Show the 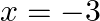 is a solution of
is a solution of 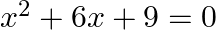
The given equation is $x^{2}+6 x+9=0$ Putting $x=-3$ in the given equation, we get $L H S=(-3)^{2}+6 \times(-3)+9=9-18+9=0=R H S$ $\therefore x=-3$ is a solution of the given equation.
Find dy/dx in each of the following: 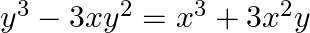
differentiating the equation on both sides with respect to x, we get,
A train covers a distance of 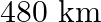 at a uniform speed. If the speed had been
at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 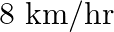 less then it would have taken 3 hours more to cover the same distance. Find the usual speed of the train.
less then it would have taken 3 hours more to cover the same distance. Find the usual speed of the train.
Let the usual speed of the train be $x \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$. $\therefore$ Reduced speed of the train $=(x-8) \mathrm{km} / \mathrm{h}$ Total distance to be covered $=480 \mathrm{~km}$ Time...
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\text { If } A=\left[\begin{array}{cc} 2 & -1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{array}\right], \text { such that } A^{2}-4 A+3 I=0 \text {, then } A^{-1}=\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7b894a5fdb230f303ed2c3138014aee7_l3.png)
(A) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{-1}{3}\left[\begin{array}{cc}2 & 1 \\ 1 & 2\end{array}\right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3de2c9c89535b15d716c4004abf378ac_l3.png) (B)
(B) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{-1}{3}\left[\begin{array}{cc}2 & -1 \\ -1 & 2\end{array}\right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2c0ef8c38089f5461a5c3cae75564dbc_l3.png) (C)
(C) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{3}\left[\begin{array}{cc}-2 & -1 \\ 1 & -2\end{array}\right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b29c7040a237cfd2f9f8fbf9de6861f6_l3.png) (D)
(D) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{3}\left[\begin{array}{ll}2 & 1 \\ 1 & 2\end{array}\right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ee435aff6cf5f9f19b76d6e3447d2f91_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\text { If } A=\left[\begin{array}{cc} 2 & -1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{array}\right], \text { such that } A^{2}-4 A+3 I=0 \text {, then } A^{-1}=\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7b894a5fdb230f303ed2c3138014aee7_l3.png)
The correct option is option (D) $\therefore \mathrm{A}^{2}=\mathrm{A} \cdot \mathrm{A}=\left[\begin{array}{cc}2 & -1 \\ -1 & 2\end{array}\right] \cdot\left[\begin{array}{cc}2 & -1 \\ -1...
A teacher on attempting to arrange the students for mass drill in the form of solid square found that 24 students were left. When he increased the size of the square by one student, he found that he was short of 25 students. Find the number of students.
Let there be $x$ rows. Then, the number of students in each row will also be $x$. $\therefore$ Total number of students $=\left(x^{2}+24\right)$ According to the question: $\begin{array}{l}...
The sum of a natural number and its square is 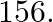 Find the number.
Find the number.
Let the required natural number be $x$. According to the given condition, $x+x^{2}=156$ $\Rightarrow x^{2}+x-156=0$ $\Rightarrow x^{2}+13 x-12 x-156=0$ $\Rightarrow x(x+13)-12(x+13)=0$...
Choose the correct statement. In conductors (A).valence band and conduction band overlap each other. (B) valence band and conduction band are separated by a large energy gap. (C) very small number of electrons are available for electrical conduction. (D) valence band and conduction band are separated by a small energy gap.
CORRECT OPTION IS OPTION (A) Valence and conduction band overlap with each other. Means electrons can easily jump from valence to conduction band. Hence, the conductivity of a conductor is highest...
Locate the following points:
(i) (1, – 1, 3),
(ii) (– 1, 2, 4)
Solution: (i) $(1, – 1, 3)$:- 4th octant, (ii) $(– 1, 2, 4)$:- 2nd octant,
The graphic representation of the equations 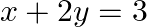 and
and 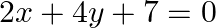 gives a pair of
gives a pair of
(a) parallel lines
(b) intersecting lines
(c) coincident lines
(d) none of these
Answer: (a) parallel lines Solution: The given system can be writlen us follows: $x+2 y-3=0$ and $2 x+4 y+7=0$ Given equations are of the following form: $a_{1} x+b_{1} x+c_{1}=0$ and $a_{2} x+b_{2}...
The potential differences that must be applied across the parallel and series combination of 3 identical capacitor(C
The correct option is option (C) $\frac{1}{3}$. Let $C$ be the capacity of each capacitor. The equivalent capacitance of three capacitors in parallel combination will be $C_{p}=3 C$ and in series...
Find the roots of the each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula: 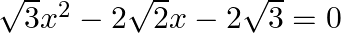 .
.
The given equation is $\sqrt{3} x^{2}-2 \sqrt{2} x-2 \sqrt{3}=0$. Comparing it with $a x^{2}+b x+c=0$, we get $a=\sqrt{3}, b=-2 \sqrt{2}$ and $c=-2 \sqrt{3}$ $\therefore$ Discriminant, $D=b^{2}-4 a...
Find the roots of the each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula: 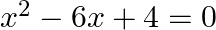
Given: $x^{2}-6 x+4=0$ On comparing it with $a x^{2}+b x+c=0$, we get: $a=1, b=-6$ and $c=4$ Discriminant $D$ is given by: $ \begin{array}{l} D=\left(b^{2}-4 a c\right) \\ =(-6)^{2}-4 \times 1...
Find the roots of the given equation: 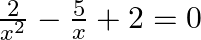
$\frac{2}{x^{2}}-\frac{5}{x}+2=0$ $\Rightarrow \frac{2-5 x+2 x^{2}}{x^{2}}=0$ $\Rightarrow 2 x^{2}-5 x+2=0$ $\Rightarrow 4 x^{2}-10 x+4=0 \quad$ (Multiplying both sides by 2) $\Rightarrow 4 x^{2}-10...
Find the roots of the given equation: 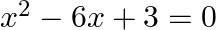
$\begin{array}{l} x^{2}-6 x+3=0 \\ \Rightarrow x^{2}-6 x=-3 \\ \Rightarrow x^{2}-2 \times x \times 3+3^{2}=-3+3^{2} \\ \Rightarrow(x-3)^{2}=-3+9=6 \\ \Rightarrow x-3=\pm \sqrt{6} \end{array}$...
Find the roots of the given equation: 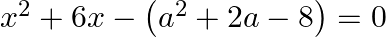
We write, $6 x=(a+4) x-(a-2) x$ as $\begin{array}{l} x^{2} \times\left[-\left(a^{2}+2 a-8\right)\right]=-\left(a^{2}+2 a-8\right) x^{2}=(a+4) x \times[-(a-2) x] \\ \therefore x^{2}+6 x-\left(a^{2}+2...
Find the roots of the given equation: 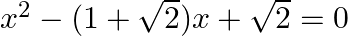
$\begin{array}{l} x^{2}-(1+\sqrt{2}) x+\sqrt{2}=0 \\ \Rightarrow x^{2}-x-\sqrt{2} x+\sqrt{2}=0 \\ \Rightarrow x(x-1)-\sqrt{2}(x-1)=0 \\ \Rightarrow(x-\sqrt{2})(x-1)=0 \\ \Rightarrow x-\sqrt{2}=0...
If 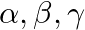 be the zeroes of the polynomial
be the zeroes of the polynomial 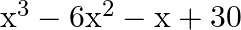 , then
, then 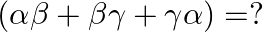 (a)
(a) 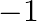 (b) 1 (c)
(b) 1 (c) 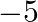 (d) 30
(d) 30
The correct option is option(a) $-1$ It is given that $\alpha, \beta$ and $\gamma$ are the zeroes of $x^{3}-6 x^{2}-x+30$ $\therefore(\alpha \beta+\beta \gamma+\gamma \alpha)=\frac{\text {...
Find the roots of the given equation: 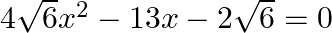
$\begin{array}{l} 4 \sqrt{6} x^{2}-13 x-2 \sqrt{6}=0 \\ \Rightarrow 4 \sqrt{6} x^{2}-16 x+3 x-2 \sqrt{6}=0 \\ \Rightarrow 4 \sqrt{2} x(\sqrt{3} x-2 \sqrt{2})+\sqrt{3}(\sqrt{3} x-2 \sqrt{2})=0 \\...
Find all the zeroes of 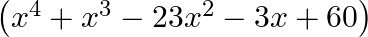 , if it is given that two of its zeroes are
, if it is given that two of its zeroes are 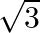 and
and 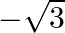
Let f(x)=x4+x3-23x2-3x+60 \text { Let } f(x)=x^{4}+x^{3}-23 x^{2}-3 x+60 Since $\sqrt{3}$ and $-\sqrt{3}$ are the zeroes of $f(x)$, it follows that each one of $(x-\sqrt{3})$ and...
If f(x) = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[{{\mathbf{x}}^{4}}\text{ }\mathbf{3}{{\mathbf{x}}^{2}}+\text{ }\mathbf{4x}\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ad7d2f8a80aafc2cbfd35725299b1e1f_l3.png)
is divided by g(x)= ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\text{ }{{\text{x}}^{2}}-x+1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-23f385949259538522e3d43bf4dca4a8_l3.png)
Quotient $q(x)=x^{2}+x-3$ Remainder $r(x)=8$
In the following cases, find the distance of each of the given points from the corresponding given plane. Point Plane
(a) (0, 0, 0) 3x – 4y + 12 z = 3
(b) (3, -2, 1) 2x – y + 2z + 3 = 0
Solution: (a) The distance of the point $(0,0,0)$ from the plane $3 x-4 y+12=3 \Rightarrow$ $3 x-4 y+12 z-3=0$ is $\begin{array}{l} \frac{\left|a x_{1}+b y_{1}+c...
In the following cases, determine whether the given planes are parallel or perpendicular, and in case they are neither, find the angles between them.
(a) 7x + 5y + 6z + 30 = 0 and 3x – y – 10z + 4 = 0
(b) 2x + y + 3z – 2 = 0 and x – 2y + 5 = 0
Solution: (a) $7 x+5 y+6 z+30=0$ and $3 x-y-10 z+4=0$ It is given that The eq. of the given planes are $7 x+5 y+6 z+30=0$ and $3 x-y-10 z+4=0$ Two planes are $\perp$ if the direction ratio of the...
Find the angle between the planes whose vector equations are 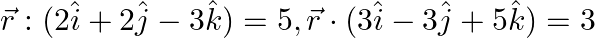
Solution: It is given that The eq. of the given planes are $\vec{r}(2 \hat{i}+2 \hat{j}-3 \hat{k})=5 \text { and } \vec{r}(3 \hat{i}-3 \hat{j}+5 \hat{k})=5$ If $\mathrm{n}_{1}$ and $\mathrm{n}_{2}$...
Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the intersection of the planes 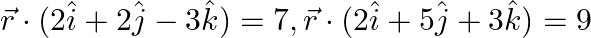 and through the point
and through the point 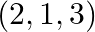
Solution: Let's consider the vector eq. of the plane passing through the intersection of the planes are $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}} \cdot(2 \hat{\mathrm{i}}+2 \hat{\mathrm{j}}-3 \hat{\mathrm{k}})=7...
Find the intercepts cut off by the plane 2x + y – z = 5.
Solution: It is given that The plane $2 x+y-z=5$ Let us express the equation of the plane in intercept form $x / a+y / b+z / c=1$ Where $a, b, c$ are the intercepts cut-off by the plane at $x, y$...
Find the vector and Cartesian equations of the planes
(a) that passes through the point 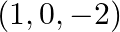 and the normal to the plane is
and the normal to the plane is 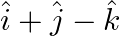
(b) that passes through the point 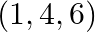 and the normal vector to the plane is
and the normal vector to the plane is 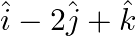
Solution: (a) That passes through the point $(1,0,-2)$ and the normal to the plane is $\hat{\mathrm{i}}+\hat{\mathrm{j}}-\hat{\mathrm{k}}$ Let's say that the position vector of the point $(1,0,-2)$...
In the following cases, find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin.
(a) x + y + z = 1
(b) 5y + 8 = 0
Solution: (a) $x+y+z=1$ Let the coordinate of the foot of $\perp \mathrm{P}$ from the origin to the given plane be $P(x, y, z)$ $x+y+z=1$ The direction ratio are $(1,1,1)$ $\begin{array}{l}...
Find the Cartesian equation of the following planes:
(a) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}} \cdot[(\mathrm{s}-2 \mathrm{t}) \hat{\mathrm{i}}+(3-\mathrm{t}) \hat{\mathrm{j}}+(2 \mathrm{~s}+\mathrm{t}) \hat{\mathrm{k}}]=15](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0789422b9ad2fd168094a22f1dd6043a_l3.png)
Solution: Let $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}$ be the position vector of $\mathrm{P}(\mathrm{x}, \mathrm{y}, \mathrm{z})$ is given by $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}=\mathrm{x} \hat{\mathrm{i}}+\mathrm{y}...
Find the vector equation of a plane which is at a distance of 7 units from the origin and normal to the vector 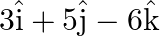
Solution: It is given that, The vector $3 \hat{\mathrm{i}}+5 \hat{\mathrm{j}}-6 \hat{\mathrm{k}}$ Vector equation of the plane with position vector $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{r}}$ is $\vec{r} \cdot...
In each of the following cases, determine the direction cosines of the normal to the plane and the distance from the origin.
(a) z = 2
(b) x + y + z = 1
Solution: (a) $z=2$ It is given that The eq. of the plane, $z=2$ or $0 x+0 y+z=2 \ldots (1) .$ The direction ratio of the normal $(0,0,1)$ Using the formula, $\begin{array}{l}...
One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards. Find the probability of getting: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{v} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77bef24f915b11d414e4c111f99ce683_l3.png)
a diamond or a spade
Solution: \[\left( v \right)\] Number of favorable outcomes for a diamond or a spade \[=\text{ }13\text{ }+\text{ }13\text{ }=\text{ }26\] So, number of favorable outcomes \[=\text{ }26\] Hence,...
One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards. Find the probability of getting: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
the jack or the queen of the hearts ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
a diamond
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Favorable outcomes for jack or queen of hearts \[=\text{ }1\text{ }jack\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }queen\] So, the number of favorable outcomes \[=\text{ }2\] Hence,...
One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards. Find the probability of getting: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
a queen of red color ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
a black face card
Solution: We have, Total possible outcomes \[=\text{ }52\] \[\left( i \right)\]Number queens of red color \[=\text{ }2\] Number of favorable outcomes\[~=\text{ }2\] Hence, P(queen of red color)...
A game consists of spinning arrow which comes to rest pointing at one of the numbers ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{5},\text{ }\mathbf{6},\text{ }\mathbf{7},\text{ }\mathbf{8},\text{ }\mathbf{9},\text{ }\mathbf{10},\text{ }\mathbf{11},\text{ }\mathbf{12};\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-67fdde3091439e8c286858207edb3f1b_l3.png)
as shown below. If the outcomes are equally likely, find the probability that the pointer will point at: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{v} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77bef24f915b11d414e4c111f99ce683_l3.png)
a number less than or equal to ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{9}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0e4d6074fdc32617fe7593f40096b31e_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{vi} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-594b0f9fe8331187f57fcaf948195301_l3.png)
a number between ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{11}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0a2999ef48d5649aa4214af7bb0afe5b_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( v \right)\] Favorable outcomes for a number less than or equal to \[9\text{ }are\text{ }1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6,\text{ }7,\text{ }8,\text{ }9\] So,...
A game of chance consists of spinning an arrow which is equally likely to come to rest pointing to one of the number, 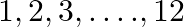 as shown in figure. What is the probability that it will point to:(iii) a number which is multiple of
as shown in figure. What is the probability that it will point to:(iii) a number which is multiple of 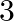 ? (iv) an even number?
? (iv) an even number?
(iii) So, Favorable outcomes i.e. to get a multiple of $3$ are $3,6,9,$ and $12$ Therefore, total number of favorable outcomes i.e. to get a multiple of $3$ is $4$ We know that the Probability =...
A game consists of spinning arrow which comes to rest pointing at one of the numbers ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{5},\text{ }\mathbf{6},\text{ }\mathbf{7},\text{ }\mathbf{8},\text{ }\mathbf{9},\text{ }\mathbf{10},\text{ }\mathbf{11},\text{ }\mathbf{12};\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-67fdde3091439e8c286858207edb3f1b_l3.png)
as shown below. If the outcomes are equally likely, find the probability that the pointer will point at: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[~~~\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9007133defbf8cecaabe61627666571d_l3.png)
a prime number ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
a number greater than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d72852d436631c1650d3154fd874ac4a_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\]Favorable outcomes for a prime number are \[2,\text{ }3,\text{ }5,\text{ }7,\text{ }11\] So, number of favorable outcomes\[~=\text{ }5\] Hence, P(the pointer will be...
Five cards are given– ten, jack, queen, king, and an ace of diamonds are shuffled face downwards. One card is picked at random. Then (i) What is the probability that the card is a queen? (ii) If a king is drawn first and put aside, then what is the probability that the second card picked up is the (a) ace? (b) king?
Given that Five cards-ten, jack, queen, king and Ace of diamond are shuffled face downwards. to find: Probability of following Total number of cards is $5$ (i) Now Total number of cards which is a...
A game consists of spinning arrow which comes to rest pointing at one of the numbers ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{5},\text{ }\mathbf{6},\text{ }\mathbf{7},\text{ }\mathbf{8},\text{ }\mathbf{9},\text{ }\mathbf{10},\text{ }\mathbf{11},\text{ }\mathbf{12};\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-67fdde3091439e8c286858207edb3f1b_l3.png)
as shown below. If the outcomes are equally likely, find the probability that the pointer will point at: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{6}~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7b9c55d8d241fd55b7e0703935f8d5f8_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
an even number
Solution: We have, Total number of possible outcomes \[=\text{ }12\] \[\left( i \right)\] Number of favorable outcomes for \[6\text{ }=\text{ }1\]6 Hence, \[P\left( the\text{ }pointer\text{...
A bag contains twenty Rs ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
coins, fifty Rs ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
coins and thirty Re ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall down when the bag is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
will neither be a Rs ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
coin nor be a Re ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
coin?
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Number of favourable outcomes for neither Re \[1\]nor Rs \[5\]coins \[=\] Number of favourable outcomes for Rs\[~2\] coins \[=\text{ }50\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( E...
A bag contains 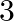 red balls and
red balls and 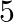 black balls. If A ball is drawn at random from the bag. Then What is the probability that the ball drawn is: (i) Red (ii) Back
black balls. If A ball is drawn at random from the bag. Then What is the probability that the ball drawn is: (i) Red (ii) Back
Given that A bag contains $3$ red, and $5$ black balls. A ball is drawn at random to find: Probability of getting a (i) red ball (ii) white ball So, Total number of balls $3+5=8$ (i) we know that...
A bag contains twenty Rs ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
coins, fifty Rs ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
coins and thirty Re ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
coins. If it is equally likely that one of the coins will fall down when the bag is turned upside down, what is the probability that the coin: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
will be a Re ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
coin? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
will not be a Rs ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
coin?
Solution: We have, Total number of coins \[=\text{ }20\text{ }+\text{ }50\text{ }+\text{ }30\text{ }=\text{ }100\] So, the total possible outcomes \[=\text{ }100\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( S \right)\]...
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Number of favorable outcomes for white or green ball \[=\text{ }16\text{ }+\text{ }8\text{ }=\text{ }24\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( E \right)\] Hence, probability for...
A bag contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{10}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5ab1e5be62c0333bfdd6391bd49aad5e_l3.png)
red balls, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{16}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec8d9d2d731b4ca460e57ad46a988282_l3.png)
white balls and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d72852d436631c1650d3154fd874ac4a_l3.png)
green balls. A ball is drawn out of the bag at random. What is the probability that the ball drawn will be: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
not red? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
neither red nor green?
Solution: Total number of possible outcomes \[=\text{ }10\text{ }+\text{ }16\text{ }+\text{ }8\text{ }=\text{ }34\] balls So, \[n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }34\] \[\left( i \right)\] Favorable...
The probability that two boys do not have the same birthday is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{897}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-eed2ac5f48177344144130443dea40b8_l3.png)
. What is the probability that the two boys have the same birthday?
Solution: We know that, P(do not have the same birthday) \[+\]P(have same birthday) \[=\text{ }1\] \[0.897\text{ }+\] P(have same birthday) \[=\text{ }1\] Thus, P(have same birthday) \[=\text{...
A bag contains 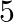 black,
black,  red and
red and  white balls. If A ball is drawn from the bag at random. Then Find the probability that the ball drawn is: (i) red (ii) black or white
white balls. If A ball is drawn from the bag at random. Then Find the probability that the ball drawn is: (i) red (ii) black or white
Given that: A bag contains $7$ red, $5$ black and $3$ white balls and a ball is drawn at random to find: Probability of getting a (i) Red ball (ii) Black or white ball (iii) Not black ball So,Total...
A bag contains a certain number of red balls. A ball is drawn. Find the probability that the ball drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
black ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
red
Solution: We have, Total possible outcomes = number of red balls. \[\left( i \right)\] Number of favourable outcomes for black balls \[=\text{ }0\] Hence\[,\text{ }P\left( black\text{ }ball...
If ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{P}\left( \mathbf{E} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{59}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1342539254f1e4119cf6b1645376ffba_l3.png)
; find ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{P}\left( \mathbf{not}\text{ }\mathbf{E} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9b91e62e47841788116487c439d0cbc8_l3.png)
Solution: We know that, \[P\left( E \right)\text{ }+\text{ }P\left( not\text{ }E \right)\text{ }=\text{ }1\] So, \[0.59\text{ }+\text{ }P\left( not\text{ }E \right)\text{ }=\text{ }1\] Hence,...
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{37}%\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a1f38c955bc170c8ba71f8eb972e1d41_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\text{ }-\mathbf{2}.\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2d7c7a6f514e622db52253ce35c9c5a4_l3.png)
Solution \[\left( iii \right)\text{ }As\text{ }0\text{ }\le \text{ }37\text{ }%\text{ }=\text{ }\left( 37/100 \right)\text{ }\le \text{ }1\] Thus, \[37\text{ }%\] can be a probability of an event....
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)~\mathbf{3}/\mathbf{7}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d60322175f300c4ae87d2e2bbf3a58e0_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{82}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-96c414065176a5df946218f1169777f8_l3.png)
Solution: We know that probability of an event E is \[0\text{ }\le \text{ }P\left( E \right)\text{ }\le \text{ }1\] \[\left( i \right)\text{ }As\text{ }0\text{ }\le \text{ }3/7\text{ }\le \text{...
Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability that the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top of the dice is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
less than or equal to ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{12}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-07c35f0f52591665e324675a6c3dbee4_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] All the outcomes are favourable to the event \[E\text{ }=\]‘sum of two numbers \[\le ~12\] Thus, \[P\left( E \right)\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( E \right)/\text{...
Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability that the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top of the dice is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2dba651f166b4a60a7ee242ceb6fa456_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{13}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-65b45659cac70a7c3ee2773e9e7803a6_l3.png)
Solution: We have, the number of possible outcomes \[=\text{ }6~\times \text{ }6\text{ }=\text{ }36\] \[\left( i \right)\] The outcomes favourable to the event ‘the sum of the two numbers is...
In a bundle of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{50}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b403d70b7357199452c3ea1a8fba91f8_l3.png)
shirts, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{44}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-284f5e31d0256f7be991395636dcc87e_l3.png)
are good, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e3cd21f5b1889aaf277b2b6f04102ab3_l3.png)
have minor defects and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
have major defects. What is the probability that: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
it is acceptable to a trader who accepts only a good shirt? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
it is acceptable to a trader who rejects only a shirt with major defects?
Solution: We have, Total number of shirts \[=\text{ }50\] Total number of elementary events \[=\text{ }50\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( S \right)\] \[\left( i \right)\] As, trader accepts only good shirts...
In a musical chairs game, a person has been advised to stop playing the music at any time within ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{40}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5a966c04db349ec3c1abfce1c5809770_l3.png)
seconds after its start. What is the probability that the music will stop within the first ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{15}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c554aaf0e077efa7da9b881aa7445bc4_l3.png)
seconds?
Solution: Total result \[=\text{ }0\text{ }sec\text{ }to\text{ }40\text{ }sec\] Total possible outcomes \[=\text{ }40\] So\[,\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }40\] Favourable results...
All the three face cards of spades are removed from a well shuffled pack of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards. A card is then drawn at random from the remaining pack. Find the probability of getting: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
a black card
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Number of black cards left \[=\text{ }23\text{ }cards\text{ }\left( 13\text{ }club\text{ }+\text{ }10\text{ }spade \right)\] Event of drawing a black card \[=\text{...
All the three face cards of spades are removed from a well shuffled pack of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards. A card is then drawn at random from the remaining pack. Find the probability of getting: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
a black face card ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
a queen
Solution: We have, Total number of cards \[=\text{ }52\] If \[3\] face cards of spades are removed Then, the remaining cards \[=\text{ }52\text{ }\text{ }3\text{ }=\text{ }49\text{ }=\] number of...
A box contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{7}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f74b766149ea54b0c54991ce3a80911a_l3.png)
red balls, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d72852d436631c1650d3154fd874ac4a_l3.png)
green balls and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
white balls. A ball is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the ball is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
white ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
neither red nor white
Solution: We have, Total number of balls in the box \[=\text{ }7\text{ }+\text{ }8\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }20\] balls Total possible outcomes \[=\text{ }20\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( S...
A man tosses two different coins (one of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{Rs}\text{ }\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a179dfbb61b1d72d2dc5dbb2b91a1890_l3.png)
and another of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{Rs}\text{ }\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8833e7680fa31d0c8ae78d0326501c36_l3.png)
) simultaneously. What is the probability that he gets: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
at least one head? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
at most one head?
Solution: We know that, When two coins are tossed simultaneously, the possible outcomes are \[\left\{ \left( H,\text{ }H \right),\text{ }\left( H,\text{ }T \right),\text{ }\left( T,\text{ }H...
A and B are friends. Ignoring the leap year, find the probability that both friends will have: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
different birthdays? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
the same birthday?
Solution: Out of the two friends, A’s birthday can be any day of the year. Now, B’s birthday can also be any day of \[365\] days in the year. We assume that these \[365\] outcomes are equally...
In a match between A and B: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
the probability of winning of A is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{83}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1e4fcef37405717c20e577f1366ab70a_l3.png)
. What is the probability of winning of B? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
the probability of losing the match is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{49}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c532bc1eecea944e3ba513bc0032287e_l3.png)
for B. What is the probability of winning of A?
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\]We know that, The probability of winning of A \[+\]Probability of losing of A \[=\text{ }1\] And, Probability of losing of A \[=\] Probability of winning of B...
From a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{v} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77bef24f915b11d414e4c111f99ce683_l3.png)
a card with number less than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d72852d436631c1650d3154fd874ac4a_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{vi} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-594b0f9fe8331187f57fcaf948195301_l3.png)
a card with number between ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{9}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0e4d6074fdc32617fe7593f40096b31e_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( v \right)\] Numbers less than \[8\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ \text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6,\text{ }7 \right\}\]\[\] Event of drawing a card with number less than...
From a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
a queen of black card ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
a card with number ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\text{ }\mathbf{or}\text{ }\mathbf{6}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-26c3b74593956359de7dc601ac6d770a_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Event of drawing a queen of black colour \[=\text{ }\left\{ Q\left( spade \right),\text{ }Q\left( club \right) \right\}\text{ }=\text{ }E\] So,\[~n\left( E...
From a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
a face card ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
not a face card
Solution: We have, the total number of possible outcomes \[=\text{ }52\] So, \[n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }52\] \[\left( i \right)~\]No. of face cards in a deck of \[52\]cards \[=\text{...
A dice is thrown once. What is the probability of getting a number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
greater than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
less than or equal to ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
?
Solution: The number of possible outcomes when dice is thrown \[=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }6\]...
A bag contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
red balls, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e3cd21f5b1889aaf277b2b6f04102ab3_l3.png)
blue balls and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
yellow ball, all the balls being identical in shape and size. If a ball is taken out of the bag without looking into it; find the probability that the ball is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
not yellow ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
neither yellow nor red
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Probability of not drawing a yellow ball \[=\text{ }1\text{ }\] Probability of drawing a yellow ball Thus, probability of not drawing a yellow ball \[=\text{...
A bag contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
red balls, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e3cd21f5b1889aaf277b2b6f04102ab3_l3.png)
blue balls and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0313c9365144662794ca80515dcd72ce_l3.png)
yellow ball, all the balls being identical in shape and size. If a ball is taken out of the bag without looking into it; find the probability that the ball is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
yellow ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
red
Solution: The total number of balls in the bag \[=\text{ }3\text{ }+\text{ }4\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }8\] balls So, the number of possible outcomes \[=\text{ }8\text{ }=\text{ }n\left( S...
If two coins are tossed once, what is the probability of getting: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)~\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b4a805e73b6419ecb10d01e0d7e095ff_l3.png)
both heads or both tails
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] E = event of getting both heads or both tails \[=\text{ }\left\{ HH,\text{ }TT \right\}\] \[n\left( E \right)\text{ }=\text{ }2\] Hence, probability of getting both...
If two coins are tossed once, what is the probability of getting: (i) both heads. (ii) at least one head.
Solution: We know that, when two coins are tossed together possible number of outcomes = {HH, TH, HT, TT} So, \[n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }4\] \[\left( i \right)\]E = event of getting both...
A pair of dice is thrown. Find the probability of getting a sum of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{10}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5ab1e5be62c0333bfdd6391bd49aad5e_l3.png)
or more, if ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
appears on the first die
Solution: In throwing a dice, total possible outcomes \[=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }6\] For two...
A book contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{85}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ce8cf3529bbf7d088edd3d48cb89a2dc_l3.png)
pages. A page is chosen at random. What is the probability that the sum of the digits on the page is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d72852d436631c1650d3154fd874ac4a_l3.png)
?
Solution: We know that, Number of pages in the book \[=\text{ }85\] Number of possible outcomes \[=\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }85\] Out of \[85\]pages, pages that sum up to \[8\text{...
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[(\mathbf{iii})\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f7fa3b0aee53ee10ab5aca160771dd2c_l3.png)
less than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{8}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d72852d436631c1650d3154fd874ac4a_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
greater than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{6}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-263adac88912153e6b4347f4b5c18c13_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] On a dice, numbers less than \[8\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\left( E \right)\text{ }=\text{...
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
less than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
greater than or equal to ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e3cd21f5b1889aaf277b2b6f04102ab3_l3.png)
Solution: We know that, In throwing a dice, total possible outcomes \[=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{...
From identical cards, numbered one card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{3}\text{ }\mathbf{and}\text{ }\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d82c473e47cf7694111772a9d7655e6d_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{3}\text{ }\mathbf{or}\text{ }\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-139417bec5d87c2b7316671b7b15ed6d_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] From numbers \[1\text{ }to\text{ }25\], there is only one number which is multiple of \[3\text{ }and\text{ }5\text{ }i.e.~\left\{ 15 \right\}\] So, favorable number...
From ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{25}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-04c165886b06185d393c73aef1d22b23_l3.png)
identical cards, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\text{ }\mathbf{1},\text{ }\mathbf{2},\text{ }\mathbf{3},\text{ }\mathbf{4},\text{ }\mathbf{5},\text{ }\ldots \ldots ,~\mathbf{24},\text{ }\mathbf{25}:\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1f2c87afd2f10bf14f5329adbf782f73_l3.png)
numbered one card is drawn at random. Find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a multiple of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d29dcd8869a616f0d150912528867b07_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-196cc0b4d2efdb4a16e4b1ad1ff50340_l3.png)
Solution: We know that, there are \[25\] cards from which one card is drawn. So, the total number of elementary events \[=\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }25\] \[\left( i \right)\]From...
$Hundred identical cards are numbered from ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\text{ }\mathbf{to}\text{ }\mathbf{100}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-656d6106f414a60095504a0e75cdbb9a_l3.png)
The cards The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on card drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{v} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77bef24f915b11d414e4c111f99ce683_l3.png)
less than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{48}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0cdef90bf558e4c0f426dd33b0767f01_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( v \right)\]From numbers \[1\text{ }to\text{ }100\], there are \[47\] numbers which are less than \[48\text{ }i.e.~\{1,\text{ }2,\text{ }\ldots \ldots \ldots ..,\]\[46,\text{...
Hundred identical cards are numbered from The cards The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on card drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
between ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{40}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5a966c04db349ec3c1abfce1c5809770_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{60}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-58eee87b7240e27500b7ecc65751410e_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
greater than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{85}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ce8cf3529bbf7d088edd3d48cb89a2dc_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] From numbers \[1\text{ }to\text{ }100\], there are \[19\] numbers which are between \[40\text{ }and\text{ }60\text{ }i.e.~\{41,\text{ }42\], \[43,\text{ }44,\text{...
Hundred identical cards are numbered from ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{1}\text{ }\mathbf{to}\text{ }\mathbf{100}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-656d6106f414a60095504a0e75cdbb9a_l3.png)
. The cards The cards are well shuffled and then a card is drawn. Find the probability that the number on card drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
a multiple of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
a multiple of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{6}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-263adac88912153e6b4347f4b5c18c13_l3.png)
Solution: We kwon that, there are \[100\] cards from which one card is drawn. Total number of elementary events \[=\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }100\] \[\left( i \right)~\] From numbers...
multiple Nine cards (identical in all respects) are numbered . A card is selected from them at random. Find the probability that the card selected will be: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
an even number and a multiple of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
an even number or a of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] From numbers \[2\text{ }to\text{ }10\], there is one number which is an even number as well as multiple of \[3\text{ }i.e.\text{ }6\] So, favorable number of events...
Nine cards (identical in all respects) are numbered ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\text{ }\mathbf{to}\text{ }\mathbf{10}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-92bb4ded3cb2bc7ffedbd443ab77380c_l3.png)
. A card is selected from them at random. Find the probability that the card selected will be: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
an even number ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
a multiple of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
Solution: We know that, there are totally \[9\] cards from which one card is drawn. Total number of elementary events \[=\text{ }n\left( S \right)\text{ }=\text{ }9\] \[\left( i \right)\] From...
In a T.T. match between Geeta and Ritu, the probability of the winning of Ritu is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{73}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4fd200ede5f2e7ec8fd2d3c84e2532c2_l3.png)
. Find the probability of: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
winning of Geeta ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
not winning of Ritu
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\] Winning of Geeta is a complementary event to winning of Ritu Thus, P(winning of Ritu) \[+\]P(winning of Geeta) \[=\text{ }1\] P(winning of Geeta) \[=\text{ }1\text{...
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
If A and B are two complementary events then what is the relation between ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{P}\left( \mathbf{A} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-42a345a0e28239be82ba34d9e51d6bfa_l3.png)
and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{P}\left( \mathbf{B} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cc9778b7f224c7e17f5afb4a80f83224_l3.png)
? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
If the probability of happening an event A is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{0}.\mathbf{46}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-740f3d30093c73bf7c7c169b2926085e_l3.png)
. What will be the probability of not happening of the event A?
Solution: \[\left( i \right)\] Two complementary events, taken together, include all the outcomes for an experiment and the sum of the probabilities of all outcomes is \[1.\]...
From a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will:(v) be a face card of red colour
Solution: \[\left( v \right)\]There are \[26\] red cards in a deck, and \[6\] of these cards are face cards (\[2\] kings, \[2\]queens and \[2\]jacks). The number of favourable outcomes for the event...
From a well shuffled deck of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{52}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d3c2ee289e803b11d76d5473900dfaff_l3.png)
cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
be a red card. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
be a face card
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] Number of red cards in a deck \[=\text{ }26\] The number of favourable outcomes for the event of drawing a red card \[=\text{ }26\] Then, probability of drawing a...
From a well shuffled deck of 52 cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
be a black card. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
not be a red card
Solution: We know that, Total number of cards \[=\text{ }52\] So, the total number of outcomes \[=\text{ }52\] There are \[13\] cards of each type. The cards of heart and diamond are red in colour....
In a single throw of a die, find the probability that the number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
will be an odd number
Solution: \[\left( iii \right)\] If \[E\text{ }=\]event of getting an odd number \[=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }3,\text{ }5 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\left( E \right)\text{ }=\text{ }3\] Then,...
In a single throw of a die, find the probability that the number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
will be an even number. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
will not be an even number.
Solution: Here, the sample space \[=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6 \right\}\] \[n\left( s \right)\text{ }=\text{ }6\] \[\left( i \right)\] If \[E\text{ }=\]event...
In a single throw of a die, find the probability of getting a number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
not greater than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e3cd21f5b1889aaf277b2b6f04102ab3_l3.png)
\[\left( iii \right)\text{ }E\text{ }=\] event of getting a number not greater than \[4\text{ }=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\text{ }\left( E...
In a single throw of a die, find the probability of getting a number: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec4588e8cb8288d41d93726c3b60fee0_l3.png)
greater than ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}.\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6ce6e6d6192b518eaed98ca65ceef276_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a4cc96f58fba9e185f598e5aebb7decb_l3.png)
less than or equal to ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{4}.\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6ce6e6d6192b518eaed98ca65ceef276_l3.png)
Solution: Here, the sample space \[=\text{ }\left\{ 1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5,\text{ }6 \right\}\] So\[,\text{ }n\text{ }\left( s \right)\text{ }=\text{ }6\] \[\left( i \right)\]If...
A bag contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
white, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
black and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{v} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77bef24f915b11d414e4c111f99ce683_l3.png)
not a black ball.
Solution: \[\left( v \right)\] There are \[3\text{ }+\text{ }2\text{ }=\text{ }5\] balls which are not black So, the number of favourable outcomes \[=\text{ }5\] Thus, P(getting a white ball)...
A bag contains ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{3}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-215281f3010e0d54a225c07b29796308_l3.png)
white, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{5}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a776c358a8cf31774e7e50698744b5e6_l3.png)
black and ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{2}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d651857e4c78c89b56c03d51a899277b_l3.png)
red balls, all of the same shape and size. A ball is drawn from the bag without looking into it, find the probability that the ball drawn is: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-512b94d74fc4a9de10e783f6743c6b28_l3.png)
a white ball. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-87dbc162d5b48495d80940f09e793b2f_l3.png)
not a red ball.
Solution \[\left( iii \right)\]There are \[3\] white balls So, the number of favourable outcomes \[=\text{ }3\] Thus, P(getting a white ball) \[=~3/10\text{ }=\text{ }3/10\] \[\left( iv...
If a coin is tossed two times, describe the sample space associated to this experiment.
We know that if two coins are tossed, that means two probabilities will occur at same time. So, S = {HT, TH, HH, TT} ∴ Sample space is {HT, HH, TT, TH}
Find the multiplicative inverse of the following complex numbers:
(i) 1 – i
(ii) (1 + i √3)2
Solution: (i) $1-\mathrm{i}$ Given that It is known that the multiplicative inverse of a complex number $(\mathrm{Z})$ is $\mathrm{Z}^{-1}$ or $1 / \mathrm{Z}$ Therefore, $\begin{array}{l}...
(i) If tan A = 5/6 and tan B = 1/11, prove that A + B = π/4 (ii) If tan A = m/(m–1) and tan B = 1/(2m – 1), then prove that A – B = π/4
As per the question given: \[tan\text{ }A\text{ }=\text{ }5/6\text{ }and\text{ }tan\text{ }B\text{ }=\text{ }1/11\] Since,\[tan\text{ }\left( A\text{ }+\text{ }B \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\left(...
Find the area enclosed between the parabola 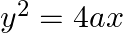 and the line
and the line 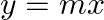
Solution: Area enclosed between the parabola, $y^{2}=4 a x$, and the line, $y=m x$, is represented by the shaded area $\mathrm{OABO}$ as Points of intersection of both the curves are $(0,0)$ and...
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola  and the
and the 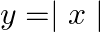 .
.
Solution: The area bounded by the parabola, $x^{2}=y$, and the line, $y=|x|$, can be represented as The given area is symmetrical about $y$-axis. $\therefore$ Area $\mathrm{OACO}=$ Area...
Write the negation of the following simple statements
(i) Cow has four legs.
(ii) A leap year has 366 days.
(i) "Not p" is the negation of the assertion p. The negation of p is represented by $\sim p$. The truth value of $\sim p$ is the opposite of the truth value of p. The negation of the statement is...
Write the negation of the following simple statements
(i) Violets are blue.
(ii) √5 is a rational number.
(i) "Not p" is the negation of the assertion p. The negation of p is represented by $\sim p$. The truth value of $\sim p$ is the opposite of the truth value of p. The negation of the statement is...
Find the component statements of the following compound statements.
A rectangle is a quadrilateral or a 5 – sided polygon.
A compound statement is made up of two or more statements (Components). As a result, the elements of the given statement "A rectangle is a quadrilateral or a 5-sided polygon" are as follows: p: A...
Find the component statements of the following compound statements.
(i) Plants use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
(ii) Two lines in a plane either intersect at one point or they are parallel.
(i) A compound statement is made up of two or more statements (Components). As a result, the parts of the supplied statement "Plants use sunshine, water, and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis" are...
Find the component statements of the following compound statements.
(i) The number 100 is divisible by 3, 11 and 5.
(ii) Chandigarh is the capital of Haryana and U.P.
(i) A compound statement is made up of two or more statements (Components). As a result, the components of the provided statement "The number 100 is divisible by 3, 11, and 5" are as follows. p: 100...
Find the area bounded by the curve y = sin x between x = 0 and x = 2p.
Find the area bounded by the curve y = √x , x = 2y + 3 in the first quadrant and x-axis.
The curves are y = √x and line x = 2y + 3 Solving y = √x and x = 2y + 3, we get
Find the area enclosed by the curve y = –x^2 and the straight-line x + y + 2 = 0.
The curve y = –x2 or x2 = –y and the line x + y + 2 = 0 Solving the two equation, we get \[x\text{ }-\text{ }{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }2\text{ }=\text{ }0\] \[{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }-x\text{ }\text{ }-2\text{...
Find the area of the region bounded by y = √x and y = x.
The equations of curve y = √x and line y = x Solving the equations y = √x ⇒ y2 = x and y = x, we get \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }x \\ {{x}^{2}}~-\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\...
Determine the area under the curve y = √(a^2 – x^2) included between the lines x = 0 and x = a.
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} y~=\text{ }\surd \left( {{a}^{2}}~-~{{x}^{2}} \right)\text{ }\Rightarrow ~{{y}^{2}}~=~{{a}^{2}}~-~{{x}^{2}} \\ {{x}^{2~}}+~{{y}^{2}}~=~{{a}^{2}} \\ \end{array}\] which is...
Draw a rough sketch of the curve y = √(x – 1) in the interval [1, 5]. Find the area under the curve and between the lines x = 1 and x = 5.
The curve is \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} y~=\text{ }\surd \left( x~-\text{ }1 \right) \\ \Rightarrow \text{ }{{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }x\text{ }-\text{ }1 \\ \end{array}\] Plotting the curve and finding...
Calculate the area under the curve y = 2 √x included between the lines x = 0 and x = 1.
Sketch the region {(x, 0) : y = √(4 – x^2)} and x-axis. Find the area of the region using integration.
Given, {(x, 0) : \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} y~=\text{ }\surd \left( 4\text{ }~-{{x}^{2}} \right)\ \\ So,\text{ }{{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }4\text{ }-\text{ }{{x}^{2}} \\ {{x}^{2}}~+\text{...
Find the area of region bounded by the line x = 2 and the parabola y^2 = 8x
The equation of line x = 2 and parabola y2 = 8x Putting value of x in the other equation, we have \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }8\left( 2 \right) \\ {{y}^{2}}~=\text{ }16 \\...
Find the area of the region included between y^2 = 9x and y = x
The curves are y2 = 9x and y = x Solving the above equations, we have \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }9x\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ }{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }-9x\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ x\left(...
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y^2 = 4x and x^2 = 4y.
The curves are y2 = 4x … (i) and x2 = 4y … (ii) On solving the equations, we get From (ii), y = x2/4 Putting value of y in (i), we have \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{\left( {{x}^{2}}/4...
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y = x^3 and y = x + 6 and x = 0.
The curves are y = x3, y = x + 6 and x = 0 On solving y = x3 and y = x + 6, we have \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{3}}~=\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }6 \\ {{x}^{3}}~\text{ }-x\text{ }-\text{ }6\text{...
Find the area of the region bounded by the curves y^2 = 9x, y = 3x.
Given curves are y2 = 9x and y = 3x solving the two equations we have \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{\left( 3x \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }9x \\ 9{{x}^{2}}~=\text{ }9x \\ 9{{x}^{2}}~\text{ }-9x\text{...
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
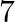 audio cassettes and
audio cassettes and 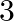 videocassettes cost
videocassettes cost 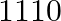 , while
, while 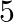 audio cassettes and
audio cassettes and 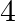 videocassettes cost
videocassettes cost 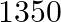 . Find the cost of audio cassettes and a video cassette.
. Find the cost of audio cassettes and a video cassette.
Let’s assume the cost of an audio cassette and that of a video cassette be ₹a and ₹b, respectively. Then forming equations according to the question, we have $7a+3b=1110$…(a) $5a+4b=1350$… (b) On...
Find the coefficient of 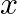 in the expansion of
in the expansion of 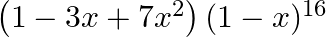
Given function is $\left(1-3 x+7 x^{2}\right)(1-x)^{16}$ Expansion of the function is, $=\left(1-3 x+7 x^{2}\right)\left({ }^{16} C_{0}-{ }^{16} C_{1} x^{1}+{ }^{16} C_{2} x^{2}+\ldots+{ }^{16}...
Find the term independent of 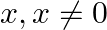 , in the expansion of
, in the expansion of 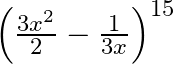
Given function is $\left(\frac{3 x^{2}}{2}-\frac{1}{3 x}\right)^{15}$ We know, the standard formula of $T_{r+1}$ will be, $T_{r+1}={ }^{15} C_{r}\left(\frac{3...
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
A group consists of 4 girls and 7 boys. In how many ways can a team of 5 members be selected if the team has (i) no girls (ii) at least one boy and one girl
Solution: It is known that ${ }^{n} C_{r}$ $=\frac{n !}{r !(n-r) !}$ (i) No girls The total no. of ways the team can have no girls $={ }^{4} \mathrm{C}_{0}{ }^{7} \mathrm{C}_{5}=21$ (ii) at least...
solve the following:
14. Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
Solve the following:
Solution:
Solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
solve the following:
Solution:
Verify the following:
Solution:
Find the equation of each of the following parabolas (c) Focus at (–1, –2), directrix x – 2y + 3 = 0
Find the equation of each of the following parabolas (a) Directrix x = 0, focus at (6, 0) (b) Vertex at (0, 4), focus at (0, 2)
(a) The distance of any point on the parabola from its focus and its directrix is same. Given that, directrix, x = 0 and focus = (6, 0) If a parabola has a vertical axis, the standard form of the...
Find the equation of a circle passing through the point (7, 3) having radius 3 units and whose centre lies on the line y = x – 1.
the equation of a circle having centre (h, k), having radius as r units, is (x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2Centre lies on the line i.e., y = x – 1, Co – Ordinates are (h, k) = (h, h – 1)...
Find the equation of a circle of radius 5 which is touching another circle x2 + y2 – 2x – 4y – 20 = 0 at (5, 5).
Given \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} {{x}^{2}}~\text{ }-2x\text{ }+\text{ }{{y}^{2}}~\text{ }-4y\text{ }-\text{ }20\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ {{x}^{2}}~\text{ }-2x\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }+{{y}^{2}}~\text{...
Find the equation of a circle whose centre is (3, –1) and which cuts off a chord of length 6 units on the line 2x – 5y + 18 = 0.
Using Pythagoras Theorem, (Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Perpendicular)2 = (3)2 + (√29)2 = 29 + 9 = √38 Hypotenuse = √38 units (radius) Since, the radius bisects the chord into two equal halves, Since,...
Find the equation of the circle which passes through the points (2, 3) and (4, 5) and the centre lies on the straight line y – 4x + 3 = 0.
the equation of a circle having centre (h, k), having radius as r units, is \[{{\left( x\text{ }-\text{ }h \right)}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{\left( y\text{ }-\text{ }k \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }{{r}^{2}}\ldots...
If the lines 2x – 3y = 5 and 3x – 4y = 7 are the diameters of a circle of area 154square units, then obtain the equation of the circle.
Since, diameters of a circle intersect at the centre of a circle, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2x\text{ }-\text{ }3y\text{ }=\text{ }5\text{ }\ldots \ldots \ldots 1 \\ 3x\text{ }-\text{ }4y\text{...
Find the equation of the hyperbola with eccentricity 3/2 and foci at (± 2, 0).
Find the eccentricity of the hyperbola 9y^2 – 4x^2 = 36.
If the distance between the foci of a hyperbola is 16 and its eccentricity is √2, then obtain the equation of the hyperbola.
If the line y = mx + 1 is tangent to the parabola y2 = 4x then find the value of m.
equations are, y = mx + 1 & y2 = 4x By solving given equations we get (mx + 1)2 = 4x Expanding the above equation we get \[{{m}^{2}}{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }2mx\text{ }+\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }4x\]...
If the points (0, 4) and (0, 2) are respectively the vertex and focus of a parabola, then find the equation of the parabola.
Find the length of the line-segment joining the vertex of the parabola y2 = 4axand a point on the parabola where the line-segment makes an angle q to the x-axis.
Find the coordinates of a point on the parabola y2 = 8x whose focal distance is 4.
equation of an ellipse is y2 = 4ax, Also we have length of latus rectum = 4a Now by comparing the above two equations, 4a = 8 Therefore \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} a\text{ }=\text{ }2 \\...
Find the distance between the directrices of the ellipse x^2/36 + y^2/20 = 1
Find the equation of ellipse whose eccentricity is 2/3 , latus rectum is 5 and the centre is (0, 0).
If the eccentricity of an ellipse is 5/8 and the distance between its foci is 10, then find latus rectum of the ellipse.
Given the ellipse with equation 9x^2 + 25y^2 = 225, find the eccentricity and foci.
If the latus rectum of an ellipse is equal to half of minor axis, then find its eccentricity.
Find the equation of a circle concentric with the circle x^2 + y^2 – 6x + 12y + 15 = 0 and has double of its area.
Given equation of the circle is \[{{x}^{2}}~-\text{ }6x\text{ }+\text{ }{{y}^{2}}~+\text{ }12y\text{ }+\text{ }15\text{ }=\text{ }0\] The above equation can be written as \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
If the line y = √3x + k touches the circle x2 + y2 = 16, then find the value of k.
Find the equation of the circle having (1, –2) as its centre and passing through 3x + y = 14, 2x + 5y = 18
Solving the given equations, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 3x\text{ }+\text{ }y\text{ }=\text{ }14\text{ }\ldots \ldots \ldots .1 \\ 2x\text{ }+\text{ }5y\text{ }=\text{ }18\text{ }\ldots \ldots \ldots...
Find the equation of a circle which touches both the axes and the line 3x – 4y + 8 = 0 and lies in the third quadrant.
The equation of the given circle is \[{{x}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{y}^{2}}~+\text{ }4x\text{ }+\text{ }4y\text{ }+\text{ }4\text{ }=\text{ }0.\]
If the lines 3x – 4y + 4 = 0 and 6x – 8y – 7 = 0 are tangents to a circle, then find the radius of the circle.
Given lines are 6x – 8y + 8 = 0 and 6x – 8y – 7 = 0. Distance d between two parallel lines y = mx + c1 and y = mx + c2 is given by d = |C1–C2|/√(A2 + B2 ) These parallel lines are tangent to a...
Find the equation of the circle which touches x-axis and whose centre is (1, 2).
Since the circle has a centre (1, 2) and also touches x-axis. Radius of the circle is, r = 2 The equation of a circle having centre (h, k), having radius as r units, is \[{{\left( x\text{ }-\text{...
If a circle passes through the point (0, 0) (a, 0), (0, b) then find the coordinates of its centre.
The equation of a circle having centre (h, k), having radius as r units, is \[{{\left( x\text{ }-\text{ }h \right)}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{\left( y\text{ }-\text{ }k \right)}^{2}}~=\text{ }{{r}^{2}}\]...
Show that the point (x,y) given by x= 2at/1+t^2 and y= a(1-t^2)/1+t^2 lies on a circle for all real values of t such that -1<=t<=1 where a is any given real number
Find the equation of the circle which touches the both axes in first quadrant and whose radius is a.
The circle touches both the x and y axes in the first quadrant and the radius is a. For a circle of radius a, the centre is (a, a). The equation of a circle having centre (h, k), having radius as r...
The distance of the point of intersection of the lines 2x – 3y + 5 = 0 and 3x + 4y = 0 from the line 5x – 2y = 0 is
SOLUTION: The correct option is option(a) Explanation: Given two lines are \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2x\text{ }-\text{ }3y\text{ }+\text{ }5\text{ }=\text{ }0~\ldots \text{ }\left( i \right) \\...
The tangent of angles between the lines whose intercepts on the axes are a,-b and b, -a, respectively is: (A) a^2-b^2/ab (B) b^2-a^2/2 (C) b^2-a^2/2ab (D) none of these
The correct option is option(C)-
The equation of the straight line passing through the point (3, 2) and perpendicular to the line y = x is A. x – y = 5 B. x + y = 5 C. x + y = 1 D. x – y = 1
The correct option is option(B)- x + y = 5 straight line passing through the point (3, 2) And perpendicular to the line y = x Let the equation of line L be \[y\text{ }-\text{ }{{y}_{1}}~=\text{...
Slope of a line which cuts off intercepts of equal lengths on the axes is A. – 1 B. – 0 C. 2 D. √3
The correct option is option(A)- – 1
A line cutting off intercept – 3 from the y-axis and the tangent at angle to the x-axis is 3/5, its equation is
A. 5y – 3x + 15 = 0 B. 3y – 5x + 15 = 0 C. 5y – 3x – 15 = 0 D. None of these SOLUTION: The correct option is option(A)- 5y – 3x + 15 = 0
If p is the length of the perpendicular from origin on the line x/a=y/b=1 and a2,p2,and b2 ae in AP.Then show that a4+b4=0.
Solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \Rightarrow ~\left( {{a}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{b}^{2}} \right)\text{ }\left( {{a}^{2}}~+\text{ }{{b}^{2}} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }2\left( {{a}^{2}}{{b}^{2}} \right) \\...
p1 and p2 are points on either of the two lines y-√3 and |x|=2 at a distance of 5units from their point of intersection.Find the coordinates of the foot of perpendicular drawn from p1 and p2 on the bisector of theangle between the given lines.
Since, \[y\text{ }-\text{ }\surd 3\left| x \right|\text{ }=\text{ }2\]If x ≥ 0, then \[y\text{ }-\text{ }\surd 3x\text{ }=\text{ }2\text{ }\ldots ..\text{ }\left( i \right)\] If x < 0,...
If the sum of the distances of a moving point in a plane from the axes is 1, then find the locus of the point.
SOLUTION: Let the coordinates of point P be (a, b) Since, the sum of the distance from the axes to the point is always 1 \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \therefore ~\left| x \right|\text{ }+\text{ }\left|...
Find the equations of the lines through the point of intersection of the lines x – y + 1 = 0 and 2x – 3y + 5 = 0 and whose distance from the point (3, 2) is 7/5.
Squaring both the sides, we get
Find the equation of the line which passes through the point (– 4, 3) and the portion of the line intercepted between the axes is divided internally in the ratio 5 : 3 by this point.
On cross multiplication we get \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \Rightarrow ~-72x\text{ }+\text{ }160y\text{ }=\text{ }768 \\ \Rightarrow ~-36x\text{ }+\text{ }80y\text{ }=\text{ }384 \\ \Rightarrow...
A straight line moves so that the sum of the reciprocals of its intercepts made on axes is constant. Show that the line passes through a fixed point.
In what direction should a line be drawn through the point (1, 2) so that its point of intersection with the line x + y = 4 is at a distance √6/3 from the given point.
A variable line passes through a fixed point P. The algebraic sum of the perpendiculars drawn from the points (2, 0), (0, 2) and (1, 1) on the line is zero. Find the coordinates of the point P.
\[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \Rightarrow ~2a\text{ }-\text{ }1\text{ }+\text{ }2b\text{ }-\text{ }1\text{ }+\text{ }a\text{ }+\text{ }b\text{ }-\text{ }1\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ \Rightarrow ~3a\text{...
If the equation of the base of an equilateral triangle is x + y = 2 and the vertex is (2, – 1), then find the length of the side of the triangle.
Find the equation of one of the sides of an isosceles right angled triangle whose hypotenuse is given by 3x + 4y = 4 and the opposite vertex of the hypotenuse is (2, 2).
Find the equation of a straight line on which length of perpendicular from the origin is four units and the line makes an angle of 120° with the positive direction of x-axis.
intercept of a line between the coordinate axes is divided by the point (–5, 4) in the ratio 1:2, then find the equation of the line.
For what values of a and b the intercepts cut off on the coordinate axes by the line ax + by + 8 = 0 are equal in length but opposite in signs to those cut off by the line 2x – 3y + 6 = 0 on the axes.
Show that the tangent of an angle between lines x/a+y/b=1 and x/a-y/b=1 is 2ab/a^2-b^2
Find the points on the line x + y = 4 which lie at a unit distance from the line 4x + 3y = 10.
Putting the value of y1 = 4 – x1 in equation 3, we get \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 4{{x}_{1}}~+\text{ }3\left( 4\text{ }-\text{ }{{x}_{1}} \right)\text{ }=\text{ }5 \\ \Rightarrow ~4{{x}_{1}}~+\text{...
Find the equation of the lines which passes through the point (3, 4) and cuts off intercepts from the coordinate axes such that their sum is 14.
Find the angle between: y=2-√3(x+5) and y=2+√3(x-7)
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (5, 2) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (2, 3) and (3, – 1).
The points are A (5, 2), B (2, 3) and C (3, -1)
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point (1, – 2) and cuts off equal intercepts from axes.
Given A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, S = {(x, y) : x ∈ A, y ∈ A}. Find the ordered pairs which satisfy the conditions given below:(i) x + y = 5(ii) x + y < 5
Given, A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, S = {(x, y) : x ∈A, y ∈A} (i) x + y = 5 Finding the ordered pair such that x + y = 5, where x and y belong to the given set A: 1 + 1 = 2≠5 1 + 2 = 3≠5 1 + 3 = 4≠5 1 + 4 =...
In each of the following cases, find a and b. (i) (2a + b, a – b) = (8, 3) (ii) (a/4 , a – 2b) = (0, 6 + b)
(i) Given, (2a + b, a – b) = (8, 3) The corresponding elements will be equal because the ordered pairs are equal. Hence, 2a + b = 8 and a–b = 3 Now a–b = 3 ⇒a = 3 + b On putting the value of a in...
Show that the following system of linear inequalities has no solution x + 2y ≤ 3, 3x + 4y ≥ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 1
SOLUTION: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} x\text{ }+\text{ }2y\text{ }\le \text{ }3 \\ {} \\ \end{array}\] \[Line:\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }2y\text{ }=\text{ }3\] x 3 1 y 0 1 Also, (0, 0) satisfies...
