of the lens in the diagram above. The created picture serves as...
Mark the incorrect statements.
(i) Catalyst provides an alternative pathway to a reaction mechanism. (ii) Catalyst raises the activation energy. (iii) A catalyst lowers the activation energy. (iv) Catalyst alters enthalpy change...
Which of the following graphs is correct for a zero-order reaction?
Correct Answers: Option (ii) Option (iv) Explanation: The graphs (ii) and (iv) represents a proper zero-order reaction.
Which of the following graphs is correct for a first-order reaction?
Correct Answers: Option (i) Option (iv) Explanation: The graphs (i) and (iv) represents a proper first-order reaction.
What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
The distance between the sun and the earth is known to be enormous. We also know that the sun is spherical and that it may be thought of as a point source of light that can be seen from a great...
Professor C.V.Raman surprised his students by suspending freely a ting light ball in a transparent vacuum chamber by shining a laser beam on it. Which property of EM waves was he exhibiting? Give one more example of this property.
Professor CV Raman demonstrated the radiation pressure property of EM waves.
The magnetic field of a beam emerging from a filter facing a floodlight is given by 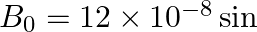
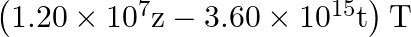 . What is the average intensity of the beam?
. What is the average intensity of the beam?
$\begin{array}{l} B_{0}=12 \times 10^{-8} \sin \left(1.20 \times 10^{7} z-3.60 \times 10^{15} \mathrm{t}\right) \mathrm{T} \\ \mathrm{B} 0=12 \times 10^{-8} \mathrm{~T} \\ \mathrm{lav}=1.71...
Compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react according to the following chemical equation. A (g) + 2 B (g) → 2C (g)
The concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ was changed keeping the concentrations of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration. Following results were...
Which of the following statement is not correct for the catalyst?
(i) It catalyses the forward and backward reaction to the same extent. (ii) It alters ∆G of the reaction. (iii) It is a substance that does not change the equilibrium constant of a reaction. (iv) It...
The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction ____________.
(i) depends on the concentration of reactants present in a small amount. (ii) depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess. (iii) is independent of the concentration of reactants....
Consider the reaction A B. The concentration of both the reactants and the products varies exponentially with time. Which of the following figures correctly describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time?
Correct Answer: Option (ii) Explanation: The graph in the option (ii) describes the change in concentration of reactants and products with time.
Rate law cannot be determined from the balanced chemical equation if _______.
(i) the reverse reaction is involved. (ii) it is an elementary reaction. (iii) it is a sequence of elementary reactions. (iv) any of the reactants is in excess Correct Answers: (i) the...
Which of the following statements apply to a balanced chemical equation of an elementary reaction?
(i) Order is the same as molecularity. (ii) Order is less than the molecularity. (iii) Order is greater than the molecularity. (iv) Molecularity can never be zero. Correct Answers: (i) Order...
The source of electromagnetic waves can be a charge
a) moving with a constant velocity
b) moving in a circular orbit
c) at rest
d) falling in an electric field
The correct options are: b) moving in a circular orbit d) falling in an electric field
There are materials which absorb photons of shorter wavelength and emit photons of longer wavelength. Can there be stable substances which absorb photons of larger wavelength and emit light of shorter wavelength?
When the frequency of a photon drops, the wavelength of the photon rises. There are two alternative scenarios: case one, in which the photons have a shorter wavelength and the energy is consumed...
(i) In the explanation of the photoelectric effect, we assume one photon of frequency ν collides with an electron and transfers its energy. This leads to the equation for the maximum energy Emax of the emitted electron as Emax = hν – φ0 where φ0 is the work function of the metal. If an electron absorbs 2 photons (each of frequency ν ) what will be the maximum energy for the emitted electron? (ii) Why is this fact (two-photon absorption) not taken into consideration in our discussion of the stopping potential?
i)According to the question, the electron absorbs two protons with frequencies of v and v'= 2v, where v' is the frequency of the released electron. Emax = hv – ϕ0 ii) There is no emission since the...
Consider Fig. 11.7 in the NCERT textbook of physics for Class XII. Suppose the voltage applied to A is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of θ that (a) will be larger than the earlier value (b) will be the same as the earlier value (c) will be less than the earlier value (d) will depend on the target
The correct answer is c) will be less than the earlier value
Consider a beam of electrons (each electron with energy E0) incident on a metal surface kept in an evacuated chamber. Then (a) no electrons will be emitted as only photons can emit electrons (b) electrons can be emitted but all with an energy, E0 (c) electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0 – φ (φ is the work function) (d) electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0
The correct answer is d) electrons can be emitted with any energy, with a maximum of E0
The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly (a) 1.2 nm (b) 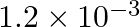 nm (c)
nm (c) 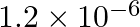 nm (d)
nm (d) nm
nm
The correct answer is b) 1.2 × 10–3 nm
Prove n^3 – 7n + 3 is divisible by 3, for all natural numbers n.
As per the inquiry, \[P\left( n \right)\text{ }=\text{ }n3\text{ }\text{ }7n\text{ }+\text{ }3\] is distinguishable by 3. Along these lines, subbing various qualities for n, we get, \[P\left( 0...
An electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction: 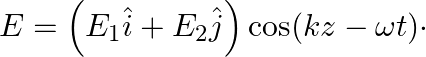 Choose the correct options from the following:
Choose the correct options from the following:
a) the associated magnetic field is given as 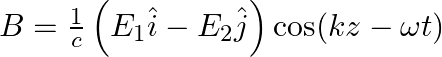
b) the associated magnetic field is given as 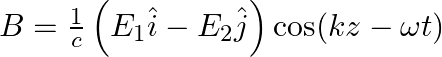
c) the given electromagnetic field is circularly polarised
d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
a) the associated magnetic field is given as $B=\frac{1}{c}\left(E_{1} \hat{i}-E_{2} \hat{j}\right) \cos (k z-\omega t)$ d) the given electromagnetic waves is plane polarised
An EM wave radiates outwards from a dipole antenna, with 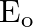 as the amplitude of its electric field vector. The electric field
as the amplitude of its electric field vector. The electric field 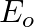 which transports significant energy from the source falls off as
which transports significant energy from the source falls off as
a) 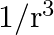
b) 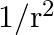
c) 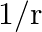
d) remains constant
c) $1 / \mathrm{r}$
The ratio of contributions made by the electric field and magnetic field components to the intensity of an EM wave is
a) 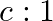
b) 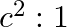
c) 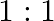
d) 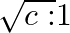
c) $1: 1$
If 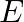 and
and 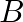 represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is along
represent electric and magnetic field vectors of the electromagnetic wave, the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave is along
a) 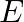
b) 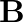
c) 
d) 
d) $E \times B$
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 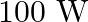 bulb at a
bulb at a 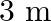 distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from
distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 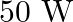 bulb at the same distance is
bulb at the same distance is
a) 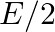
b) 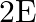
c) 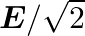
d) 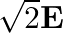
c) $\mathrm{E} / \sqrt{2}$
Light with an energy flux of 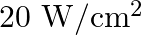 falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of
falls on a non-reflecting surface at normal incidence. If the surface has an area of 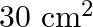 , the total momentum delivered during 30 minutes is
, the total momentum delivered during 30 minutes is
a) 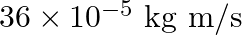
b) 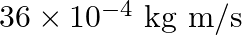
c) 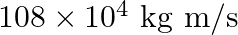
d) 
b) $36 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave given as 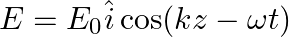 is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at
is incident normally on a perfectly reflecting infinite wall at  .
.
Assuming that the material of the wall is optically inactive, the reflected wave will be given as
a)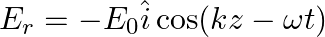
b)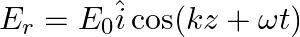
c)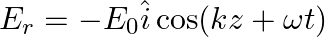
d)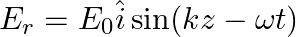
b)$E_{r}=E_{0} \hat{i} \cos (k z+\omega t)$
One requires 11eV of energy to dissociate a carbon monoxide molecule into carbon and oxygen atoms. The minimum frequency of the appropriate electromagnetic radiation to achieve the dissociation lies in
a) visible region
b) infrared region
c) ultraviolet region
d) microwave region
c) ultraviolet region
For an LCR circuit driven at frequency ω, the equation reads L di/dt + Ri + q/C = vi = vm sin ꞷ t
(i) Cast the equation in the form of a conservation of energy statement
(ii) Integrate the equation over one cycle to find that the phase difference between v and i must be acute.
i) The first equation is in the form of conservation of energy ii) We get dt as positive when we integrate the equation from $0$ to $T$, which is possible when the phase difference is constant and...
Consider the LCR circuit such that the net current i and the phase of i. Show that i = V/Z . Find the impedance Z for this circuit.
The impedance $Z$ for the given circuit is represented as, $1 / \mathrm{Z}=\left[1 / \mathrm{R}^{2}+1 /(1 / \omega \mathrm{C}-\omega \mathrm{L})^{2}\right]^{1 / 2}$
An electrical device draws 2kW power from AC mains (voltage 223V (rms) = 50,000 V). The current differs (lags) in phase by φ (tan φ = -3/4) as compared to voltage.
Find (i) R,
(ii) 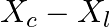 ,
,
and (iii) 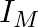 . Another device has twice the values for
. Another device has twice the values for 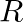 ,
, 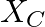 and
and 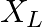 . How are the answers affected?
. How are the answers affected?
Impedance is given as Z = 25 ohms $635=25R^{2}/16$ a) Resistance can be calculated as, $R=\sqrt 25\times 16=\sqrt 400=20 ohms$ b) $X_{c}-X_{l}=-3R/4=-15ohms$ c) Main current will be...
Explain why the reactance provided by a capacitor to an alternating current decreases with increasing frequency.
Because capacitance reactance is inversely proportional to frequency, and capacitors have a tendency to pass high-frequency current while blocking low-frequency currents, the reactance delivered by...
A coil of 0.01-henry inductance and 1-ohm resistance is connected to 200 volt, 50 Hz ac supply. Find the impedance of the circuit and time lag between max. alternating voltage and current.
Inductance L is given as 0.01 H Resistance R is given as 1 ohm Voltage is given as 200 V Frequency is given as 50 Hz Impedance is given Z = 3.3 ohms Phase difference will be 72 × π/180 rad 0.004 sec...
Both alternating current and direct current are measured in amperes. But how is the ampere defined for an alternating current?
The phenomenon called Joule's law of heating is used to determine the ampere for an alternating current. According to Joule's law of heating in a one-ohm resistance, AC is the current produced in a...
A device ‘X’ is connected to an a.c source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in the figure.
(a) Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
(b) What is the average power consumption over a cycle?
Solution: a) The greatest amplitude of the power curve is equal to the product of the voltage and current amplitudes. As a result, curve A denotes power. b) Because the whole cycle in the graph...
The alternating current in a circuit is described by the graph shown in the figure. Show rms current in this graph.
Solution: $I_{rms}=1.6A$
Can the instantaneous power output of an ac source ever be negative? Can the average power output be negative?
a) When P < 0, then AC source's instantaneous power output can be negative. b) The average power output cannot be negative as $P_{av}>0$.
Draw the effective equivalent circuit of the circuit shown in the figure, at very high frequencies and find the effective impedance.
Solution: The effective impedance will be, $Z_{eq}=R_{1}+R_{3}$
The line that draws power supply to your house from street has
(a) zero average current.
(b) 220 V average voltage.
(c) voltage and current out of phase by 90°.
(d) voltage and current possibly differing in phase φ such that |φ| < π/2.
The correct options are: (a) zero average current. (d) voltage and current possibly differing in phase φ such that |φ| < π/2.
For an LCR circuit, the power transferred from the driving source to the driven oscillator is P = I2Z cos φ.
(a) Here, the power factor cos 0, 0. φ ≥ ≥ P
(b) The driving force can give no energy to the oscillator (P = 0) in some cases.
(c) The driving force cannot syphon out (P < 0) the energy out of oscillator.
(d) The driving force can take away energy out of the oscillator.
The correct options are: (a) Here, the power factor cos 0, 0. φ ≥ ≥ P (b) The driving force can give no energy to the oscillator (P = 0) in some cases. (c) The driving force cannot syphon out (P...
In an alternating current circuit consisting of elements in series, the current increases on increasing the frequency of supply. Which of the following elements are likely to constitute the circuit?
(a) Only resistor.
(b) Resistor and an inductor.
(c) Resistor and a capacitor.
(d) Only a capacitor.
The correct options are: (c) Resistor and a capacitor. (d) Only a capacitor.
The output of a step-down transformer is measured to be 24 V when connected to a 12 watt light bulb. The value of the peak current is
(a) 1/ √2 A.
(b) √2 A.
(c) 2 A.
(d) 2 √2 A
(a) 1/ √2 A.
A first-order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?
(i) 1.26 × 1015 s (ii) 2.52 × 1014 s (iii) 2.52 × 1028 s (iv) infinite Correct Answer: (iv) infinite Explanation: The time taken for the 100% completion of the reaction is...
Which of the following combinations should be selected for better tuning of an LCR circuit used for communication?
(a) R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H, C = 35µF.
(b) R = 25 Ω, L = 2.5 H, C = 45µF.
(c) R = 15 Ω, L = 3.5 H, C = 30µF.
(d) R = 25 Ω, L = 1.5 H, C = 45µF.
(c) R = 15 Ω, L = 3.5 H, C = 30µF.
Which of the following statements is incorrect about the collision theory of chemical reaction?
(i) It considers reacting molecules or atoms to be hard spheres and ignores their structural features. (ii) A number of effective collisions determine the rate of reaction. (iii) The collision of...
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is
(a) 5 √2 A
(b) 5 √3/2 A
(c) 5/6 A
(d) 5/ √2 A
(b) 5 √3/2 A
The rate law for the reaction A + 2B → C is found to be Rate = k [A][B]. The concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled, keeping the concentration of ‘A’ constant, the value of rate constant will be______.
(i) the same (ii) doubled (iii) quadrupled (iv) halved Correct Answer: (i) the same Explanation: For the given rate law of the reaction, if the concentration of reactant ‘B’ is doubled,...
Which of the following graph represents the exothermic reaction?
(i) (a) only (ii) (b) only (iii) (c) only (iv) (a) and (b) Correct Answer: (i) (a) only Explanation: The graph (a) represents the exothermic reaction.
Which of the following expressions is correct for the rate of reaction given below? 5Br–(aq) + BrO3–(aq) + 6H+(aq) → 3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l)
Correct Answer: Option (iii) Explanation: The third option shows the correct expression for the rate of the reaction.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) The rate of a reaction decreases over time as the concentration of reactants decreases. (ii) The rate of a reaction is the same at any time during the reaction. (iii) The rate of a reaction is...
Consider the graph given in Figure. Which of the following options does not show the instantaneous rate of reaction at 40th second?
(i) V5-V2/50-30 (ii) V4-V2/50-30 (iii) V3-V2/40-30 (iv) V3-V1/40-20 Correct Answer: (i) V5-V2/50-30 Explanation: V5-V2/50-30 do not show instantaneous rate of reaction at 40th...
Which of the following statements is not correct about an order of a reaction.
(i) The order of a reaction can be a fractional number. (ii) Order of a reaction is experimentally determined quantity. (iii) The order of a reaction is always equal to the sum of the stoichiometric...
A graph of volume of hydrogen released vs time for the reaction between zinc and dil.HCl is given in Figure. On the basis of this mark the correct option.
(i) Average rate up to 40s is V3-V2/40 (ii) Average rate up to 40s is V3-V2/40-30 (iii) Average rate up to 40 seconds is V3/40 (iv) Average rate up to 40 seconds is V3-V1/40-20 Correct...
Consider the Arrhenius equation given below and mark the correct option. a–E /RT k = A e
(i) Rate constant increases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing temperature. (ii) Rate constant decreases exponentially with increasing activation energy and decreasing...
According to Arrhenius equation rate constant k is equal to A e–E /RT a. Which of the following options represents the graph of ln k vs 1/T
Correct Answer: Option (i) Explanation: According to Arrhenius equation, the graph represented in the first option is a straight line with negative slope.
Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given: A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
The initial pressure of the system before decomposition of A was pi. After lapse of time ‘t’, total pressure of the system increased by x units and became ‘pt The rate constant k for the reaction is...
Consider the Figure and mark the correct option.
(i) The activation energy of forwarding reaction is E1 + E2 and the product is less stable than reactant. (ii) The activation energy of forwarding reaction is E1+E2and product is more stable than...
Draw areal velocity versus time graph for mars.
The areal velocity of mars around the sun does not change while it revolves around the sun, according to Kepler's law. As a result, the areal velocity versus time graph is a straight line.
Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by _____________.
(i) determining the rate constant at standard temperature. (ii) determining the rate constants at two temperatures. (iii) determining the probability of collision. (iv) using catalyst. ...
In the presence of a catalyst, the heat evolved or absorbed during the reaction ___________.
(i) increases. (ii) decreases. (iii) remains unchanged. (iv) may increase or decrease. Correct Answer: (iii) remains unchanged Explanation: The enthalpy change of the reaction will not be...
The role of a catalyst is to change ______________.
(i) gibbs energy of reaction. (ii) enthalpy of reaction. (iii) activation energy of reaction. (iv) equilibrium constant. Correct Answer: (iii) activation energy of reaction Explanation: The...
Consider the following diagram in which an electrochemical cell is coupled to an electrolytic cell. What will be the polarity of electrodes ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the electrolytic cell?
Zinc leaves behind the electrons on Electrode A during the reaction giving a negative charged whereas the Copper deposits on the Electrode B with positive charge. The polarity of electrode A...
Why is alternating current used for measuring the resistance of an electrolytic solution?
The concentration of ions is kept constant with the alternating current whereas the concentration of ion changes a lot in the direct current. So, the alternating current is used for measuring the...
A galvanic cell has an electrical potential of 1.1V. If an opposing potential of 1.1V is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
If the opposing potential is equal to electrical potential, then the cell reaction and the current flow through the cell will be stopped leading to no chemical reaction.
How will the pH of brine (aq. NaCl solution) be affected when it is electrolyzed?
Reaction on Cathode - H2O(l ) + e–→ 1/2 H2(g) + OH– (aq) Reaction on Anode - Cl– (aq) → 1/2 Cl2(g) + e– Complete Reaction: NaCl(aq)+H2O(l)→NaOH(aq)+H2(g)+Cl2(g) NaOH turns the brine solution basic...
Unlike dry cell, the mercury cell has a constant cell potential throughout its useful life. Why?
The electrolyte is not consumed in the cell and so the current gets delivered at a constant potential till the end. The reaction contains no ions whose concentration can change over time. Thus, the...
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B are diluted. The of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
Electrolyte B - strong electrolyte During dilution the number of ions remains the same and the interionic attraction decreases. Thus, the increase in Λm is small.
When acidulated water (dil.H2SO4 solution) is electrolysed, will the pH of the solution be affected? Justify your answer.
Reaction on Anode - 2H2O(l)→ O2(g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e– Reaction on Cathode - 4H+ + 4e-→ 2H2 Complete Reaction: 2H2O(l) → O2(g) + 2H2(g) The pH will not be affected and stays the same.
In an aqueous solution, how does specific conductivity of electrolytes change with the addition of water?
In an aqueous solution, when water is added the electrolyte gets diluted thus leading to the decrease in the specific conductivity of the electrolytes.
Which reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes?
The reference electrode which is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes is the Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) which has a value of zero.
Consider a cell given: Cu|Cu2+|| Cl—|Cl2, Pt Write the reactions that occur at anode and cathode.
Reaction in Anode: Oxidation half-cell Cu(s) → Cu2+ + 2e- Reaction in Cathode: Reduction half-cell Cl2(g)+ 2e-→ 2Cl- Hence, the anode Cu gets oxidised in this cell reaction.
Write the Nernst equation for the cell reaction in the Daniel cell. How will the ECell be affected when the concentration of Zn2+ ions is increased?
Nernst Equation: Ecell = E°cell – RT[Zn2+]/ nF[Cu2+] Galvanic cell reaction: Zn(s)|Zn2+(aq)||Cu2+(aq)|Cu(s) Reaction in Anode: oxidation half-cell Zn(s) → Zn2+ (aq)+ 2e Reaction in Cathode:...
What advantage do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batteries?
Advantages of Fuel cells: 1.Fuel cells can convert the energy of combustion of fuels like hydrogen, methanol into electrical energy. 2.Fuel cells can run continuously as long as reactants are...
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
While discharging the battery, the water dilutes the concentration of the dilute sulphuric acid which leads to a decrease in the density of the solution. Reaction Involved: Pb(s)+PbO2(s)+2H2SO4(aq)→...
Why on dilution the ˄m of CH3COOH increases drastically, while that of CH3COONa increases gradually?
Weak Electrolyte: CH3COOH Strong Electrolyte: CH3COONa . When diluted, the dissociation degree increases, and the number of ions present also increases which leads to the drastic increase of CH3COOH...
What is electrode potential?
Electrode potential is the potential difference which is developed between the electrode and the electrolyte.
Value of standard electrode potential for the oxidation of Cl– ions is more positive than that of water, even then in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride, why is Cl–oxidised at anode instead of water?
The oxidation of water to oxygen is kinetically not good and requires a lot of energy which is said to have more energy. What can be very powerful is the excess energy needed to drive the reaction...
Depict the galvanic cell in which the cell reaction is Cu + 2Ag+→ 2Ag + Cu2+
In the cell reaction Cu + 2Ag+→ 2Ag + Cu2+, Anode is the oxidation half-cell Reaction - Cu → Cu2+ + 2e- Cathode is the reduction half-cell Reaction - 2Ag+ + 2e- →2Ag
Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. Will, the mass of copper and silver, deposited on the cathode be the same or different? Explain your answer.
W = itE/96500 W = 1×10×60×31.75/96500 Equivalent mass of Cu2+ and Ag+ is different so that the mass of copper and silver deposited will not be same.
What does the negative sign in the expression E°Zn2+/Zn = -0.76V mean?
The disadvantage is that hydrogen gas is much more stable than reduced species. Here, the reduced form (Zn) is unstable. It is difficult to reduce Zn2 + to Zn. Therefore, distortion is more likely...
Under what condition is ECell = 0 or ΔrG = 0?
Electrolysis happens when a redox reaction happens. On equilibrium, the cell is completely depleted, and the cell's energy drops to zero. ∆rG= -nF E cell =0
Can E°cell or ΔrG° for cell reaction ever be equal to zero?
A cell of E ° or G G ° cannot be equal to zero. The only standard electrode power is randomly assigned is the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). As everything else is measured in relation to SHE;...
Can absolute electrode potential of an electrode be measured?
No. It cannot be measured. We can only estimate the electrode power difference between two and a half cells. We can also estimate the potential electrode differences associated with a standard...
For the given cell, Mg|Mg2+|| Cu2+|Cu
(i) Mg is cathode (ii) Cu is cathode (iii) The cell reaction is Mg + Cu2+ → Mg2+ + Cu (iv) Cu is the oxidising agent Correct Answers: (ii) Cu is cathode (iii) The cell reaction is Mg + Cu2+ →...
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on ___________.
(i) temperature. (ii) distance between electrodes. (iii) the concentration of electrolytes in solution. (iv) the surface area of electrodes. Correct Answers: (i) temperature. (iii) the...
Conductivity κ , is equal to ____________.
(i) 1/R l/A (ii) G*/R (iii) ˄m (iv) l/A Correct Answers: (i) 1/R l/A (ii) G*/R Explanation: Conductivity κ , is equal to 1/R l/A & G*/R
What will happen during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO4 in the presence of Cu electrodes?
(i) Copper will deposit at the cathode. (ii) Copper will dissolve at the anode. (iii) Oxygen will be released at anode. (iv) Copper will deposit at the anode. Correct Answers: (i) Copper will...
What will happen during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuSO4 by using platinum electrodes?
(i) Copper will deposit at the cathode. (ii) Copper will deposit at the anode. (iii) Oxygen will be released at anode. (iv) Copper will dissolve at the anode Correct Answers: (i) Copper will...
˄0m(H2O) is equal to ______________.
(i) ˄0m(HCl) + ˄0m(NaOHl) – ˄0m(NaCl) (ii) ˄0m(HNO3) + ˄0m(NaNO3) – ˄0m(NaOH) (iii) ˄0m(HNO3) + ˄0m(NaOH) – ˄0m(NaNO3) (iv) ˄0m(NH4OH) + ˄0m(HCl) – ˄0m(NH4Cl) Correct Answers: (i) ˄0m(HCl) +...
Conductivity of an electrolytic solution depends on ____________.
(i) nature of electrolyte. (ii) the concentration of electrolyte. (iii) power of AC source. (iv) distance between the electrodes. Correct Answers: (i) nature of electrolyte. (ii) the...
E°Cell = 1.1V for Daniel cell. Which of the following expressions are correct description of state of equilibrium in ths cell?
(i) 1.1 = Kc (ii) 2.303RT/2F logKc = 1.1 (iii) log Kc = 2.2/0.059 (iv) log Kc = 1.1 Correct Answers: (ii) 2.303RT/2F logKc = 1.1 (iii) log Kc = 2.2/0.059
E°Cell for some half cell reactions are given below. Based on these mark the correct answer.
(a) H+(aq) + e– →1/2H2(g) ; E°cell = 0.00V (b) 2H2O (l) → O2 (g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e–: E°cell = 1.23V (c) 2SO42– (aq) → S2O82– (aq) + 2e– ; E°cell = 1.96V (i) In dilute sulphuric acid solution, hydrogen...
The positive value of the standard electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu indicates that ____________.
(i) this redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple. (ii) this redox couple is a stronger oxidising agent than H+/H2. (iii) Cu can displace H2 from acid. (iv) Cu cannot displace...
In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution which of the half cell reaction will occur at anode?
(i) Na+(aq) + e– → Na (s); E°Cell = –2.71V (ii) 2H2O (l) → O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e– : E°Cell = 1.23V (iii) H+(aq) + e–→1/2H2 (g); E°Cell = 0.00V (iv) Cl–(aq) →1/2Cl2(g) + e– ; E°Cell = 1.36V ...
˄0m(NH4OH) is equal to ______________.
(i) ˄0m(NH4OH) + ˄0m(NH4Cl) – ˄0(HCl) (ii) ˄0m(NH4Cl) + ˄0m(NaOH) – ˄0(NaCl) (iii) ˄0m(NH4Cl) + ˄0m(NaCl) – ˄0(NaOH) (iv) ˄0m(NaOH) + ˄0m(NaCl) – ˄0(NH4Cl) Correct Answer: (ii) ˄0m(NH4Cl) +...
While charging the lead storage battery ______________.
(i) PbSO4 anode is reduced to Pb (ii) PbSO4 cathode is reduced to Pb (iii) PbSO4 cathode is oxidised to Pb (iv) PbSO4 anode is oxidised to PbO2 Correct Answer: (i) PbSO4 anode is reduced to...
The cell constant of a conductivity cell _____________.
(i) changes with the change of electrolyte. (ii) changes with the change of concentration of electrolyte. (iii) changes with the temperature of the electrolyte. (iv) remains constant for a cell....
The quantity of charge required to obtain one mole of aluminium from Al2O3 is ___________.
(i) 1F (ii) 6F (iii) 3F (iv) 2F Correct Answer: (iii) 3F Explanation: 3F of charge is required to obtain 1 mole of Al from the Al2O3
Use the data of Q.8 and find out the most stable oxidised species.
(i) Cr3+ (ii) MnO4– (iii) Cr2O72– (iv) Mn2+ Correct Answer: (i) Cr3+ Explanation: Cr3+ is the most stable oxidised species when compared to the rest of the options.
Use the data given in Q.8 and find out the most stable ion in its reduced form.
(i) Cl– (ii) Cr3+ (iii) Cr (iv) Mn2+ Correct Answer: (iv) Mn2+ Explanation: Mn2+ in its reduced form is observed to be more stable.
Using the data given in Q.8 find out in which option the order of reducing power is correct.
(i) Cr3+ < Cl–< Mn2+ < Cr (ii) Mn2+ < Cl–< Cr3+ < Cr (iii) Cr3+ < Cl–< Cr2O72– < MnO4– (iv) Mn2+ < Cr3+ < Cl–< Cr Correct Answer: (ii) Mn2+ < Cl–<...
Use the data given in Q.8 and find out which of the following is the strongest oxidising agent.
(i) Cl– (ii) Mn2+ (iii) MnO4– (iv) Cr3+ Correct Answer: (iii) MnO4– Explanation: The higher the value of the normal reduction of the strength of the metal ion, the higher will be its...
Using the data given below to find out the strongest reducing agent.
EᶱCr2O72-/Cr3+ = 1.33V EᶱMnO4–/Mn2+ = 1.51V EᶱCl2/Cl– = 1.36V EᶱCr3+/Cr = -0.74V (i) Cl– (ii) Cr (iii) Cr3+ (iv) Mn Correct Answer: (ii) Cr Explanation: The most powerful reducing agent is...
Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct?
(i) The conductivity of the solution depends upon the size of ions. (ii) Conductivity depends upon the viscosity of the solution. (iii) Conductivity does not depend upon solvation of ions present in...
An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell when ____________.
(i) Ecell = 0 (ii) Ecell > Eext (iii) Eext > Ecell (iv) Ecell = Eext Correct Answer: (iii) Eext > Ecell
Which of the following statement is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell?
(i) It does not participate in the cell reaction. (ii) It provides surface either for oxidation or for the reduction reaction. (iii) It provides a surface for conduction of electrons. (iv) It...
The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called ___________.
(i) Cell potential (ii) Cell emf (iii) Potential difference (iv) Cell voltage Correct Answer: (ii) Cell emf Explanation: Electromotive force or e.m.f. is the power provided by the cell or...
Which of the following statement is correct?
(i) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are extensive properties. (ii) ECell and ∆rG of cell reaction both are intensive properties. (iii) ECell is an intensive property while ∆rG of cell reaction...
Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation EMg2+/Mg = EᶱMg2+/Mg – 0.0591/2 log1/[Mg2+ ] . The graph of EMg2+/Mg Vs log [Mg2+] is
Correct Answer: Option (ii)
Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode?
(i) Pt (s) H2(g,0.1 bar) H+ (aq.,1 M) Cu2+(aq.,1M) Cu (ii) Pt(s) H2 (g, 1 bar) H+ (aq.,1 M) Cu2+ (aq.,2 M) Cu (iii) Pt(s) H2(g, 1 bar) H+ (aq.,1 M) Cu2+ (aq.,1 M) Cu (iv) Pt(s) H2 (g, 1 bar)...
Match the terms given in Column I with expressions given in Column II.
Column I Column II (i) Mass percentage (a)Number of moles of the solute component/ The volume of solution in litres (ii) Volume percentage (b) Number of moles of a component/...
Match the laws given in Column I with expressions given in Column II.
Column I Column II (i) Raoult’s law (a) ∆Tf= Kfm (ii) Henry’s law (b) Π = CRT (iii) Elevation of boiling point (c) p = x1P10+ X2P20 (iv) Depression in freezing point (d) ∆Tb= Kbm (v) Osmotic...
Match the items given in Column I with the type of solutions given in Column II.
Column I Column II (i) Soda water (a) A solution of the gas in solid (ii) Sugar solution (b) A solution of the gas in gas (iii) German silver (c) A solution of...
Match the items given in Column I and Column II.
Column I Column II (i) Saturated solution (a) Solution having the same osmotic pressure at a given temperature as that of the given solution. (ii) Binary solution (b) A solution whose...
Give an example of a material used for making semipermeable membrane for carrying out reverse osmosis.
Examples: Cellulose acetate Polyamides
What is a “semi-permeable membrane”?
Semi-permeable membrane is a membrane that allows only the movement of solvent molecules but not solute molecules. Examples: Cellulose acetate and phospholipid bilayer in biological cells.
How does sprinkling of salt help in clearing the snow-covered roads in hilly areas? Explain the phenomenon involved in the process.
Salt is an agent for de-icing and can be used to dissolve ice. If the freezing point is lowered the ice begins to melt. Thus, the addition of salt to ice reduces the freezing point from O ℃ drop.
Why is the vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of glucose lower than that of water?
An example of water and glucose can be taken to illustrate this. In water, the surface of this liquid will settle with water molecules. If we put glucose into it, some of these areas will be...
On the basis of information given mark the correct option. Information: On adding acetone to methanol some of the hydrogen bonds between methanol molecules break.
(i) At specific composition, methanol-acetone mixture will form minimum boiling azeotrope and will show positive deviation from Raoult’s law. (ii) At specific composition, methanol-acetone mixture...
(a) Explain the following phenomena with the help of Henry’s law. (i) A painful condition known as bends. (ii) Feeling of weakness and discomfort in breathing at high altitude. (b) Why soda water bottle kept at room temperature fizzes on opening?
(a) (i) The bend is a condition that occurs in scuba divers. They have to breathe air under high pressure under water. Nitrogen gas does not dissolve in normal pressure. Under water, they will...
Why are aquatic species more comfortable in cold water in comparison to warm water?
Because of the availability of O2 and the presence of more solubility in the cold water makes the aquatic species feel more comfortable when present in the cold water.
What is the significance of Henry’s Law constant KH?
Significance of Henry’s Law constant KH: Henry's law states that in the solution, "the pressure in the gas component at the vapor fraction (p) is equal to the fraction of the gas molecule (x) in...
Concentration terms such as mass percentage, ppm, mole fraction and molality are independent of temperature, however, molarity is a function of temperature. Explain.
Any change in the temperature causes a change in the volume, so it changes the molarity of the solution. Therefore, terms such as high percentage, ppm, mole fraction, and molality of a solution are...
Explain the solubility rule “like dissolves like” in terms of intermolecular forces that exist in solutions.
"Like dissolves like" term is used when the solvent dissolves in the solvent if its interactions between molecules are the same. This is because polar solutions can be dissolved in polar solvents...
Explain why on the addition of 1 mol of NaCl to 1 litre of water, the boiling point of water increases, while the addition of 1 mol of methyl alcohol to one litre of water decreases its boiling point.
Adding 1 mol of NaCl to 1 liter of water, a point of boiling water rises, while the addition of 1 mol of methyl alcohol to one liter of water reduces its boiling point because when added to a stable...
Components of a binary mixture of two liquids A and B were being separated by distillation. After some time separation of components stopped and the composition of the vapour phase became the same as that of a liquid phase. Both the components started coming in the distillate. Explain why this happened.
An azeotropic mixture is shown when both the liquids A & B starts coming in the distillate and the vapour and liquid phase will have the same composition. Via distillation an azeotropic mixture...
Colligative properties are observed when _____________.
(i) a non-volatile solid is dissolved in a volatile liquid. (ii) a non-volatile liquid is dissolved in another volatile liquid. (iii) a gas is dissolved in non-volatile liquid. (iv) a volatile...
For a binary ideal liquid solution, the variation in total vapour pressure versus the composition of the solution is given by which of the curves?
Correct Answers: Option (ii) Option (iv) Explanation: For the binary solution, the difference in vapor pressure versus the composition of the solution is given in graphs B and D where, the...
In isotonic solutions ________________.
(i) solute and solvent both are same. (ii) osmotic pressure is the same. (iii) solute and solvent may or may not be same. (iv) a solute is always the same solvent may be different. Correct...
Which of the following binary mixtures will have the same composition in the liquid and vapour phase?
(i) Benzene – Toluene (ii) Water-Nitric acid (iii) Water-Ethanol (iv) n-Hexane – n-Heptane Correct Answers: (ii) Water-Nitric acid (iii) Water-Ethanol Explanation: In a particular...
Isotonic solutions must have the same _____________.
(i) solute (ii) density (iii) elevation in boiling point (iv) depression in freezing point Correct Answers: (iii) elevation in boiling point (iv) depression in freezing point Explanation:...
Van’t Hoff factor is given by the expression _____________.
(i) i = Normal molar mass/Abnormal molar mass (ii) i = Abnormal molar mass/ Normal molar mass (iii) i= Observed colligative property/calculated colligative property (iv) i = Calculated colligative...
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because _____________.
(i) It depends on the concentration of a non-electrolyte solute in a solution and does not depend on the nature of the solute molecules. (ii) It depends on a number of particles of electrolyte...
Intermolecular forces between two benzene molecules are near to same strength as those between two toluene molecules. For a mixture of benzene and toluene, which of the following are not true?
(i) ∆mix H = zero (ii) ∆mix V = zero (iii) These will form a minimum boiling azeotrope. (iv) These will not form the ideal solution. Correct Answers: (iii) These will form a minimum boiling...
Which of the following factor (s) affect the solubility of a gaseous solute in a fixed volume of liquid solvent? (a) nature of solute (b) temperature (c) pressure
(i) (a) and (c) at constant T (ii) (a) and (b) at constant P (iii) (b) and (c) only (iv) (c) only Correct Answers: (i) (a) and (c) at constant T (ii) (a) and (b) at constant P Explanation: At...
KH value for Ar(g), CO2(g), HCHO (g) and CH4(g) are 40.39, 1.67, 1.83×10–5 and 0.413 respectively. Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility.
(i) HCHO < CH4< CO2 < Ar (ii) HCHO < CO2< CH4< Ar (iii) Ar < CO2< CH4< HCHO (iv) Ar < CH4 < CO2 < HCHO Correct Answer: (iii) Ar < CO2< CH4< HCHO...
4L of 0.02 M aqueous solution of NaCl was diluted by adding one litre of water. The molality of the resultant solution is _____________.
(i) 0.004 (ii) 0.008 (iii) 0.012 (iv) 0.016 Correct Answer: (iv) 0.016 Explanation: Let us take, M1 and V1 - molarity and volume of the given solution. M2 and V2 - molarity and volume of...
If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then _______________.
(i) A–B interactions are stronger than those between A–A or B–B. (ii) vapour pressure of solution increases because more number of molecules of liquids A and B can escape from the solution. (iii)...
Two beakers of capacity 500 mL were taken. One of these beakers, labeled as “A”, was filled with 400 mL water whereas the beaker labelled “B” was filled with 400 mL of 2 M solution of NaCl. At the same temperature, both the beakers were placed in closed containers of the same material and same capacity as shown in Figure. At a given temperature, which of the following statement is correct about the vapour pressure of pure water and that of NaCl solution.
(i) the vapour pressure in container (A) is more than that in a container (B). (ii) the vapour pressure in container (A) is less than that in the container (B). (iii) vapour pressure is equal in...
On the basis of information given below mark the correct option. Information:
(A) In bromoethane and chloroethane mixture intermolecular interactions of A–A and B–B type are nearly the same as A–B type interactions. (B) In ethanol and acetone mixture A–A or B–B type...
We have three aqueous solutions of NaCl labelled as ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ with concentrations 0.1M, 0.01M and 0.001M, respectively. The value of van’t Hoff factor for these solutions will be in the order______.
(i) iA< iB< iC (ii) iA> iB> iC (iii) iA= iB= iC (iv) iA<iB> iC Correct Answer: (iii) iA= iB= iC
Consider the Figure and mark the correct option.
(i) water will move from the side (A) to side (B) if a pressure lower than the osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B). (ii) water will move from the side (B) to side (A) if a pressure greater...
The value of Henry’s constant KH is _____________.
(i) greater for gases with higher solubility. (ii) greater for gases with lower solubility. (iii) constant for all gases. (iv) not related to the solubility of gases Correct Answer: (ii)...
Value of Henry’s constant KH ____________.
(i) increases with increase in temperature. (ii) decreases with increase in temperature. (iii) remains constant. (iv) first increases then decrease. Correct Answer: (i) increases with...
Which of the following statements is false?
(i) Units of atmospheric pressure and osmotic pressure are the same. (ii) In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower concentration of solute...
The values of Van’t Hoff factors for KCl, NaCl and K2SO4, respectively, are _____________.
(i) 2, 2 and 2 (ii) 2, 2 and 3 (iii) 1, 1 and 2 (iv) 1, 1 and 1 Correct Answer: (ii) 2, 2 and 3 Explanation: The values of van't Hoff factors for KCl,...
Which of the following statements is false?
(i) Two different solutions of sucrose of the same molality prepared in different solvents will have the same depression in freezing point. (ii) The osmotic pressure of a solution is given by the...
At a given temperature, osmotic pressure of a concentrated solution of a substance _____________.
(i) is higher than that at a dilute solution. (ii) is lower than that of a dilute solution. (iii) is same as that of a dilute solution. (iv) cannot be compared with an osmotic pressure of a dilute...
An unripe mango placed in a concentrated salt solution to prepare pickle, shrivels because _____________.
(i) it gains water due to osmosis. (ii) it loses water due to reverse osmosis. (iii) it gains water due to reverse osmosis. (iv) it loses water due to osmosis. Correct Answer: (iv) it loses...
In comparison to a 0.01 M solution of glucose, the depression in freezing point of a 0.01 M MgCl2 solution is _____________.
(i) the same (ii) about twice (iii) about three times (iv) about six times Correct Answer: (iii) about three times Explanation: The depression in freezing point of a 0.01M MgCl2 solution is...
The unit of ebulioscopic constant is _______________.
(i) K kg mol-1 or K (molality)-1 (ii) mol kg K-1 or K-1(molality) (iii) kg mol-1 K-1 or K-1(molality)-1 (iv) K mol kg-1 or K (molality) Correct Answer: (i) K kg mol-1 or K (molality)-1...
Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point?
(i) 1.0 M NaOH (ii) 1.0 M Na2SO4 (iii) 1.0 M NH4NO3 (iv) 1.0 M KNO3 Correct Answer: (ii) 1.0 M Na2SO4 Explanation: Given that a large amount of van's Hoff will increase the boiling point of...
Colligative properties depend on ____________.
(i) the nature of the solute particles dissolved in solution. (ii) the number of solute particles in solution. (iii) the physical properties of the solute particles dissolved in solution. (iv) the...
Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law?
(i) Methanol and acetone. (ii) Chloroform and acetone. (iii) Nitric acid and water. (iv) Phenol and aniline. Correct Answer: (i) Methanol and acetone Explanation: The mixture of methanol and...
Low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitude is due to ____________.
(i) low temperature (ii) low atmospheric pressure (iii) high atmospheric pressure (iv) both low temperature and high atmospheric pressure Correct Answer: (ii) low atmospheric pressure...
The maximum amount of a solid solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of a given liquid solvent does not depend upon ____________.
(i) Temperature (ii) Nature of solute (iii) Pressure (iv) Nature of solvent Correct Answer: (iii) Pressure Explanation: Changes in pressure do not affect the solubility of solids and the...
A beaker contains a solution of a substance ‘A’. Precipitation of substance ‘A’ takes place when a small amount of ‘A’ is added to the solution. The solution is _________.
(i) saturated (ii) supersaturated (iii) unsaturated (iv) concentrated Correct Answer: (ii) supersaturated Explanation: Most of the substance does not dissolve when we add more solute will not...
At equilibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is __________.
(i) less than the rate of crystallisation (ii) greater than the rate of crystallisation (iii) equal to the rate of crystallisation (iv) zero Correct Answer: (iii) equal to the rate of...
On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature solution feels cool to touch. Under which of the following cases dissolution of sugar will be most rapid?
(i) Sugar crystals in cold water. (ii) Sugar crystals in hot water. (iii) Powdered sugar in cold water. (iv) Powdered sugar in hot water. Correct Answer: (iv) Powdered sugar in hot water...
Which of the following units is useful in relating the concentration of a solution with its vapour pressure?
(i) mole fraction (ii) parts per million (iii) mass percentage (iv) molality Correct Answer: (i) mole fraction Explanation: According to Raoult's law, the reduction associated with vapor...
A multirange current meter can be constructed by using a galvanometer circuit shown in the figure. We want a current meter that can measure 10 mA, 100 mA, and 1 A using a galvanometer of resistance 10Ω and that produces maximum deflection for a current of 1 mA. Find S1, S2, and S3 that have to be used.
I1 is measured as = 10 mA = IGG = (I1 – IG)(S1 + S2 + S3) I2 is measured as = 100 mA = IG(G+S1)=(I2-IG)(S2-S3) I3 is measured as = 1 A = IG(G+S1+S2)=(I3-IG)(S3) S1 = 1 Ω S2 = 0.1 Ω S3 = 0.01...
Consider a circular current-carrying loop of radius R in the x-y plane with centre at the origin. Consider the line integral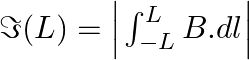 a) show that
a) show that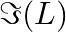 monotonically increases with L b) use an appropriate Amperian loop to that
monotonically increases with L b) use an appropriate Amperian loop to that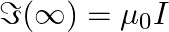 where I is the current in the wire c) verify directly the above result d) suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about
where I is the current in the wire c) verify directly the above result d) suppose we replace the circular coil by a square coil of sides R carrying the same current I. What can you say about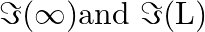
a) A circular current-carrying loop's magnetic field is given as \(\Im (L)=\int_{-L}^{+L}{Bdl}=2Bl\) It is a L function that increases monotonically. b) The Amperian loop is defined as follows:...
How might you clarify the higher soundness of BCl3 when contrasted with TlCl3?
Solution: Thallium and boron have a place with bunch 13 of the intermittent table and +1 oxidation state turns out to be more steady as we drop down the gathering. Boron is more steady than thallium...
An electron enters with a velocity v = v0i into a cubical region in which there are uniform electric and magnetic fields. The orbit of the electron is found to spiral down inside the cube in the plane parallel to the x-y plane. Suggest a configuration of fields E and B that can lead to it.
The spiral route is formed by the fields E and B in their current configuration.
A current-carrying loop consists of 3 identical quarter circles of radius R, lying in the positive quadrants of the x-y, y-z, and z-x planes with their centres at the origin, joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of B at the origin.
The quarter's vector sum of the magnetic field at the origin is given as \({{\vec{B}}_{net}}=\frac{1}{4}\left( \frac{{{\mu }_{0}}I}{2R} \right)(\widehat{i}+\widehat{j}+\widehat{k})\)
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
The time period of the radio frequency is halved when the frequency is doubled, resulting in a half revolution of the charges.
Two identical current-carrying coaxial loops, carry current I in an opposite sense. A simple amperian loop passes through both of them once. Calling the loop as C, a)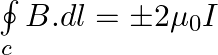 b) the value of
b) the value of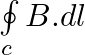 c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular d) B vanishes everywhere on C
c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular d) B vanishes everywhere on C
b) the value of \(\oint\limits_{c}{B.dl\) is independent of sense of C c) there may be a point on C where B and dl are perpendicular
The gyro-magnetic ratio of an electron in an H-atom, according to Bohr model is a) independent of which orbit it is in b) negative c) positive d) increases with the quantum number n
a) independent of which orbit it is in b) negative
