Solution: Option (i) and (iv) are the answers. Group 13 elements create electron-deficient compounds and are thus Lewis acids. Electron-rich hydrides have lone pairs of extra electrons. Compounds of...
Which of the following statements is correct? (i) Elements of group 15 form electron deficient hydrides. (ii) All elements of group 14 form electron precise hydrides. (iii) Electron precise hydrides have tetrahedral geometries. (iv) Electron rich hydrides can act as Lewis acids.
Solution: Option (ii) and (iii) are the answers. Inorganic electron-specific hydrides are those hydrides in which the exact quantity of electrons required to form a typical covalent bond is present....
The hardness of water may be temporary or permanent. Permanent hardness is due to the presence of (i) Chlorides of Ca and Mg in water (ii) Sulphates of Ca and Mg in water (iii) Hydrogen carbonates of Ca and Mg in water (iv) Carbonates of alkali metals in water
Solution: Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. Permanent hardness is caused by the presence of soluble magnesium and calcium salts in the form of chorides and sulphates in the water, which causes...
Some of the properties of water are described below. Which of them is/are not correct? (i) Water is known to be a universal solvent. (ii) Hydrogen bonding is present to a large extent in liquid water. (iii) There is no hydrogen bonding in the frozen state of water. (iv) Frozen water is heavier than liquid water.
Solution: Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers. In ice, there is a great deal of hydrogen bonding. Because of the empty spaces found in tetrahedrons generated by hydrogen bonding, ice is...
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct in the case of heavy water? (i) Heavy water is used as a moderator in a nuclear reactor. (ii) Heavy water is more effective as a solvent than ordinary water. (iii) Heavy water is more associated than ordinary water. (iv) Heavy water has a lower boiling point than ordinary water.
Solution: Option (i) and (iii) are the answers. Heavy water is a moderator in nuclear reactors. It has a greater boiling point than regular water. It is thus more associated than plain water....
Dihydrogen can be prepared on a commercial scale by different methods. In its preparation by the action of steam on hydrocarbons, a mixture of CO and H2 gas is formed. It is known as ____________. (i) Water-gas (ii) Syngas (iii) Producer gas (d) Industrial gas
Solution: Option (i) and (ii) are the answers. It is used to produce hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other products from hydrocarbons like natural gas. This is done in a reformer, which uses...
Which of the following statements are not true for hydrogen? (i) It exists as a diatomic molecule. (ii) It has one electron in the outermost shell. (iii) It can lose an electron to form a cation which can freely exist (iv) It forms a large number of ionic compounds by losing an electron
Solution: Option (iii) and (iv) are the answers. Because hydrogen has only one electron in its outermost shell, it can form diatomic molecules by covalent bonding. Its high ionisation enthalpy...
Only one element of ________ forms hydride. (i) group 6 (ii) group 7 (iii) group 8 (iv) group 9
Solution: Option (i) is the answer. Chromium (Cr), the single element in group 6, is capable of forming hydride. Because of their poor affinity for hydrogen, the other elements do not combine to...
Elements of which of the following group(s) of periodic table do not form hydrides. (i) Groups 7, 8, 9 (ii) Group 13 (iii) Groups 15, 16, 17 (iv) Group 14
Solution: Option (i) is the answer. The elements in groups 7, 8, and 9 have a low affinity for hydrogen, as a result of which they have little potential to combine with hydrogen to create...
Which of the following compounds is used for water softening? (i) Ca3 (PO4) (ii) Na3PO4 (iii) Na6P6O18 (iv) Na2HPO4
Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. Water softening is done with sodium hexametaphosphate (Calgon). Calgon interacts with calcium/magnesium salts in hard water to create inactive complex anions...
Which of the following ions will cause hardness in the water sample? (i) Ca2+ (ii) Na+ (iii) Cl– (iv) K+
Solution: Option (i) is the answer. Ca++ ions in the form of Ca(HCO3)2 or CaCl2 or CaSO4 causing hardness in water, or more specifically, soluble calcium salts, is possible.
Which of the following reactions is an example of use of water gas in the synthesis of other compounds? (i) CH4 (g) + H2O (g) → (1270KNi) CO (g) + H2 (g) (ii) CO (g) + H2O (g) → (Catalyst673K) CO2 (g) + H2 (g) (iii) CnH2n+2 + nH2O (g) → (1270KNi) nCO + (2n+1) H2 (iv) CO (g) + 2H2 (g) Cobalt → (Catalyst) CH3OH (l)
Solution: Option (iv) is the answer. The mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen is referred to as water gas. The term "synthesis gas" or "syngas" refers to the mixture of carbon monoxide and...
Hydrogen peroxide is obtained by the electrolysis of ______. (i) water (ii) sulphuric acid (iii) hydrochloric acid (iv) fused sodium peroxide
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. The simplest peroxide (oxygen-oxygen single bond) is hydrogen peroxide. It is an oxidizing agent utilized in many synthetic processes. In the industrial...
When sodium peroxide is treated with dilute sulphuric acid, we get ______. (i) sodium sulphate and water (ii) sodium sulphate and oxygen (iii) sodium sulphate, hydrogen and oxygen (iv) sodium sulphate and hydrogen peroxide
Solution: Option (iv) is the answer. In the reaction of sodium peroxide with dilute sulphuric acid, we obtain the byproduct sodium sulphate and hydrogen peroxide as a result.
Why does the water show a high boiling point as compared to hydrogen sulphide? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer: The presence of electronegative elements like oxygen, fluorine, and nitrogen causes particularly stable intermolecular hydrogen bonding (bonding with other molecules of the same or other...
Why is water molecule polar?
Answer: A polar molecule is one that has a charge distribution that is slightly positive on one side and slightly negative on the other. It is possible to increase polarity by increasing the...
With the help of suitable examples, explain the property of H2O2 that is responsible for its bleaching action?
Answer: H2O2, also known as hydrogen peroxide, is a powerful oxidizing agent that can be used in both acidic and basic conditions. Because of the release of nascent oxygen, it has the effect of...
An acidic solution of hydrogen peroxide behaves as an oxidising as well as the reducing agent. Illustrate it with the help of a chemical equation.
Answer: Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is an oxygen hydride with the chemical formula H2O2. It has the ability to serve as an oxidizing as well as a reducing agent in both acidic and basic mediums,...
Write the Lewis structure of hydrogen peroxide.
Answer: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule, as well as any lone pairs of electrons that may occur.
What is the importance of heavy water?
Answer: Heavy water is defined as water that contains a high concentration of heavy hydrogen (D2O). It is utilised as a moderator in nuclear reactors and exchange processes, and it is also employed...
The basic principle of a hydrogen economy is transportation and storage of energy in the form of liquid or gaseous hydrogen. Which property of hydrogen may be useful for this purpose? Support your answer with the chemical equation if required.
Answer: It is easier to transport because it is a liquid and consumes less volume than other forms of transportation. Consequently, the most fundamental attribute of hydrogen that is advantageous...
Why is the Ionisation enthalpy of hydrogen higher than that of sodium?
Answer: A valence electron from the H atom is harder to remove than from the Na atom because of the higher nuclear attraction, and hence more energy would be required. As a result, the ionization...
Hydrogen generally forms covalent compounds. Give reason.
Answer: Because hydrogen has just one electron in its outermost shell, it can either lose or gain an electron in order to achieve the noble gas configuration. Hydrogen has a high ionization...
Give reasons why hydrogen resembles alkali metals?
Answer: In its electronic form, hydrogen shares features with alkalis and halogens. Like alkali metals (ns1), hydrogen (1s1) has only one electron in its valence shell. So if they lose one electron,...
Rohan heard that instructions were given to the laboratory attendant to store a particular chemical i.e., keep it in the darkroom, add some urea in it, and keep it away from dust. This chemical acts as an oxidising as well as a reducing agent in both acidic and alkaline media. This chemical is important for use in the pollution control treatment of domestic and industrial effluents (i) Write the name of this compound. (ii) Explain why such precautions are taken for storing this chemical.
Answer: The compound hydrogen peroxide, which functions as both an oxidising and reducing agent in both acidic and alkaline conditions, is referred to as hydrogen peroxide. After coming into touch...
When the first element of the periodic table is treated with dioxygen, it gives a compound whose solid-state floats on its liquid state. This compound can act as an acid as well as a base. What products will be formed when this compound undergoes authorisation?
Answer: The first element, hydrogen, interacts with dioxygen to make water. Water is amphoteric, meaning it is both acid and basic. Water's solid state is ice. Due to its decreased density, it...
Explain why HCl is a gas and HF is a liquid.
Answer: In order to break the H-F bond, a large amount of energy must be expended in order to build a strong and stable hydrogen bond. As a result, the boiling point of HF is higher than that of...
Melting point, enthalpy of vapourisation and viscosity data of H2O and D2O is given below :Based on this data explain in which of these liquids intermolecular forces are stronger?
Answer: The values associated with the attributes of D2O are higher than those associated with H2O. As a result, we can conclude that the intermolecular forces in D2O are stronger.
(i) Draw the gas phase and solid phase structure of H2O2. (ii) H2O2 is a better oxidising agent than water. Explain.
Answer: i) The diagram shows the gas phase and solid phase structure of H2O2. ii) When the oxygen atom on H2O2 is reduced to -1, it is considered to be in an intermediate state of oxidation. Meaning...
Calculate the strength of 5 volume H2O2 solution.
Answer: $H_2O_2$ has a molar mass of 34gm and is a gas. According to this reaction, 2 moles of peroxide are involved, resulting in a total mass of 68g. We already know that 1mole of any gas occupies...
Write one chemical reaction for the preparation of 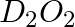
Answer: When $D_2SO_4$ interacts with $BaO_2, D_2O_2$ is generated, which is then followed by the formation of barium sulphate ($BaSO_4$). In the presence of $D_2SO_4 + BaO_2 → D_2O_2 +...
How is heavy water prepared? Compare its physical properties with those of ordinary water.
Answer: Heavy water, which is composed primarily of deuterium oxide (D2O), is produced primarily by the electrolysis of regular water. 1. Ordinary water has a molecular mass of 18.015 while heavy...
Molecular hydrides are classified as electron-deficient, electron precise and electron-rich compounds. Explain each type with two examples.
Answer: Molecular hydrides are classed as electron-deficient, electron-rich, or precise. B2H6 is an oxyhydroxide. They lack an octet. Generally, group 13 elements like B, Al, etc. create them. This...
Discuss briefly de-mineralisation of water by ion exchange resin.
Answer: Water is demineralized by passing it through anion and cation exchange resin. It has many of SO3H and COOH groups. A cation exchanger removes cations like Na+ and Mg+ from the water. OH-,...
What do you understand by the term ‘auto protolysis of water’? What is its significance?
Answer: Water that has undergone auto protolysis has undergone self ionisation. It is a chemical property of water that is important to understand. In this case, two identical molecules react to...
Complete the following equations. a) 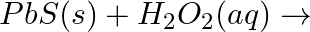 b)
b) 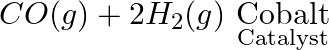
Answer: (i) $PbS (s) + H_2O_2 (aq) → PbSO_4 + 4H_2O$ This is a redox reaction. PbS (oxidation state -2) is oxidized to PbSO4 (oxidation state +6) and H2O2 by hydrogen peroxide (oxidation state of O...
If the same mass of liquid water and a piece of ice is taken, then why is the density of ice less than that of liquid water?
Answer: When water freezes, it expands, resulting in a volume of ice that is more than the volume of the water for the same quantity of water. We can state that ice has a lower density than water...
What are metallic/interstitial hydrides? How do they differ from molecular hydrides?
Answer: Heat conductivity and electrical conductivity of metal hydrides are quite high, while the conductivity and electrical conductivity of molecular hydrides are extremely low. Metallic hydrides...
How can production of hydrogen from water gas be increased by using water gas shift reaction?
Answer: It is necessary to apply the water shift gas process in the generation of synthesis gas (a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide). CO is transformed to CO2 in this...
Hydrogen peroxide is _________. (i) an oxidising agent (ii) a reducing agent (iii) both an oxidising and a reducing agent (iv) neither oxidising nor reducing agent
Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. It is also known as dioxide or peroxide. It has a mild odor and is colorless in solution. With a stabilizer, it is non-flammable and somewhat acidic. An...
Which of the following equations depict the oxidising nature of 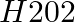 ? (i)
? (i) 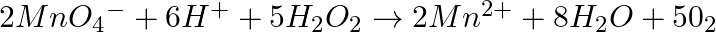 (ii)
(ii) 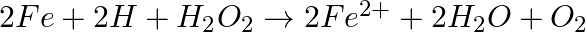 (iii)
(iii) 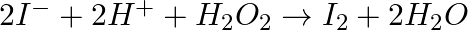 (iv)
(iv) 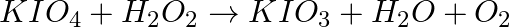
Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. The oxidising characteristic of $H _2 O _2$ indicates that it oxidises other substances while simultaneously reducing itself. In such reactions, $O _2$ does not...
The oxide that gives H2O2 on treatment with dilute H2SO4 is — (i) PbO2 (ii) BaO2 .8H2O + O2 (iii) MnO2 (iv) TiO2
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. The oxide that gives $H _{2} O _{2}$ on treatment with dilute $H _{2} SO _{4}$ is $BaO _{2} \cdot 8 H _{2} O$....
Consider the reactions (A) H2O2 + 2HI → I2 + 2H2O (B) HOCl + H2O2 → H3O++ Cl–+ O2 Which of the following statements is correct about H2O2 with reference to these reactions? Hydrogen peroxide is ________. (i) an oxidising agent in both (A) and (B) (ii) an oxidising agent in (A) and reducing agent in (B) (iii) a reducing agent in (A) and oxidising agent in (B) (iv) a reducing agent in both (A) and (B)
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. (A) $H_2O_2 + 2HI → I_2 + 2H_2O$ Iodine undergoes oxidation, transitioning from the -1 oxidation state to the 0 oxidation state. As a result, H2O2 works as an...
Radioactive elements emit α, β and γ rays and are characterised by their halflives. The radioactive isotope of hydrogen is (i) Protium (ii) Deuterium (iii) Tritium (iv) Hydronium
Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. The concentration of tritium is approximately one atom per $10^18$ atoms of protium in the sample. Only tritium is radioactive and emits low-energy beta...
Which of the following hydrides is electron-precise hydride? (i) B2H6 (ii) NH3 (iii) H2O (iv) CH4
Solution: Option (iv) is the answer. The hydrides indicate an anion form of hydrogen atoms. ...
Metal hydrides are ionic, covalent or molecular in nature. Among LiH, NaH, KH, RbH, CsH, the correct order of increasing ionic character is (i) LiH > NaH > CsH > KH>RbH (ii) LiH < NaH < KH < RbH CsH > NaH > KH > LiH (iv) NaH > CsH > RbH > LiH > KH
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. As we advance down the group, the ionic nature rises. As ionisation enthalpy drops from top to bottom in a group, metal tends to lose electron. So ionic...
Why does H+ ion always get associated with other atoms or molecules? (i) Ionisation enthalpy of hydrogen resembles that of alkali metals. (ii) Its reactivity is similar to halogens. (iii) It resembles both alkali metals and halogens. (iv) Loss of an electron from hydrogen atom results in a nucleus of very small size as compared to other atoms or ions. Due to the small size, it cannot exist free.
Solution: Option (iv) is the answer. Hydrogen has one electron in its s orbital and like alkali metals, it can lose one electron from its outer shell. So hydrogen is like alkalis. Onions reacting...
Hydrogen resembles halogens in many respects for which several factors are responsible. Of the following factors which one is most important in this respect? (i) Its tendency to lose an electron to form a cation. (ii) Its tendency to gain a single electron in its valence shell to attain stable electronic configuration. (iii) Its low negative electron gain enthalpy value. (iv) Its small size.
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. Hydrogen, like halogens, prefers to gain an electron to achieve a stable noble gas structure. Hydrogen's electrical configuration is 1s. The electrical...
The exhibition of the highest co-ordination number depends on the availability of vacant orbitals in the central atom. Which of the following elements is not likely to act as a central atom in MF6 3–? (i) B (ii) Al (iii) Ga (iv) In
Option I is the correct response.
A string of mass 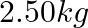 is under a tension of
is under a tension of 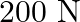 . The length of the stretched string is
. The length of the stretched string is 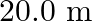 . If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
Mass of the string is given as $M=2.50 kg$ Tension in the string is given as $T=200 N$ Length of the string is given as $\mid=20.0 m$ Mass per unit length will be, $\mu=\mathrm{M} / \mathrm{I}=5 /...
A vessel of 120 mL limit contains a specific measure of gas at 35°C and 1.2 bar pressure. The gas is moved to one more vessel of volume 180 mL at 35°C. What might be its tension?
Solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} ~P1\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }bar \\ P2\text{ }=\text{ }? \\ ~V1=\text{ }500\text{ }dm3 \\ V2=200\text{ }dm3 \\ \end{array}\] As temperature stays steady at...
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 at 30°C?
Solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} ~P1\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }bar \\ P2\text{ }=\text{ }? \\ ~V1=\text{ }500\text{ }dm3 \\ V2=200\text{ }dm3 \\ \end{array}\] As temperature stays steady at...
A mild steel wire of cross-sectional area 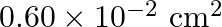 and length
and length 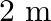 is stretched ( not beyond its elastic limit ) horizontally between two columns. If a
is stretched ( not beyond its elastic limit ) horizontally between two columns. If a 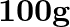 mass is hung at the midpoint of the wire, find the depression at the midpoint.
mass is hung at the midpoint of the wire, find the depression at the midpoint.
Solution: Let $Y Z$ be a mild steel wire with a cross sectional area of $A=0.60 \times 10^{-2} cm^{2}$ and a length of 2m. As indicated in the image, a mass of $m=100g=0.1kg$ is hanged from the...
Two strips of metal are riveted together at their ends by four rivets, each of diameter 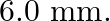 What is the maximum tension that can be exerted by the riveted strip if the shearing stress on the rivet is not to exceed
What is the maximum tension that can be exerted by the riveted strip if the shearing stress on the rivet is not to exceed  Pa? Assume that each rivet is to carry one-quarter of the load.
Pa? Assume that each rivet is to carry one-quarter of the load.
Diameter of the metal strips is given as $6 \mathrm{~mm}=6 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}$ Radius will be then, $r=3 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}$ Shearing stress on the rivet is given as $6.9 \times...
A rod of length 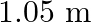 having negligible mass is supported at its ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional areas of wires
having negligible mass is supported at its ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths as shown in the figure. The cross-sectional areas of wires 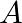 and
and 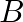 are
are 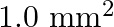 and
and 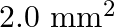 , respectively. At what point along the rod should a mass
, respectively. At what point along the rod should a mass 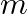 be suspended in order to produce (a) equal stresses and (b) equal strains in both steel and aluminium wires.
be suspended in order to produce (a) equal stresses and (b) equal strains in both steel and aluminium wires.
Solution: Cross-sectional area of wire A is given as $a_{1}=1.0 \mathrm{~mm}^{2}=1.0 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~m}^{2}$ Cross-sectional area of wire B is given as $a_{2}=2 m m^{2}=2 \times 10^{-6}...
Anvils made of single crystals of diamond, with the shape as shown in the figure, are used to investigate the behaviour of materials under very high pressures. Flat faces at the narrow end of the anvil have a diameter of 0.50 mm, and the wide ends are subjected to a compressional force of 50,000 N. What is the pressure at the tip of the anvil?
The diameter of the flat faces at the narrow end of the anvil is given as, $d=0.50mm=0.5\times 10^{-3} m$ Radius will be, $r=d/2=0.25\times 10^{-3} m$ Compressional force is given as $F=50000N$...
How much should the pressure on a litre of water be changed to compress it by 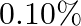 ?
?
Volume of water is given as $V=1$ litre Water should be compressed by $0.10 \%$ is given The fractional change in volume will be, $\Delta \mathrm{V} N=(0.1 / 100) \times 1=10^{-3}$ Bulk modulus,...
What is the density of water at a depth where pressure is 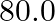 atm, given that its density at the surface is
atm, given that its density at the surface is 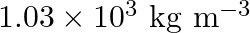 ?
?
Let the depth be 'd' Pressure at the given depth is given as $p=60\times1.01\times10^{5}Pa$ Density of water at the surface is given as $\rho_{1}=1.03\times10^{3}$ $kg$ $m^{3}$ Let $\rho_{2}$ be the...
A rigid bar of mass 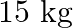 is supported symmetrically by three wires each
is supported symmetrically by three wires each 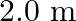 long. Those at each end are of copper and the middle one is of iron. Determine the ratios of their diameters if each is to have the same tension.
long. Those at each end are of copper and the middle one is of iron. Determine the ratios of their diameters if each is to have the same tension.
The extension of each wire will be the same because the stress on the wires is the same. Now that the wires are the same length, the tension on them will be the same. Now, we know: $Y=Stress /...
A steel cable with a radius of 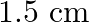 supports a chairlift at a ski area. If the maximum stress is not to exceed
supports a chairlift at a ski area. If the maximum stress is not to exceed 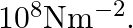 What is the maximum load the cable can support?
What is the maximum load the cable can support?
Radius of the steel cable is given as $r=1.5 \mathrm{~cm}=0.015 \mathrm{~m}$ Cross-sectional area of the cable will be, $\pi r^{2}=3.14 \times(0.015)^{2}$ $=7.06 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}$ Maximum...
Four identical hollow cylindrical columns of mild steel support a big structure of a mass 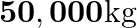 . The inner and outer radii of each column are
. The inner and outer radii of each column are 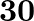 and
and 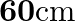 respectively. Assuming the load distribution to be uniform, calculate the compressional strain of each column.
respectively. Assuming the load distribution to be uniform, calculate the compressional strain of each column.
Mass of the big structure is given as $M=50,000 \mathrm{~kg}$ Total force exerted on the four columns will be equal to the total weight of the structure, that is, $50000 \times 9.8 \mathrm{~N}$ The...
The edge of an aluminium cube is 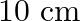 long. One face of the cube is firmly fixed to a vertical wall. A mass of
long. One face of the cube is firmly fixed to a vertical wall. A mass of 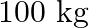 is then attached to the opposite face of the cube. The shear modulus of aluminium is
is then attached to the opposite face of the cube. The shear modulus of aluminium is 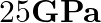 . What is the vertical deflection of this face?
. What is the vertical deflection of this face?
Edge of the aluminium cube is given as $L=10 \mathrm{~cm}=10 / 100=0.1 \mathrm{~m}$ Area of each face wil be, $A=(0.1)^{2}=0.01 \mathrm{~m}^{2}$ Mass attached to the opposite face of the cube is...
Two wires of diameter 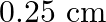 , one made of steel and the other made of brass are loaded as shown in Fig. The unloaded length of steel wire is
, one made of steel and the other made of brass are loaded as shown in Fig. The unloaded length of steel wire is 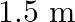 and that of brass wire is
and that of brass wire is 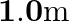 . Compute the elongations of the steel and the brass wires. [Young’s modulus of steel is
. Compute the elongations of the steel and the brass wires. [Young’s modulus of steel is 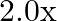
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left.10^{11} \mathrm{~Pa} .\left(1 \mathrm{~Pa}=1 \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~m}^{2}\right)\right]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-36c8cbb599d2f5fc96ae57f00cbbd2ee_l3.png)
Diameter of the two wires is given as $d=0.25 \mathrm{~m}$ Radius of the wires is given as $r=d / 2=0.125 \mathrm{~cm}$ Unloaded length of the steel wire is given as $l_{1}=1.5 \mathrm{~m}$ Unloaded...
The stress-strain graphs for materials  and
and  are shown in the figure below.
are shown in the figure below.
(a) Which of the materials has the greater Young's modulus? (b) Which of the two is the stronger material? Solution: (a) We can observe from the graphs that for a given strain, $A$ has a higher...
A steel wire of length 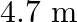 and cross-sectional area
and cross-sectional area 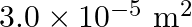 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length
stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 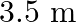 and cross-sectional area of
and cross-sectional area of 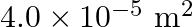 under a given load. What is the ratio of Young’s modulus of steel to that of copper?
under a given load. What is the ratio of Young’s modulus of steel to that of copper?
Length of the steel wire is given as $l_{1}=4.7 \mathrm{~m}$ Cross-sectional area of the steel wire is given as $a_{1}=3.0 \times 10^{-5} \mathrm{~m}^{2}$ Length of the copper wire is given as...
On a frictionless track, a trolley moves with a speed of 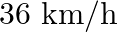 with a mass of
with a mass of 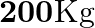 . A child whose mass is 20 kg runs on the trolley with a speed of
. A child whose mass is 20 kg runs on the trolley with a speed of 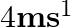 from one end to other which is
from one end to other which is 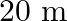 . The speed is relative to the trolley in the direction opposite to its motion. Find the final speed of the trolley and the distance the trolley moved from the time the child began to run.
. The speed is relative to the trolley in the direction opposite to its motion. Find the final speed of the trolley and the distance the trolley moved from the time the child began to run.
Mass is given as $m=200 \mathrm{Kg}$ Speed is given as $v=36 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ Mass of boy is given as $=20 \mathrm{Kg}$ Initial momentum will be, $(M+m) v$...
A bolt of mass 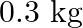 falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down with a uniform speed of
falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down with a uniform speed of 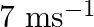 . It hits the floor of the elevator (length of elevator
. It hits the floor of the elevator (length of elevator 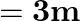 ) and does not rebound. What is the heat produced by the impact? Would your answer be different if the elevator were stationary?
) and does not rebound. What is the heat produced by the impact? Would your answer be different if the elevator were stationary?
Mass of the bolt is given as $m=0.3 \mathrm{~kg}$ Potential energy of the bolt is given as $m g h=0.3 \times 9.8 \times 3=8.82\rfloor$ The bolt does not return to its original position. As a result,...
A 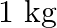 block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of spring constant 100
block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of spring constant 100 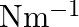 as shown in Fig. The block is released from rest with the spring in the unstretched position. The block moves
as shown in Fig. The block is released from rest with the spring in the unstretched position. The block moves  down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of friction between the block and the incline. Assume that the spring has a negligible mass and the pulley is frictionless.
down the incline before coming to rest. Find the coefficient of friction between the block and the incline. Assume that the spring has a negligible mass and the pulley is frictionless.
Solution: Spring constant is given as $\mathrm{k}=100 \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~m}^{m}$ Displacement in the block is given as $\mathrm{x}=10 \mathrm{~cm}=0.1 \mathrm{~m}$ At equilibrium: Normal reaction...
A bullet of mass 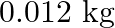 and horizontal speed
and horizontal speed 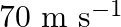 strikes a block of wood of mass
strikes a block of wood of mass 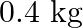 and instantly comes to rest with respect to the block. The block is suspended from the ceiling by means of thin wires. Calculate the height to which the block rises. Also, estimate the amount of heat produced in the block.
and instantly comes to rest with respect to the block. The block is suspended from the ceiling by means of thin wires. Calculate the height to which the block rises. Also, estimate the amount of heat produced in the block.
Mass of the bullet is given as $m_{1}=0.012 \mathrm{~kg}$ Initial speed of the bullet is given as $u_{1}=70 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ Mass of the wooden block is given as $m_{2}=0.4 \mathrm{~kg}$...
A person trying to lose weight (dieter) lifts a 10 kg mass, one thousand times, to a height of 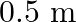 each time. Assume that the potential energy lost each time she lowers the mass is dissipated. (a) How much work does she do against the gravitational force? (b) Fat supplies
each time. Assume that the potential energy lost each time she lowers the mass is dissipated. (a) How much work does she do against the gravitational force? (b) Fat supplies 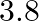
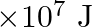 of energy per kilogram which is converted to mechanical energy with a
of energy per kilogram which is converted to mechanical energy with a 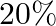 efficiency rate. How much fat will the dieter use up?
efficiency rate. How much fat will the dieter use up?
Mass is given as $\mathrm{m}=10 \mathrm{~kg}$ Height to which the mass is lifted is given as $h=0.5 \mathrm{~m}$ Number of times is hiven as $n=1000$ (a) Work done against gravitational force can be...
A body of mass 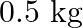 travels in a straight line with velocity
travels in a straight line with velocity 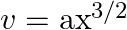 where
where 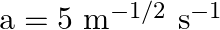 . What is the work done by the net force during its displacement from
. What is the work done by the net force during its displacement from 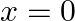 to
to 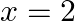 m?
m?
Let the mass of the body be $m$ $m=0.5 \mathrm{~kg}$ Velocity of the body is represented by $v=a x^{3 / 2}$ where, $a=5 \mathrm{~m}^{-1 / 2} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$. Initial velocity at $x=0$ will be...
The bob of a pendulum is released from a horizontal position. If the length of the pendulum is 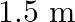 , what is the speed with which the bob arrives at the lowermost point, given that it dissipated
, what is the speed with which the bob arrives at the lowermost point, given that it dissipated 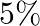 of its initial energy against air resistance?
of its initial energy against air resistance?
Length of the pendulum is given as $\mid=1.5 \mathrm{~m}$ Potential of the bob at the horizontal position is given as $=m g h=m g \mid$ When the bob goes from the horizontal position to the lowest...
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table is hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed 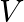 . If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?
. If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?
Solution: The mass of the ball bearing is given as $\mathrm{m}$ Before the collision, Total Kinetic Energy of the system will be $=1 / 2 m v^{2}+0=1 / 2 m v^{2}$ After the collision, Total Kinetic...
A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with speed 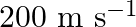 and angle
and angle 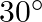 with the normal, and rebounds with the same speed. Is momentum conserved in the collision? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
with the normal, and rebounds with the same speed. Is momentum conserved in the collision? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
For an elastic or inelastic collision, momentum is always preserved. The molecule approaches and rebounds with the same speed of $200 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. $u=v=200 \mathrm{~m}...
An electron and a proton are detected in a cosmic ray experiment, the first with kinetic energy 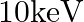 , and the second with
, and the second with 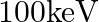 . Which is faster, the electron or the proton? Obtain the ratio of their speeds. (electron mass
. Which is faster, the electron or the proton? Obtain the ratio of their speeds. (electron mass 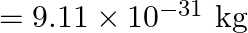 , proton mass
, proton mass 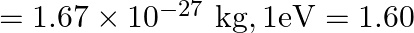
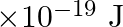 )
)
Electron mass is given as $m_{e}=9.11 \times 10^{-31} \mathrm{~kg}$ Proton mass is given as $m_{p}=1.67 \times 10^{-27} \mathrm{~kg}$ Electron's kinetic energy can be calculated as...
A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of constant power. Its dis placement in time t is proportional to
(i) 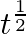
(ii) 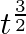
(iii) 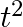
(iv) 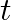
Power is given by, $P=F V$ $=\operatorname{mav}=\operatorname{mv} \frac{d v}{d t}$ vdv $=\frac{k}{m} \mathrm{dt}$ On integration, we get, 10 $\frac{v^{2}}{2}=\frac{k}{m} d t$...
Answer carefully, with reasons :
(a) In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
Is the total linear momentum conserved during the short time of an inelastic collision of two balls?
(b) If the potential energy of two billiard balls depends only on the separation distance between their centres, is the collision elastic or inelastic? (Note, we are talking here of potential energy corresponding to the force during a collision, not gravitational potential energy).
(a) In an inelastic collision, there will be a loss of kinetic energy. After a collision, the K.E is always lower than the K.E before the impact. In an inelastic collision, the system's total linear...
State if each of the following statements is true or false. Give reasons for your answer
(a) Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
(b) In an inelastic collision, the final kinetic energy is always less than the initial kinetic energy of the system.
(a) False. The work done by the conservative force on the moving body in a closed loop is zero. (b) True
Underline the correct alternative:
(a) The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the external force/sum of the internal forces on the system
(b) In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision is the total kinetic energy/total linear momentum/total energy of the system of two bodies.
(a) External force Internal forces, regardless of their direction, cannot cause a change in momentum. As a result, the change in total momentum is proportional to the system's external force. (b)...
Underline the correct alternative:
(a) When a conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body increases/decreases/remains unaltered.
(b) Work done by a body against friction always results in a loss of its kinetic/potential energy.
(a) Decreases When a body is displaced in the direction of the force, the conservative force does positive work on it, causing the body to migrate to the center of force. As a result, the distance...
Answer the following:
(a) An artificial satellite orbiting the earth in a very thin atmosphere loses its energy gradually due to dissipation against atmospheric resistance, however small. Why then does its speed increase progressively as it comes closer and closer to the earth?(b) In the Figure, the man walks 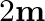 carrying a mass of
carrying a mass of 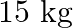 on his hands. In Fig., he walks the same distance pulling the rope behind him. The rope goes over a pulley, and a mass of
on his hands. In Fig., he walks the same distance pulling the rope behind him. The rope goes over a pulley, and a mass of 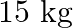 hangs at its other end. In which case is the work done greater?
hangs at its other end. In which case is the work done greater?
Solution: (a) As the satellite approaches the Earth, its potential energy drops, and since the system's total energy should remain constant, the kinetic energy increases. As a result, the...
The potential energy function for a particle executing linear simple harmonic motion is given by 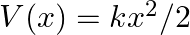 , where
, where 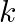 is the force constant of the oscillator. For
is the force constant of the oscillator. For 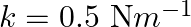 , the graph of
, the graph of 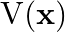 versus
versus 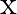 is shown in Figure. Show that a particle of total energy
is shown in Figure. Show that a particle of total energy 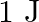 moving under this potential must ‘turn back’ when it reaches
moving under this potential must ‘turn back’ when it reaches 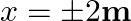 .
.
Solution: Energy of the particle will be, $\mathrm{E}=1 \mathrm{~J}$ $\mathrm{K}=0.5 \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~m}^{-1}$ $\mathrm{K} . \mathrm{E}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{mv}^{2}$ Based on law of conservation...
Given in Figure, are examples of some potential energy functions in one dimension. The total energy of the particle is indicated by a cross on the ordinate axis. In each case, specify the regions, if any, in which the particle cannot be found for the given energy. Also, indicate the minimum total energy the particle must have in each case. Think of simple physical contexts for which these potential energy shapes are relevant.
(a) (b) The total energy is given by the relation, $E=K . E .+P . E$. So, $K_{. E}=E-P . E .$ There can never be a negative amount of kinetic energy. In the region where K.E. becomes negative, the...
A body of mass 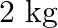 initially at rest moves under the action of an applied horizontal force of
initially at rest moves under the action of an applied horizontal force of 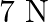 on a table with the coefficient of kinetic friction
on a table with the coefficient of kinetic friction 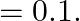 Compute the
Compute the
(a) work done by the net force on the body in 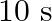 ,
,
(b) change in kinetic energy of the body in 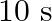 .
.
Mass of the body is given as $2 \mathrm{~kg}$ Horizontal force applied is given as $7 \mathrm{~N}$ Coefficient of kinetic friction is given as $0.1$ Acceleration produced by the applied force can be...
The sign of work done by a force on a body is important to understand. State carefully if the following quantities are positive or negative:
Work done by the resistive force of air on a vibrating pendulum in bringing it to rest.
Work completed is negative. It is noticed that the bob's orientation and the air resistance acting on it are in different directions.
The sign of work done by a force on a body is important to understand. State carefully if the following quantities are positive or negative:
(a) work done by friction on a body sliding down an inclined plane,
(b) work done by an applied force on a body moving on a rough horizontal plane with uniform velocity
(a) The direction of motion of the object is opposite the direction of the frictional force, as can be seen. As a result, the work completed is negative. (b) The frictional force acting on an object...
Assertion (A): The black body is an ideal body that emits and absorbs radiations of all frequencies. Reason (R): The frequency of radiation emitted by a body goes from a lower frequency to higher frequency with an increase in temperature.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the explanation of A. (iii) A is true and R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false. ...
Assertion (A): It is impossible to determine the exact position and exact the momentum of an electron simultaneously. Reason (R): The path of an electron in an atom is clearly defined.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true and R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false....
Assertion (A): All isotopes of a given element show the same type of chemical behaviour. Reason (R): The chemical properties of an atom are controlled by the number of electrons in the atom.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true but R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false....
Match species are given in Column 1 with the electronic configuration given in Column 2.
Column 1 Column 2 (i) Cr (a) [Ar]3d84s0 (ii) Fe2+ (b) [Ar]3d104s1 (iii) Ni2+ (c) [Ar]3d64s0 (iv) Cu (d) [Ar] 3d54s1 (e) [Ar]3d64s2 Column 1 Column 2 (i) Cr (d) [Ar]...
Match the following
Column 1 Column 2 (i) Photon (a)Value is 4 for N shell (ii) Electron (b)Probability density (iii) ψ2 (c)Always a positive value (iv) The principal quantum number n (d)Exhibits both momentum...
Match the following
Column 1 Column 2 (i) X-rays (a) ν = 100-0 104 Hz (ii) UV (b) ν = 1010Hz (iii) Long radio waves (c) ν = 1016 Hz (iv) Microwave (d) ν = 1018Hz Column 1 Column 2 (i) X-rays (d) ν = 1018Hz (ii) UV...
Match the following
Rule Principle (i) Hund’s Rule (a) No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. (ii) Aufbau Principle (b) Half-filled and filled orbitals have extra stability....
Match the quantum numbers with the information provided by these Quantum number Information provided
Column 1 Column 2 (i) Principal quantum number (a) orientation of the orbital (ii) Azimuthal quantum number (b) energy and size of orbital (iii) Magnetic quantum number (c) spin of an electron (iv)...
Match the following species with their corresponding ground state electronic configuration.
Atom / Ion Electronic configuration (i) Cu (a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 (ii) Cu2+ (b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 (iii) Zn2+ (c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 (iv) Cr3+ (d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d9 (e) 1s2...
The hydrogen atom has only one electron, so mutual repulsion between electrons is absent. However, in multielectron atoms mutual repulsion between the electrons is significant. How does this affect the energy of an electron in the orbitals of the same principal quantum number in multielectron atoms?
Hydrogen atom has only one electron, so the mutual repulsion between the electrons is non-existent. However, in multielectron atoms the interaction between electrons is important. This is because,...
The effect of the uncertainty principle is significant only for the motion of microscopic particles and is negligible for the macroscopic particles. Justify the statement with the help of a suitable example.
The uncertainty principle is applicable only for microscopic particles and can be concluded from the uncertainty measurement. Example: Take a particle of mass = 1 milligram ∆x. ∆ν = 60626*10-34/...
Table-tennis ball has a mass 10 g and a speed of 90 m/s. If speed can be measured within an accuracy of 4% what will be the uncertainty in speed and position?
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle: ∆x. ∆p ≥ h/4π Mass of the ball = 4 g Speed is = 90 m /s Uncertainity of speed, ∆v = 4/100 × 90 ∆v = 3.6 m/s ∆x = h/4πm∆v ∆x = 6.26 × 10-34 / 4 × 3.14...
What is the difference between the terms orbit and orbital?
Orbit represents a clear circular path for electrons to surround the nucleus. Represents the two-dimensional movement of electrons around the nucleus, the orbital is not that well defined because it...
Chlorophyll present in green leaves of plants absorbs light at 4.620 × 1014 Hz. Calculate the wavelength of radiation in nanometer. Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does it belong to?
The relationship between the wavelength and the frequency: λ = c/ν c - Velocity of light v - Frequency of the radiation. λ = 3 x 108 ms-1 / 4.620 x 1014 Hz Hence, λ = 0.6494...
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is shown in Figure. Find out the wavelength of the radiation.
Distance between the two identical successive points in a wave is called the wavelength. Given, In the hypothetical wave, Wavelength, λ = 4 × 2.16 pm Hence, Wavelength, λ = 8.64 pm.
Out of electron and proton which one will have, a higher velocity to produce matter waves of the same wavelength? Explain it.
The electron which is a lighter particle will have the higher velocity and will also produce matter waves having the same wavelength. This is because, if the mass is less, then the velocity increases.
What is the experimental evidence in support of the idea that electronic energies in an atom are quantized?
The bright line spectrum shows that the atomic energy levels are measured. These lines are found to be the result of electronic transitions between energy and the atomic spectrum would have shown...
According to de Broglie, the matter should exhibit dual behavior that is both particle and wave-like properties. However, a cricket ball of mass 100 g does not move like a wave when it is thrown by a bowler at a speed of 100 km/h. Calculate the wavelength of the ball and explain why it does not show wave nature.
Calculation: Given, Mass, m = 100g / 0.1kg Velocity = 100km/h Velocity =100×1000 / 60×60 Velocity = 1000/36m/s λ =h/mν λ = 2.387 × 10-34 m
The Balmer series in the hydrogen spectrum corresponds to the transition from n1 = 2 to n2 = 3,4,………. This series lies in the visible region. Calculate the wavenumber of the line associated with the transition in Balmer series when the electron moves to n = 4 orbit. (RH= 109677 cm-1)
Calculation: According to Bohr’s model for the hydrogen atom; ν = RH(1/n12-1/ n22)cm-1 Given, n1 = 2 n2 = 4 H (Rydberg’s constant) = 109677 Wave number = 109677 ( ¼-1/16) Hence, Wave number =...
The electronic configuration of the valence shell of Cu is 3d10 4s1 and not 3d94s2. How is this configuration explained?
Great stability is established to the orbitals which are half or completely filled. In the given electronic configuration 3d104s1 of Copper (Cu), the stability is assured (d orbitals - filled, s...
Wavelengths of different radiations are given below :
λ(A) = 300 nm λ(B) = 300 μm λ(c) = 3 nm λ (D) 30 A° Arrange these radiations in the increasing order of their energies. Given, λ(A) = 300 nm λ(A) = 300 x 10-9 m λ(A) = 3 x 10 -7 m λ(B)...
An atom having atomic mass number 13 has 7 neutrons. What is the atomic number of the atom?
Calculation: Atomic mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons Number of protons = atomic mass number – number of neutrons. Hence, atomic number of an atom = 13 – 7 = 6.
Which of the following will not show deflection from the path on passing through an electric field? Proton, cathode rays, electron, neutron
Neutron shows no deflection from the path passing through the electric field. This is due to the neutrality of neutron particles. Therefore, it has no charge and is not affected by any electrical...
The arrangement of orbitals based on energy is based upon their (n+l ) value. Lower the value of (n+l ), lower is the energy. For orbitals having the same values of (n+l), the orbital with a lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy (a) 1s, 2s, 3s, 2p (b) 4s, 3s, 3p, 4d (c) 5p, 4d, 5d, 4f, 6s (d) 5f, 6d, 7s, 7p Based upon the...
Calculate the total number of angular nodes and radial nodes present in 3p orbital.
The region where the probability of finding the electrons is zero, it is considered as the nodes and is it present among the orbitals. Example: In the np orbitals, Nodes = n – l – 1 Nodes = 3 –1 – 1...
Which of the following orbitals are degenerate? 3dxy, 4dxy, 3dz2 , 3dyx, 4dyx, 4dzz
The electron energy in a multielectron atom, in contrast to the hydrogen atom, depends not only on its quantum number, but also on its azimuthal quantum number. The same electron shells and the same...
Nickel atom can lose two electrons to form Ni2+ ion. The atomic number of nickel is 28. From which orbital will nickel lose two electrons.
1 Ni atom = 28 electrons and its electronic configuration is 4s2 3d8 It turns to Ni2+ by losing 2 electrons and its electronic configuration becomes 4s0 3d8 According to the Aufbau principle, Ni...
Show the distribution of electrons in oxygen atom (atomic number 8) using orbital diagram.
Distribution of electrons in oxygen atom: 1s22s22p4
Arrange s, p and d sub-shells of a shell in the increasing order of effective nuclear charge (Zeff) experienced by the electron present in them.
Arrangement of the subshells: d<p<s The s-orbitals shield the electrons a lot more when compared to the p-orbitals from the nucleus.
Which of the following statements concerning the quantum numbers are correct?
(i) The angular quantum number determines the three-dimensional shape of the orbital. (ii) The principal quantum number determines the orientation and energy of the orbital. (iii) The magnetic...
In which of the following pairs, the ions are iso-electronic?
(i) Na+, Mg2+ (ii) Al3+, O– (iii) Na+, O2- (iv) N3-, Cl– Correct Answers: (i) Na+, Mg2+ (iii) Na+, O2- Explanation: Isoelectronic species are the atoms / ions that has the same number...
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers is correct? n l m n l m
(i) 1 1 +2 (ii) 2 1 +1 (iii) 3 2 –2 (iv) 3 4 –2 Correct Answers: (ii) 2 1 +1 (iii) 3 2 –2 Explanation: The correct sets of quantum numbers are, n = 2, l = 1, m = +1 n = 3, l = 2, m =...
Out of the following pairs of electrons, identify the pairs of electrons present in degenerate orbitals :
(i) (a) n = 3, l = 2, ml = –2, ms= − ½ (b) n = 3, l = 2, ml = –1, ms= − 1/2 (ii) (a) n = 3, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = + ½ (b) n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = +1/2 (iii) (a) n = 4, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +...
Identify the pairs which are not of isotopes?
(i) 6X12, 6Y13 (ii) 17X35, 6Y37 (iii) 6X14, 7Y14 (iv) 4X8, 5Y8 Correct Answers: (iii) 6X14, 7Y14 (iv) 4X8, 5Y8 Explanation: Isotopes are the atoms having same atomic number but...
If travelling at the same speeds, which of the following matter waves have the shortest wavelength?
(i) Electron (ii) An alpha particle (He2+) (iii) Neutron (iv) Proton Correct Answer: (ii) An alpha particle (He2+) Explanation: According to de Broglie's equation, the alpha particles...
For the electrons of an oxygen atom, which of the following statements is correct?
(i) Zeff for an electron in a 2s orbital is the same as Zeff for an electron in a 2p orbital. (ii) An electron in the 2s orbital has the same energy as an electron in the 2p orbital. (iii) Zeff for...
The pair of ions having same electronic configuration is __________.
(i) Cr3+, Fe3+ (ii) Fe3+, Mn2+ (iii) Fe3+, Co3+ (iv) Sc3+, Cr3+ Correct Answer: (ii) Fe3+, Mn2+ Explanation: Fe - Z=26 : 3d64s2 Fe3+- 3d5 Mn - Z=25 : 3d54s2 Mn2+ : 3d5 Hence,...
Orbital angular momentum depends on __________.
(i) l (ii) n and l (iii) n and m (iv) m and s Correct Answer: (i) l Explanation: Orbital angular momentum depends on the value of l which is referred to as the azimuthal quantum number.
A total number of orbitals associated with the third shell will be __________.
(i) 2 (ii) 4 (iii) 9 (iv) 3 Correct Answer: (iii) 9 Explanation: The total number of orbitals in nth shell = n2 Hence, the total number of orbitals associated with the third shell will...
Which of the following is responsible to rule out the existence of definite paths or trajectories of electrons? (i) Pauli’s exclusion principle. (ii) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. (iii) Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity. (iv) Aufbau principle.
Correct Answer: (ii) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Explanation: The Heisenberg's uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know the exact position and speed of an object...
Number of angular nodes for 4d orbital is __________.
(i) 4 (ii) 3 (iii) 2 (iv) 1 Correct Answer: (iii) 2 Explanation: The Number of angular nodes = l (azimuthal quantum number) Hence, the number of angular nodes for 4d orbital is...
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is __________.
(i) 3 (ii) 4 (iii) 2 (iv) 1 Correct Answer: (iv) 1 Explanation: Number of radial nodes for 3p orbital = 3−1−1 Number of radial nodes for 3p orbital = 3−2 Number of radial nodes for 3p...
Two atoms are said to be isobars if.
(i) they have the same atomic number but a different mass number. (ii) they have the same number of electrons but a different number of neutrons. (iii) they have the same number of neutrons but a...
Which of the following properties of an atom could be explained correctly by Thomson Model of an atom?
(i) Overall neutrality of atom. (ii) Spectra of a hydrogen atom. (iii) Position of electrons, protons and neutrons in an atom. (iv) Stability of atom. Correct Answer: (i) Overall...
Which of the following statements about the electron is incorrect?
(i) It is a negatively charged particle. (ii) The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron. (iii) It is a basic constituent of all atoms. (iv) It is a constituent of cathode rays....
Which of the following statement is not correct about the characteristics of cathode rays?
(i) They start from the cathode and move towards the anode. (ii) They travel in a straight line in the absence of an external electrical or magnetic field. (iii) Characteristics of cathode rays do...
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region. Based on the above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect? (i) 1s and 2s...
Which of the following options does not represent ground state electronic configuration of an atom?
(i) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2 (ii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 4s2 (iii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 (iv) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s1 Correct Answer: (ii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 4s2...
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α -particle scattering experiment?
(i) Most of the space in the atom is empty. (ii) The radius of the atom is about 10–10 m while that of a nucleus is 10–15 m. (iii) Electrons move in a circular path of fixed energy called orbits....
A box contains some identical red coloured balls, labelled as A, each weighing 2 grams. Another box contains identical blue coloured balls, labelled as B, each weighing 5 grams. Consider the combinations AB, AB2, A2B and A2B3 and show that the law of multiple proportions is applicable.
AB ab2 A,B A2B3 Mass of A (in g) 2 2 4 415 Mass of B (in g) 5 10 5 According to the law of multiple proportions, Masses of B combines with a constant mass of A are 10g, 20g, 5g, 15g Simple...
Define the law of multiple proportions. Explain it with two examples. How does this law point to the existence of atoms?
When two elements combine to form two or more chemical compounds, then the mass of one of the compounds in a fixed mass of the other holds a simple measure of each other is the law of equality....
Calcium carbonate reacts with aqueous HCl to give CaCl2 and CO2 according to the reaction given below:
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) What mass of CaCl2 will be formed when 250 mL of 0.76 M HCl reacts with 1000 g of CaCO3? Name the limiting reagent. Calculate the number of moles...
A vessel contains 1.6 g of dioxygen at STP (273.15K, 1 atm pressure). The gas is now transferred to another vessel at a constant temperature, where the pressure becomes half of the original pressure. Calculate: (i) the volume of the new vessel. (ii) a number of molecules of dioxygen.
(i) Calculation: Moles of oxygen = 1.6/32 Moles of oxygen = 0.05mol 1 mol of oxygen= 22.4L (at STP) Volume of Oxygen (V1) = 22.4 × 0.05 Volume of Oxygen (V1) = 1.12L V2 =? P1 = 1atm P2 = ½ P2 =...
Assertion (A): Combustion of 16 g of methane gives 18 g of water. Reason (R): In the combustion of methane, water is one of the products. (i) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (ii) A is true but R is false. (iii) A is false but R is true. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (iii) A is false but R is true Explanation: Combustion of 16 g of methane gives 36 g of water.
Assertion (A): Significant figures for 0.200 is 3 whereas for 200 it is 1. Reason (R): Zero at the end or right of a number are significantly provided they are not on the right side of the decimal point. (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true but R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (iii) A is true but R is false Explanation: Zero at the end of a number without the decimal point is not significantly based on the rate of accuracy.
Assertion (A): One atomic mass unit is defined as one-twelfth of the mass of one carbon-12 atom. Reason (R): Carbon-12 isotope is the most abundant isotope of carbon and has been chosen as the standard. (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true but R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A Explanation: The carbon 12 isotope defines the mass of atoms and molecules.
Assertion (A): The empirical mass of ethene is half of its molecular mass. Reason (R): The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number the ratio of various atoms present in a compound. (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) A is true but R is false. (iii) A is false but R is true. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A Explanation: The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number the ratio of various atoms present in a...
Match the following
Physical quantity Unit (i) Molarity (a) g mL–1 (ii) Mole fraction (b) mol (iii) Mole (c) Pascal (iv) Molality (d) Unitless (v) Pressure (e) mol L–1 (vi) Luminous intensity (e) mol L–1 (vii) Density...
Match the following
(i) 88 g of CO2 (a) 0.25 mol (ii) 6.022 ×1023 molecules of H2O (b) 2 mol (iii) 5.6 litres of O2 at STP (c) 1 mol (iv) 96 g of O2 (d) 6.022 × 1023 molecules (v) 1 mol of any gas (e) 3 mol ...
The reactant which is entirely consumed in the reaction is known as limiting reagent. In the reaction 2A + 4B → 3C + 4D, when 5 moles of A react with 6 moles of B, then (i) which is the limiting reagent? (ii) calculate the amount of C formed?
(i) The reactant B is the the limiting reagent. (ii) Calculation: Let us consider that the reactant B got completely consumed as it is the limiting reagent. 4 mol of B gives 3 mol of C 6 mol of B...
If 4 g of NaOH dissolves in 36 g of H2O, calculate the mole fraction of each component in the solution. Also, determine the molarity of the solution (specific gravity of solution is 1g mL–1).
Calculation: Mole fraction of H2O = Number of moles of H2O / Total number of moles (H2O +NaOH) Number of moles of H2O = 36/18 Number of moles of H2O =2 moles Number of moles of NaOH = 4/40 Number of...
The volume of a solution changes with change in temperature, then, will the molality of the solution be affected by temperature? Give a reason for your answer.
The Mass do not change when the temperature changes and so the molality of a solution do not change as well. Molality of a substance is defined as the number of mass of solute per mass of the...
The density of 3 molal solutions of NaOH is 1.110 g mL–1. Calculate the molarity of the solution.
Calculation: 3 molal solution of NaOH = 3 moles of NaOH dissolved in water 3 mole of NaOH = 120g Density of solution = 1.110gmL-1 Volume = mass/density Volume = 1120g/1.110gmL-1 Volume =1.009L...
Hydrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory by reacting dilute HCl with granulated zinc. Following reaction takes place.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 Calculate the volume of hydrogen gas liberated at STP when 32.65 g of zinc reacts with HCl. 1 mol of a gas occupies 22.7 L volume at STP; atomic mass of Zn = 65.3 u. ...
Calculate the average atomic mass of hydrogen using the following data :
Isotope % Natural abundance Molar mass 1H 99.985 1 2H 0.015 2 Calculation: Average atomic mass of Hydrogen \[=099.985\times 1+\frac{0.015\times 2}{100}\] ...
If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in whole-number ratio. (a) Is this statement true? (b) If yes, according to which law? (c) Give one example related to this law.
(a) If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in whole-number ratio and this statement is true....
45.4 L of dinitrogen reacted with 22.7 L of dioxygen and 45.4 L of nitrous oxide was formed. The reaction is given below:
2N2(g) + O2(g) → 2N2O(g) Which law is being obeyed in this experiment? Write the statement of the law? Answer: The Gay-Lussac’s law is used in the given reaction. The Gay-Lussac’s law states...
Calculate the mass percent of calcium, phosphorus and oxygen in calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)
Calculation: Molecular mass of Ca3(PO4) = (3 X 40) + (2 X 31) + (8 X 16) Molecular mass of Ca3(PO4) = 310 Mass percentage of Ca = \[\frac{3\times 40}{310\times 100}\] Mass percentage of Ca = 38.71%...
What is the difference between molality and molarity?
Molarity Molality Number of moles per volume of the solution in litres Number of mass of solute per mass of the solvent in liters Unit - M Unit - m
What is the symbol for the SI unit of a mole? How is the mole defined?
Mole is the amount of substance containing more entities because there are atoms in 12 g of carbon. SI unit symbol – mol
How many significant figures should be present in the answer of the following calculations? 2.5×1.25×3.5/ 2.01
Number Significant figures 2.5 2 1.25 3 3.5 2 2.01 3 In the given calculation, involving both the multiplication and division, the significant figures present is 2. Hence, the result cannot have...
What will be the mass of one atom of C-12 in grams?
1 mole of carbon atom = 12g Therefore, Mass of one atom of C-12 in grams= 1.99 × 1023 grams.
One of the statements of Dalton’s atomic theory is given below: “Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed ratio” Which of the following laws is not related to this statement? (i) Law of conservation of mass (ii) Law of definite proportions (iii) Law of multiple proportions (iv) Avogadro’s law
Correct Answers: (i) Law of conservation of mass; (iv) Avogadro's law Explanation: According to the Dalton's atomic theory, The Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of various elements join in a...
Which of the following terms is unitless?
(i) Molality (ii) Molarity (iii) Mole fraction (iv) Mass per cent Answer: Correct Answers: (iii) Mole fraction; (iv) Mass per cent Explanation: Unit of Molality - Molal or moles per kg Unit...
16 g of oxygen has the same number of molecules as in
(i) 16 g of CO (ii) 28 g of N2 (iii) 14 g of N2 (iv) 1.0 g of H2 Answer: Correct Answers: (iii) 14 g of N2; (iv) 1.0 g of H2 Explanation: The no. of molecules in N2 is 0.5 × 6.023 × 1023 The...
Which of the following solutions have the same concentration?
(i) 20 g of NaOH in 200 mL of solution (ii) 0.5 mol of KCl in 200 mL of solution (iii) 40 g of NaOH in 100 mL of solution (iv) 20 g of KOH in 200 mL of solution Answer: Correct Answers: (i)...
Which of the following pairs have the same number of atoms?
(i) 16 g of O2(g) and 4 g of H2(g) (ii) 16 g of O2 and 44 g of CO2 (iii) 28 g of N2 and 32 g of O2 (iv) 12 g of C(s) and 23 g of Na(s) Answer: Correct Answers: (iii) 28 g of N2 and 32 g of...
Sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide as follows:
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4+ 2H2O When 1L of 0.1M sulphuric acid solution is allowed to react with 1L of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution, the amount of sodium sulphate formed and its molarity in the...
One mole of oxygen gas at STP is equal to _______.
(i) 6.022 × 1023 molecules of oxygen (ii) 6.022 × 1023 atoms of oxygen (iii) 16 g of oxygen (iv) 32 g of oxygen Answer: Correct Answers: (i) 6.022 × 1023 molecules of oxygen; (iv) 32 g of...
Which of the following statements indicates that the law of multiple proportions is being followed.
(i) Sample of carbon dioxide taken from any source will always have carbon and oxygen in the ratio 1:2. (ii) Carbon forms two oxides namely CO2 and CO, where masses of oxygen which combine with a...
Which of the following reactions is not correct according to the law of conservation of mass.
(i) 2Mg(s) + O2(g) →2MgO(s) (ii) C3H8(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) (iii) P4(s) + 5O2(g) → P4O10(s) (iv) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O (g) Answer: Correct Answer: (ii) C3H8(g) + O2(g) →...
Both the cell and the ammeter in the diagram below have minimal resistance. The resistors are all the same. The ammeter reads 0.6A when switch K is open. When the switch is turned off, what will the ammeter read?
Effective resistance = 1/R + 1/R = 2/R Current, I = V/(R/2) = 0.6A V/R = 0.3A switch is closed, Effective Resistance = Re 1/Re = 1/R + 1/R + 1/R = 3/R Re = R/3 Therefore, final current, I = V/(R/3)...
Explain how to find the resistance of a combination of three resistors of resistance R1, R2, and R3 connected in parallel using a labelled circuit diagram.
answer: Total current = I = I1 + I2 + I3 from ohms law I = V/R, I1 = V/R1 I2 = V/R2 I3 = V/R3 V/R = V/R1 + V/R2 + V/R3 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3
Which of the following statements is correct about the reaction given below: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(g) (i) The total mass of iron and oxygen in reactants = total mass of iron and oxygen in product therefore it follows the law of conservation of mass. (ii) The total mass of reactants = total mass of product; therefore, the law of multiple proportions is followed. (iii) Amount of Fe2O3 can be increased by taking any one of the reactants (iron or oxygen) in excess. (iv) Amount of Fe2O3 produced will decrease if the amount of any one of the reactants (iron or oxygen) is taken in excess.
Correct Answer: (i) The total mass of iron and oxygen in reactants = total mass of iron and oxygen in product therefore it follows the law of conservation of mass. Explanation: From the reaction,...
Which of the following statements about a compound is incorrect? (i) A molecule of a compound has atoms of different elements. (ii) A compound cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical methods of separation. (iii) A compound retains the physical properties of its constituent elements. (iv) The ratio of atoms of different elements in a compound is fixed.
Correct Answer: (iii) A compound retains the physical properties of its constituent elements Explanation: Molecule of a compound is made up of atoms of various elements which cannot be separated...
For the circuit shown in the diagram given below, find i) Total resistance ii) Current shown by the ammeter A
Answer: i) Total resistance = R Given, R1 = 5 ohms R2 = 3+2 = 5 ohms 1/R = 1/5 + 1/5 R = 2.5 ohms ii) Current flowing through the circuit, I = V/R = 1.6 amps
If the density of a solution is 3.12 g mL-1, the mass of 1.5 mL solution in significant figures is _______. (i) 4.7g (ii) 4680 × 10 -3g (iii) 4.680g (iv) 46.80g
Correct Answer: (i) 4.7g Explanation: Given, Density of solution = 3.12 g mL-1 Volume of solution = 1.5 mL Formula for Mass = Volume × Density Hence, Mass = 4.7 g
The empirical formula and molecular mass of a compound are CH2O and 180 g respectively. What will be the molecular formula of the compound? (i) C9H18O9 (ii) CH2O (iii) C6H12O6 (iv) C2H4O2
Correct Answer: (iii) C6H12O6 Explanation: Given, Molar mass of Carbon=12 Molar mass of Hydrogen=1 Molar mass of Oxygen=16 So, The molecular weight of compound is 6 and so the molecular formula of...
What is the mass per cent of carbon in carbon dioxide? (i) 0.034% (ii) 27.27% (iii) 3.4% (iv) 28.7%
Correct Answer: (ii) 27.27% Explanation: Carbon dioxide is a gas with a density of about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a double carbon atom combined with two...
What will be the molality of the solution containing 18.25 g of HCl gas in 500 g of water? (i) 0.1 m (ii) 1 M (iii) 0.5 m (iv) 1 m
Correct Answer: (iv) 1 m Explanation: According to molality of a substance which is the number of mass of solute per mass of the solvent in liters, the molality of the solution containing 18.25 g of...
If the concentration of glucose (C6H12O6) in the blood is 0.9 g L-1, what will be the molarity of glucose in the blood? (i) 5 M (ii) 50 M (iii) 0.005 M (iv) 0.5 M
Correct Answer: (iii) 0.005 M Explanation: According to the molarity of a substance which is defined as the number of moles per volume of the solution in litres, the molarity of the glucose in blood...
The number of atoms present in one mole of an element is equal to Avogadro number. Which of the following element contains the greatest number of atoms? (i) 4g He (ii) 46g Na (iii) 0.40g Ca (iv) 12g He
Correct Answer: (iv) 12g He Explanation: The number of atoms present in 4g of Helium – 1 NA The number of atoms present in 46g of Sodium - 2 NA The number of atoms present in 0.04g of Calcium – 0.01...
If 500 mL of a 5M solution is diluted to 1500 mL, what will be the molarity of the solution obtained? (i) 1.5 M (ii) 1.66 M (iii) 0.017 M (iv) 1.59 M
Correct Answer: (ii) 1.66 M Explanation: According to the Using M1V1= M2V2 formula, the value of M2 is 1.66 M.
Determine the equivalent resistance of two resistances linked in parallel with the help of a circuit diagram.
Answer: The above circuit shows resistances R1 and R2 connected in series with a battery of V volts Total current = I = I1 + I2 apply ohms law, I=V/R I1 = V/R1 I2 = V/R2 V/R = V/R1 + V/R2 1/R = 1/R1...
Q36. The electrical resistivities of five substances A, B, C, S, and E are given below: A = 5.20×10-8 Ωm B = 110×10-8 Ωm C = 2.60×10-8 Ωm D = 10.0×10-8 Ωm E = 1.70×10-8 Ωmc) Which substance would you advice to be used for making heating elements of electric irons? Why? d) Which two substances should be used for making electric wires? Why?
c) B can be used in the making of the heating elements of an electric iron because the resistivity of B is the highest . d) C and E are the two substances that should be used for making electric...
Q36. The electrical resistivities of five substances A, B, C, S, and E are given below: A = 5.20×10-8 Ωm B = 110×10-8 Ωm C = 2.60×10-8 Ωm D = 10.0×10-8 Ωm E = 1.70×10-8 Ωm a) Which substance is the best conductor of electricity? Why? b) Which one is a better conductor: A or C? Why?
Answer: a) E is the best conductor of electricity because it has the least resistivity . b) C is a better conductor between A and C because the resistivity of C is lesser than that of A .
Calculate the following for the circuit shown in the diagram given below, total effective resistance of the circuit
Answer: Effective resistance = R 1/R = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 1/R=1/30 + 1/10 +1/5 R=3 ohm
Q35. The electrical resistivities of four materials A, B, C, and D are given below: A = 110×10-8 Ωm B = 1.0×1010 Ωm C = 10.0×10-8 Ωm D = 2.3×103 ΩmWhich material is: c) Insulator d) Semiconductor
Answer : c) Insulator is B = 1.0×1010 Ωm . d) Semiconductor is D = 2.3×103 Ωm .
Calculate the following for the circuit shown in the diagram below. i) Value of current through each resistor ii) total current in the circuit
Answer: A parallel circuit is a circuit in which the electricity travels over numerous separate pathways. i) Current through R1=6/5 = 1.2A Current through R2 =6/10= 0.6A Current through R3 =6/30=...
Q35. The electrical resistivities of four materials A, B, C, and D are given below: A = 110×10-8 Ωm B = 1.0×1010 Ωm C = 10.0×10-8 Ωm D = 2.3×103 Ωm Which material is: a) Good conductor b) Resistor
Answer: a) Good conductor is C = 10.0×10-8 Ωm . b) Resistor is A = 110×10-8 Ωm .
If the potential difference between the ends of a fixed resistor is halved, the electric power will becomes: a) double b) half c) four times d) one-fourth
Answer: d) one-fourth is the correct answer. We know p=v²/R where R is constant p turns 1/4 times when V is halved The electric power is one-fourth of the actual value when the potential difference...
Separation of Motion of a system of particles into motion of the centre of mass and motion about the centre of mass:
 Show
Show 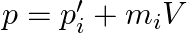 Where
Where 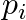 is the momentum of the
is the momentum of the 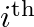 particle (of mass
particle (of mass 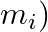 and
and 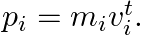 Note
Note 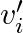 is the velocity of the
is the velocity of the 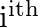 particle with respect to the centre of mass.Also, verify using the definition of the centre of mass that
particle with respect to the centre of mass.Also, verify using the definition of the centre of mass that 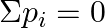
(ii) Prove that 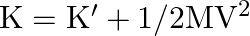 Where
Where 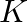 is the total kinetic energy of the system of particles,
is the total kinetic energy of the system of particles, 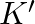 is the total kinetic energy of the system when the particle velocities are taken relative to the center of mass and
is the total kinetic energy of the system when the particle velocities are taken relative to the center of mass and 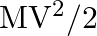 is the kinetic energy of the translation of the system as a whole.
is the kinetic energy of the translation of the system as a whole.
i)Here $\vec{r}_{i}=\vec{r}_{i}+\vec{R}+R \ldots$ also, $\vec{V}_{i}=\vec{V}_{i}+\vec{V} \ldots \ldots .$ Where $\vec{r}_{i}^{\overrightarrow{3}}$ and $\vec{v}_{i}^{\overrightarrow{3}}$ denote the...
Q34. The electrical resistivities of three materials P, Q, and R are given below: P = 2.3×103 Ωm Q = 2.63×10-8 Ωm R = 1.0×1015 Ωm Which material will you use for making? c) Solar cells
Answer : c) For making of the solar cells, P = 2.3×103 Ωm can be used because this materials is a semiconductor .
At a given time, a house is supplied with 100A at 220V. How many 75W, 220V light bulbs could be switched on in the house at the same times if they are all connected in parallel? a) 93 b) 193 c) 293 d) 393
Answer: c) 293 is the correct answer. When all 293 bulbs are linked in parallel and have 75W and 220V, a total of 293 bulbs can be used.
Determine the formula for the resulting resistance of three resistors linked in series using a diagram.
Answer: The resistances R1,R2 and R3 are linked in series with a V volt battery in the circuit above. Let V1 be the potential difference between R1 and V2 be the potential difference between R2....
Q34. The electrical resistivities of three materials P, Q, and R are given below: P = 2.3×103 Ωm Q = 2.63×10-8 Ωm R = 1.0×1015 Ωm Which material will you use for making? a) Electric wires b) Handle for soldering iron
Answer: a) For making of the electric wires, Q = 2.63×10-8 Ωm can be used because this material has a very low resistivity b) For making of the handle for soldering iron, R = 1.0×1015 Ωm can be used...
How many joules of electrical energy are transferred per second by a 6V, 0.5A lamp? a) 30 J/s b) 12 J/s c) 0.83 J/s d) 3 J/s
Answer: d) 3 J/s is the correct answer. Electrical energy transfered per second , E=VIt=6 x 0.5 x 1 When a light with a voltage of 6V and a current of 0.5A is utilised, 3 J/s of electrical energy is...
An electric kettle for use on a 230V supply is rated at 3000W. For safe working, the cable connected to it should be able to carry at least: a) 2A b) 5A c) 10A d) 15A
Answer: d) 15A is the correct answer. Current drawn by the kettle, I=P/V = 3000/230 So the cable should be able to carry more current than this and hence the answer is 15 A. An electric kettle with...
How much energy is does a 100W electric bulb transfer in 1 minutes? a) 100J b) 600J c) 3600J d) 6000J
Answer: d) 6000J is the correct answer. According to the question, Power= 100 W Time, t = 1 minute = 60 seconds P=W/t W=6000J Energy is the ability to do work. Hence, In one minute, 6000J of energy...
As indicated in the diagram, two resistances are connected in series: i) What is the value of R? ii) What is the value of V?
Answer: given V=6V, Current through 5 ohm resistor =V/R= 2A i) V = IR R = 3 ohm ii) V = 10 + 6 = 16V
Q33. A piece of wire of resistance 20Ω is drawn out so that its length is increased to twice its original length. Calculate the resistance of the wire in the new situation.
Answer: We know that, R = ρl/A Given that, l’ = 2l A’ = A/2 And ρ’ = ρ (as the material of the wire is the same) Therefore, R’ = ρ’l’/A’ = ρ2l/(A/2) = 4ρl/A = 4R Therefore, R’ = 4×20 =...
The commercial unit of energy is: a) Watt b) Watt-hour c) Kilowatt-hour d) Kilo-joule
Answer: c) Kilowatt-hour is the right answer. The commercial unit of energy is the kilowatt hour.
The SI unit of energy is: a) Joule b) Coulomb c) Watt d) Ohm-meter
Answer: a) Joule is the correct answer. The joule is the SI unit of energy.
Q32. If the area of cross-section of a resistance wire is halved, then its resistance becomes: a) One-half b) 2 times c) One-fourth d) 4 times
Answer: The correct option is b) 2 times. Reason: As, R = ρl/A so R' = ρl/(A/2) = 2ρl/A ⇒R' = 2R So , new resistance becomes 2 times the original resistance .
