Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. It is also known as dioxide or peroxide. It has a mild odor and is colorless in solution. With a stabilizer, it is non-flammable and somewhat acidic. An...
Test
Which of the following equations depict the oxidising nature of 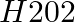 ? (i)
? (i) 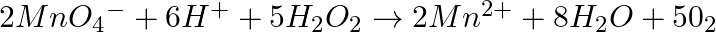 (ii)
(ii) 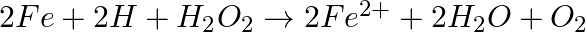 (iii)
(iii) 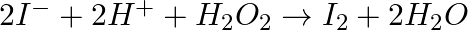 (iv)
(iv) 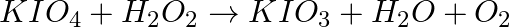
Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. The oxidising characteristic of $H _2 O _2$ indicates that it oxidises other substances while simultaneously reducing itself. In such reactions, $O _2$ does not...
The oxide that gives H2O2 on treatment with dilute H2SO4 is — (i) PbO2 (ii) BaO2 .8H2O + O2 (iii) MnO2 (iv) TiO2
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. The oxide that gives $H _{2} O _{2}$ on treatment with dilute $H _{2} SO _{4}$ is $BaO _{2} \cdot 8 H _{2} O$....
Consider the reactions (A) H2O2 + 2HI → I2 + 2H2O (B) HOCl + H2O2 → H3O++ Cl–+ O2 Which of the following statements is correct about H2O2 with reference to these reactions? Hydrogen peroxide is ________. (i) an oxidising agent in both (A) and (B) (ii) an oxidising agent in (A) and reducing agent in (B) (iii) a reducing agent in (A) and oxidising agent in (B) (iv) a reducing agent in both (A) and (B)
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. (A) $H_2O_2 + 2HI → I_2 + 2H_2O$ Iodine undergoes oxidation, transitioning from the -1 oxidation state to the 0 oxidation state. As a result, H2O2 works as an...
Radioactive elements emit α, β and γ rays and are characterised by their halflives. The radioactive isotope of hydrogen is (i) Protium (ii) Deuterium (iii) Tritium (iv) Hydronium
Solution: Option (iii) is the answer. The concentration of tritium is approximately one atom per $10^18$ atoms of protium in the sample. Only tritium is radioactive and emits low-energy beta...
Which of the following hydrides is electron-precise hydride? (i) B2H6 (ii) NH3 (iii) H2O (iv) CH4
Solution: Option (iv) is the answer. The hydrides indicate an anion form of hydrogen atoms. ...
Metal hydrides are ionic, covalent or molecular in nature. Among LiH, NaH, KH, RbH, CsH, the correct order of increasing ionic character is (i) LiH > NaH > CsH > KH>RbH (ii) LiH < NaH < KH < RbH CsH > NaH > KH > LiH (iv) NaH > CsH > RbH > LiH > KH
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. As we advance down the group, the ionic nature rises. As ionisation enthalpy drops from top to bottom in a group, metal tends to lose electron. So ionic...
Why does H+ ion always get associated with other atoms or molecules? (i) Ionisation enthalpy of hydrogen resembles that of alkali metals. (ii) Its reactivity is similar to halogens. (iii) It resembles both alkali metals and halogens. (iv) Loss of an electron from hydrogen atom results in a nucleus of very small size as compared to other atoms or ions. Due to the small size, it cannot exist free.
Solution: Option (iv) is the answer. Hydrogen has one electron in its s orbital and like alkali metals, it can lose one electron from its outer shell. So hydrogen is like alkalis. Onions reacting...
Hydrogen resembles halogens in many respects for which several factors are responsible. Of the following factors which one is most important in this respect? (i) Its tendency to lose an electron to form a cation. (ii) Its tendency to gain a single electron in its valence shell to attain stable electronic configuration. (iii) Its low negative electron gain enthalpy value. (iv) Its small size.
Solution: Option (ii) is the answer. Hydrogen, like halogens, prefers to gain an electron to achieve a stable noble gas structure. Hydrogen's electrical configuration is 1s. The electrical...
The exhibition of the highest co-ordination number depends on the availability of vacant orbitals in the central atom. Which of the following elements is not likely to act as a central atom in MF6 3–? (i) B (ii) Al (iii) Ga (iv) In
Option I is the correct response.
A vessel of 120 mL limit contains a specific measure of gas at 35°C and 1.2 bar pressure. The gas is moved to one more vessel of volume 180 mL at 35°C. What might be its tension?
Solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} ~P1\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }bar \\ P2\text{ }=\text{ }? \\ ~V1=\text{ }500\text{ }dm3 \\ V2=200\text{ }dm3 \\ \end{array}\] As temperature stays steady at...
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 1 bar to 200 dm3 at 30°C?
Solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} ~P1\text{ }=\text{ }1\text{ }bar \\ P2\text{ }=\text{ }? \\ ~V1=\text{ }500\text{ }dm3 \\ V2=200\text{ }dm3 \\ \end{array}\] As temperature stays steady at...
Assertion (A): The black body is an ideal body that emits and absorbs radiations of all frequencies. Reason (R): The frequency of radiation emitted by a body goes from a lower frequency to higher frequency with an increase in temperature.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the explanation of A. (iii) A is true and R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false. ...
Assertion (A): It is impossible to determine the exact position and exact the momentum of an electron simultaneously. Reason (R): The path of an electron in an atom is clearly defined.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true and R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false....
Assertion (A): All isotopes of a given element show the same type of chemical behaviour. Reason (R): The chemical properties of an atom are controlled by the number of electrons in the atom.
(i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true but R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false....
Match species are given in Column 1 with the electronic configuration given in Column 2.
Column 1 Column 2 (i) Cr (a) [Ar]3d84s0 (ii) Fe2+ (b) [Ar]3d104s1 (iii) Ni2+ (c) [Ar]3d64s0 (iv) Cu (d) [Ar] 3d54s1 (e) [Ar]3d64s2 Column 1 Column 2 (i) Cr (d) [Ar]...
Match the following
Column 1 Column 2 (i) Photon (a)Value is 4 for N shell (ii) Electron (b)Probability density (iii) ψ2 (c)Always a positive value (iv) The principal quantum number n (d)Exhibits both momentum...
Match the following
Column 1 Column 2 (i) X-rays (a) ν = 100-0 104 Hz (ii) UV (b) ν = 1010Hz (iii) Long radio waves (c) ν = 1016 Hz (iv) Microwave (d) ν = 1018Hz Column 1 Column 2 (i) X-rays (d) ν = 1018Hz (ii) UV...
Match the following
Rule Principle (i) Hund’s Rule (a) No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers. (ii) Aufbau Principle (b) Half-filled and filled orbitals have extra stability....
Match the quantum numbers with the information provided by these Quantum number Information provided
Column 1 Column 2 (i) Principal quantum number (a) orientation of the orbital (ii) Azimuthal quantum number (b) energy and size of orbital (iii) Magnetic quantum number (c) spin of an electron (iv)...
Match the following species with their corresponding ground state electronic configuration.
Atom / Ion Electronic configuration (i) Cu (a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 (ii) Cu2+ (b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 (iii) Zn2+ (c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 (iv) Cr3+ (d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d9 (e) 1s2...
The hydrogen atom has only one electron, so mutual repulsion between electrons is absent. However, in multielectron atoms mutual repulsion between the electrons is significant. How does this affect the energy of an electron in the orbitals of the same principal quantum number in multielectron atoms?
Hydrogen atom has only one electron, so the mutual repulsion between the electrons is non-existent. However, in multielectron atoms the interaction between electrons is important. This is because,...
The effect of the uncertainty principle is significant only for the motion of microscopic particles and is negligible for the macroscopic particles. Justify the statement with the help of a suitable example.
The uncertainty principle is applicable only for microscopic particles and can be concluded from the uncertainty measurement. Example: Take a particle of mass = 1 milligram ∆x. ∆ν = 60626*10-34/...
Table-tennis ball has a mass 10 g and a speed of 90 m/s. If speed can be measured within an accuracy of 4% what will be the uncertainty in speed and position?
According to Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle: ∆x. ∆p ≥ h/4π Mass of the ball = 4 g Speed is = 90 m /s Uncertainity of speed, ∆v = 4/100 × 90 ∆v = 3.6 m/s ∆x = h/4πm∆v ∆x = 6.26 × 10-34 / 4 × 3.14...
What is the difference between the terms orbit and orbital?
Orbit represents a clear circular path for electrons to surround the nucleus. Represents the two-dimensional movement of electrons around the nucleus, the orbital is not that well defined because it...
Chlorophyll present in green leaves of plants absorbs light at 4.620 × 1014 Hz. Calculate the wavelength of radiation in nanometer. Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does it belong to?
The relationship between the wavelength and the frequency: λ = c/ν c - Velocity of light v - Frequency of the radiation. λ = 3 x 108 ms-1 / 4.620 x 1014 Hz Hence, λ = 0.6494...
A hypothetical electromagnetic wave is shown in Figure. Find out the wavelength of the radiation.
Distance between the two identical successive points in a wave is called the wavelength. Given, In the hypothetical wave, Wavelength, λ = 4 × 2.16 pm Hence, Wavelength, λ = 8.64 pm.
Out of electron and proton which one will have, a higher velocity to produce matter waves of the same wavelength? Explain it.
The electron which is a lighter particle will have the higher velocity and will also produce matter waves having the same wavelength. This is because, if the mass is less, then the velocity increases.
What is the experimental evidence in support of the idea that electronic energies in an atom are quantized?
The bright line spectrum shows that the atomic energy levels are measured. These lines are found to be the result of electronic transitions between energy and the atomic spectrum would have shown...
According to de Broglie, the matter should exhibit dual behavior that is both particle and wave-like properties. However, a cricket ball of mass 100 g does not move like a wave when it is thrown by a bowler at a speed of 100 km/h. Calculate the wavelength of the ball and explain why it does not show wave nature.
Calculation: Given, Mass, m = 100g / 0.1kg Velocity = 100km/h Velocity =100×1000 / 60×60 Velocity = 1000/36m/s λ =h/mν λ = 2.387 × 10-34 m
The Balmer series in the hydrogen spectrum corresponds to the transition from n1 = 2 to n2 = 3,4,………. This series lies in the visible region. Calculate the wavenumber of the line associated with the transition in Balmer series when the electron moves to n = 4 orbit. (RH= 109677 cm-1)
Calculation: According to Bohr’s model for the hydrogen atom; ν = RH(1/n12-1/ n22)cm-1 Given, n1 = 2 n2 = 4 H (Rydberg’s constant) = 109677 Wave number = 109677 ( ¼-1/16) Hence, Wave number =...
The electronic configuration of the valence shell of Cu is 3d10 4s1 and not 3d94s2. How is this configuration explained?
Great stability is established to the orbitals which are half or completely filled. In the given electronic configuration 3d104s1 of Copper (Cu), the stability is assured (d orbitals - filled, s...
Wavelengths of different radiations are given below :
λ(A) = 300 nm λ(B) = 300 μm λ(c) = 3 nm λ (D) 30 A° Arrange these radiations in the increasing order of their energies. Given, λ(A) = 300 nm λ(A) = 300 x 10-9 m λ(A) = 3 x 10 -7 m λ(B)...
An atom having atomic mass number 13 has 7 neutrons. What is the atomic number of the atom?
Calculation: Atomic mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons Number of protons = atomic mass number – number of neutrons. Hence, atomic number of an atom = 13 – 7 = 6.
Which of the following will not show deflection from the path on passing through an electric field? Proton, cathode rays, electron, neutron
Neutron shows no deflection from the path passing through the electric field. This is due to the neutrality of neutron particles. Therefore, it has no charge and is not affected by any electrical...
The arrangement of orbitals based on energy is based upon their (n+l ) value. Lower the value of (n+l ), lower is the energy. For orbitals having the same values of (n+l), the orbital with a lower value of n will have lower energy.
Based upon the above information, arrange the following orbitals in the increasing order of energy (a) 1s, 2s, 3s, 2p (b) 4s, 3s, 3p, 4d (c) 5p, 4d, 5d, 4f, 6s (d) 5f, 6d, 7s, 7p Based upon the...
Calculate the total number of angular nodes and radial nodes present in 3p orbital.
The region where the probability of finding the electrons is zero, it is considered as the nodes and is it present among the orbitals. Example: In the np orbitals, Nodes = n – l – 1 Nodes = 3 –1 – 1...
Which of the following orbitals are degenerate? 3dxy, 4dxy, 3dz2 , 3dyx, 4dyx, 4dzz
The electron energy in a multielectron atom, in contrast to the hydrogen atom, depends not only on its quantum number, but also on its azimuthal quantum number. The same electron shells and the same...
Nickel atom can lose two electrons to form Ni2+ ion. The atomic number of nickel is 28. From which orbital will nickel lose two electrons.
1 Ni atom = 28 electrons and its electronic configuration is 4s2 3d8 It turns to Ni2+ by losing 2 electrons and its electronic configuration becomes 4s0 3d8 According to the Aufbau principle, Ni...
Show the distribution of electrons in oxygen atom (atomic number 8) using orbital diagram.
Distribution of electrons in oxygen atom: 1s22s22p4
Arrange s, p and d sub-shells of a shell in the increasing order of effective nuclear charge (Zeff) experienced by the electron present in them.
Arrangement of the subshells: d<p<s The s-orbitals shield the electrons a lot more when compared to the p-orbitals from the nucleus.
Which of the following statements concerning the quantum numbers are correct?
(i) The angular quantum number determines the three-dimensional shape of the orbital. (ii) The principal quantum number determines the orientation and energy of the orbital. (iii) The magnetic...
In which of the following pairs, the ions are iso-electronic?
(i) Na+, Mg2+ (ii) Al3+, O– (iii) Na+, O2- (iv) N3-, Cl– Correct Answers: (i) Na+, Mg2+ (iii) Na+, O2- Explanation: Isoelectronic species are the atoms / ions that has the same number...
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers is correct? n l m n l m
(i) 1 1 +2 (ii) 2 1 +1 (iii) 3 2 –2 (iv) 3 4 –2 Correct Answers: (ii) 2 1 +1 (iii) 3 2 –2 Explanation: The correct sets of quantum numbers are, n = 2, l = 1, m = +1 n = 3, l = 2, m =...
Out of the following pairs of electrons, identify the pairs of electrons present in degenerate orbitals :
(i) (a) n = 3, l = 2, ml = –2, ms= − ½ (b) n = 3, l = 2, ml = –1, ms= − 1/2 (ii) (a) n = 3, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = + ½ (b) n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = +1/2 (iii) (a) n = 4, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +...
Identify the pairs which are not of isotopes?
(i) 6X12, 6Y13 (ii) 17X35, 6Y37 (iii) 6X14, 7Y14 (iv) 4X8, 5Y8 Correct Answers: (iii) 6X14, 7Y14 (iv) 4X8, 5Y8 Explanation: Isotopes are the atoms having same atomic number but...
If travelling at the same speeds, which of the following matter waves have the shortest wavelength?
(i) Electron (ii) An alpha particle (He2+) (iii) Neutron (iv) Proton Correct Answer: (ii) An alpha particle (He2+) Explanation: According to de Broglie's equation, the alpha particles...
For the electrons of an oxygen atom, which of the following statements is correct?
(i) Zeff for an electron in a 2s orbital is the same as Zeff for an electron in a 2p orbital. (ii) An electron in the 2s orbital has the same energy as an electron in the 2p orbital. (iii) Zeff for...
The pair of ions having same electronic configuration is __________.
(i) Cr3+, Fe3+ (ii) Fe3+, Mn2+ (iii) Fe3+, Co3+ (iv) Sc3+, Cr3+ Correct Answer: (ii) Fe3+, Mn2+ Explanation: Fe - Z=26 : 3d64s2 Fe3+- 3d5 Mn - Z=25 : 3d54s2 Mn2+ : 3d5 Hence,...
Orbital angular momentum depends on __________.
(i) l (ii) n and l (iii) n and m (iv) m and s Correct Answer: (i) l Explanation: Orbital angular momentum depends on the value of l which is referred to as the azimuthal quantum number.
A total number of orbitals associated with the third shell will be __________.
(i) 2 (ii) 4 (iii) 9 (iv) 3 Correct Answer: (iii) 9 Explanation: The total number of orbitals in nth shell = n2 Hence, the total number of orbitals associated with the third shell will...
Which of the following is responsible to rule out the existence of definite paths or trajectories of electrons? (i) Pauli’s exclusion principle. (ii) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. (iii) Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity. (iv) Aufbau principle.
Correct Answer: (ii) Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Explanation: The Heisenberg's uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to know the exact position and speed of an object...
Number of angular nodes for 4d orbital is __________.
(i) 4 (ii) 3 (iii) 2 (iv) 1 Correct Answer: (iii) 2 Explanation: The Number of angular nodes = l (azimuthal quantum number) Hence, the number of angular nodes for 4d orbital is...
The number of radial nodes for 3p orbital is __________.
(i) 3 (ii) 4 (iii) 2 (iv) 1 Correct Answer: (iv) 1 Explanation: Number of radial nodes for 3p orbital = 3−1−1 Number of radial nodes for 3p orbital = 3−2 Number of radial nodes for 3p...
Two atoms are said to be isobars if.
(i) they have the same atomic number but a different mass number. (ii) they have the same number of electrons but a different number of neutrons. (iii) they have the same number of neutrons but a...
Which of the following properties of an atom could be explained correctly by Thomson Model of an atom?
(i) Overall neutrality of atom. (ii) Spectra of a hydrogen atom. (iii) Position of electrons, protons and neutrons in an atom. (iv) Stability of atom. Correct Answer: (i) Overall...
Which of the following statements about the electron is incorrect?
(i) It is a negatively charged particle. (ii) The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron. (iii) It is a basic constituent of all atoms. (iv) It is a constituent of cathode rays....
Which of the following statement is not correct about the characteristics of cathode rays?
(i) They start from the cathode and move towards the anode. (ii) They travel in a straight line in the absence of an external electrical or magnetic field. (iii) Characteristics of cathode rays do...
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region. Based on the above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect? (i) 1s and 2s...
Which of the following options does not represent ground state electronic configuration of an atom?
(i) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2 (ii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 4s2 (iii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 (iv) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s1 Correct Answer: (ii) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 4s2...
Which of the following conclusions could not be derived from Rutherford’s α -particle scattering experiment?
(i) Most of the space in the atom is empty. (ii) The radius of the atom is about 10–10 m while that of a nucleus is 10–15 m. (iii) Electrons move in a circular path of fixed energy called orbits....
A box contains some identical red coloured balls, labelled as A, each weighing 2 grams. Another box contains identical blue coloured balls, labelled as B, each weighing 5 grams. Consider the combinations AB, AB2, A2B and A2B3 and show that the law of multiple proportions is applicable.
AB ab2 A,B A2B3 Mass of A (in g) 2 2 4 415 Mass of B (in g) 5 10 5 According to the law of multiple proportions, Masses of B combines with a constant mass of A are 10g, 20g, 5g, 15g Simple...
Define the law of multiple proportions. Explain it with two examples. How does this law point to the existence of atoms?
When two elements combine to form two or more chemical compounds, then the mass of one of the compounds in a fixed mass of the other holds a simple measure of each other is the law of equality....
Calcium carbonate reacts with aqueous HCl to give CaCl2 and CO2 according to the reaction given below:
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) What mass of CaCl2 will be formed when 250 mL of 0.76 M HCl reacts with 1000 g of CaCO3? Name the limiting reagent. Calculate the number of moles...
A vessel contains 1.6 g of dioxygen at STP (273.15K, 1 atm pressure). The gas is now transferred to another vessel at a constant temperature, where the pressure becomes half of the original pressure. Calculate: (i) the volume of the new vessel. (ii) a number of molecules of dioxygen.
(i) Calculation: Moles of oxygen = 1.6/32 Moles of oxygen = 0.05mol 1 mol of oxygen= 22.4L (at STP) Volume of Oxygen (V1) = 22.4 × 0.05 Volume of Oxygen (V1) = 1.12L V2 =? P1 = 1atm P2 = ½ P2 =...
Assertion (A): Combustion of 16 g of methane gives 18 g of water. Reason (R): In the combustion of methane, water is one of the products. (i) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (ii) A is true but R is false. (iii) A is false but R is true. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (iii) A is false but R is true Explanation: Combustion of 16 g of methane gives 36 g of water.
Assertion (A): Significant figures for 0.200 is 3 whereas for 200 it is 1. Reason (R): Zero at the end or right of a number are significantly provided they are not on the right side of the decimal point. (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true but R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (iii) A is true but R is false Explanation: Zero at the end of a number without the decimal point is not significantly based on the rate of accuracy.
Assertion (A): One atomic mass unit is defined as one-twelfth of the mass of one carbon-12 atom. Reason (R): Carbon-12 isotope is the most abundant isotope of carbon and has been chosen as the standard. (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (iii) A is true but R is false. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A Explanation: The carbon 12 isotope defines the mass of atoms and molecules.
Assertion (A): The empirical mass of ethene is half of its molecular mass. Reason (R): The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number the ratio of various atoms present in a compound. (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (ii) A is true but R is false. (iii) A is false but R is true. (iv) Both A and R are false.
Correct Answer: (i) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A Explanation: The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number the ratio of various atoms present in a...
Match the following
Physical quantity Unit (i) Molarity (a) g mL–1 (ii) Mole fraction (b) mol (iii) Mole (c) Pascal (iv) Molality (d) Unitless (v) Pressure (e) mol L–1 (vi) Luminous intensity (e) mol L–1 (vii) Density...
Match the following
(i) 88 g of CO2 (a) 0.25 mol (ii) 6.022 ×1023 molecules of H2O (b) 2 mol (iii) 5.6 litres of O2 at STP (c) 1 mol (iv) 96 g of O2 (d) 6.022 × 1023 molecules (v) 1 mol of any gas (e) 3 mol ...
The reactant which is entirely consumed in the reaction is known as limiting reagent. In the reaction 2A + 4B → 3C + 4D, when 5 moles of A react with 6 moles of B, then (i) which is the limiting reagent? (ii) calculate the amount of C formed?
(i) The reactant B is the the limiting reagent. (ii) Calculation: Let us consider that the reactant B got completely consumed as it is the limiting reagent. 4 mol of B gives 3 mol of C 6 mol of B...
If 4 g of NaOH dissolves in 36 g of H2O, calculate the mole fraction of each component in the solution. Also, determine the molarity of the solution (specific gravity of solution is 1g mL–1).
Calculation: Mole fraction of H2O = Number of moles of H2O / Total number of moles (H2O +NaOH) Number of moles of H2O = 36/18 Number of moles of H2O =2 moles Number of moles of NaOH = 4/40 Number of...
The volume of a solution changes with change in temperature, then, will the molality of the solution be affected by temperature? Give a reason for your answer.
The Mass do not change when the temperature changes and so the molality of a solution do not change as well. Molality of a substance is defined as the number of mass of solute per mass of the...
The density of 3 molal solutions of NaOH is 1.110 g mL–1. Calculate the molarity of the solution.
Calculation: 3 molal solution of NaOH = 3 moles of NaOH dissolved in water 3 mole of NaOH = 120g Density of solution = 1.110gmL-1 Volume = mass/density Volume = 1120g/1.110gmL-1 Volume =1.009L...
Hydrogen gas is prepared in the laboratory by reacting dilute HCl with granulated zinc. Following reaction takes place.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 Calculate the volume of hydrogen gas liberated at STP when 32.65 g of zinc reacts with HCl. 1 mol of a gas occupies 22.7 L volume at STP; atomic mass of Zn = 65.3 u. ...
Calculate the average atomic mass of hydrogen using the following data :
Isotope % Natural abundance Molar mass 1H 99.985 1 2H 0.015 2 Calculation: Average atomic mass of Hydrogen \[=099.985\times 1+\frac{0.015\times 2}{100}\] ...
If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in whole-number ratio. (a) Is this statement true? (b) If yes, according to which law? (c) Give one example related to this law.
(a) If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element, are in whole-number ratio and this statement is true....
45.4 L of dinitrogen reacted with 22.7 L of dioxygen and 45.4 L of nitrous oxide was formed. The reaction is given below:
2N2(g) + O2(g) → 2N2O(g) Which law is being obeyed in this experiment? Write the statement of the law? Answer: The Gay-Lussac’s law is used in the given reaction. The Gay-Lussac’s law states...
Calculate the mass percent of calcium, phosphorus and oxygen in calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)
Calculation: Molecular mass of Ca3(PO4) = (3 X 40) + (2 X 31) + (8 X 16) Molecular mass of Ca3(PO4) = 310 Mass percentage of Ca = \[\frac{3\times 40}{310\times 100}\] Mass percentage of Ca = 38.71%...
What is the difference between molality and molarity?
Molarity Molality Number of moles per volume of the solution in litres Number of mass of solute per mass of the solvent in liters Unit - M Unit - m
What is the symbol for the SI unit of a mole? How is the mole defined?
Mole is the amount of substance containing more entities because there are atoms in 12 g of carbon. SI unit symbol – mol
How many significant figures should be present in the answer of the following calculations? 2.5×1.25×3.5/ 2.01
Number Significant figures 2.5 2 1.25 3 3.5 2 2.01 3 In the given calculation, involving both the multiplication and division, the significant figures present is 2. Hence, the result cannot have...
What will be the mass of one atom of C-12 in grams?
1 mole of carbon atom = 12g Therefore, Mass of one atom of C-12 in grams= 1.99 × 1023 grams.
One of the statements of Dalton’s atomic theory is given below: “Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed ratio” Which of the following laws is not related to this statement? (i) Law of conservation of mass (ii) Law of definite proportions (iii) Law of multiple proportions (iv) Avogadro’s law
Correct Answers: (i) Law of conservation of mass; (iv) Avogadro's law Explanation: According to the Dalton's atomic theory, The Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of various elements join in a...
Which of the following terms is unitless?
(i) Molality (ii) Molarity (iii) Mole fraction (iv) Mass per cent Answer: Correct Answers: (iii) Mole fraction; (iv) Mass per cent Explanation: Unit of Molality - Molal or moles per kg Unit...
16 g of oxygen has the same number of molecules as in
(i) 16 g of CO (ii) 28 g of N2 (iii) 14 g of N2 (iv) 1.0 g of H2 Answer: Correct Answers: (iii) 14 g of N2; (iv) 1.0 g of H2 Explanation: The no. of molecules in N2 is 0.5 × 6.023 × 1023 The...
Which of the following solutions have the same concentration?
(i) 20 g of NaOH in 200 mL of solution (ii) 0.5 mol of KCl in 200 mL of solution (iii) 40 g of NaOH in 100 mL of solution (iv) 20 g of KOH in 200 mL of solution Answer: Correct Answers: (i)...
Which of the following pairs have the same number of atoms?
(i) 16 g of O2(g) and 4 g of H2(g) (ii) 16 g of O2 and 44 g of CO2 (iii) 28 g of N2 and 32 g of O2 (iv) 12 g of C(s) and 23 g of Na(s) Answer: Correct Answers: (iii) 28 g of N2 and 32 g of...
Sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide as follows:
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4+ 2H2O When 1L of 0.1M sulphuric acid solution is allowed to react with 1L of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution, the amount of sodium sulphate formed and its molarity in the...
One mole of oxygen gas at STP is equal to _______.
(i) 6.022 × 1023 molecules of oxygen (ii) 6.022 × 1023 atoms of oxygen (iii) 16 g of oxygen (iv) 32 g of oxygen Answer: Correct Answers: (i) 6.022 × 1023 molecules of oxygen; (iv) 32 g of...
Which of the following statements indicates that the law of multiple proportions is being followed.
(i) Sample of carbon dioxide taken from any source will always have carbon and oxygen in the ratio 1:2. (ii) Carbon forms two oxides namely CO2 and CO, where masses of oxygen which combine with a...
Which of the following reactions is not correct according to the law of conservation of mass.
(i) 2Mg(s) + O2(g) →2MgO(s) (ii) C3H8(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) (iii) P4(s) + 5O2(g) → P4O10(s) (iv) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O (g) Answer: Correct Answer: (ii) C3H8(g) + O2(g) →...
Which of the following statements is correct about the reaction given below: 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(g) (i) The total mass of iron and oxygen in reactants = total mass of iron and oxygen in product therefore it follows the law of conservation of mass. (ii) The total mass of reactants = total mass of product; therefore, the law of multiple proportions is followed. (iii) Amount of Fe2O3 can be increased by taking any one of the reactants (iron or oxygen) in excess. (iv) Amount of Fe2O3 produced will decrease if the amount of any one of the reactants (iron or oxygen) is taken in excess.
Correct Answer: (i) The total mass of iron and oxygen in reactants = total mass of iron and oxygen in product therefore it follows the law of conservation of mass. Explanation: From the reaction,...
Which of the following statements about a compound is incorrect? (i) A molecule of a compound has atoms of different elements. (ii) A compound cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical methods of separation. (iii) A compound retains the physical properties of its constituent elements. (iv) The ratio of atoms of different elements in a compound is fixed.
Correct Answer: (iii) A compound retains the physical properties of its constituent elements Explanation: Molecule of a compound is made up of atoms of various elements which cannot be separated...
If the density of a solution is 3.12 g mL-1, the mass of 1.5 mL solution in significant figures is _______. (i) 4.7g (ii) 4680 × 10 -3g (iii) 4.680g (iv) 46.80g
Correct Answer: (i) 4.7g Explanation: Given, Density of solution = 3.12 g mL-1 Volume of solution = 1.5 mL Formula for Mass = Volume × Density Hence, Mass = 4.7 g
The empirical formula and molecular mass of a compound are CH2O and 180 g respectively. What will be the molecular formula of the compound? (i) C9H18O9 (ii) CH2O (iii) C6H12O6 (iv) C2H4O2
Correct Answer: (iii) C6H12O6 Explanation: Given, Molar mass of Carbon=12 Molar mass of Hydrogen=1 Molar mass of Oxygen=16 So, The molecular weight of compound is 6 and so the molecular formula of...
What is the mass per cent of carbon in carbon dioxide? (i) 0.034% (ii) 27.27% (iii) 3.4% (iv) 28.7%
Correct Answer: (ii) 27.27% Explanation: Carbon dioxide is a gas with a density of about 53% higher than that of dry air. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a double carbon atom combined with two...
What will be the molality of the solution containing 18.25 g of HCl gas in 500 g of water? (i) 0.1 m (ii) 1 M (iii) 0.5 m (iv) 1 m
Correct Answer: (iv) 1 m Explanation: According to molality of a substance which is the number of mass of solute per mass of the solvent in liters, the molality of the solution containing 18.25 g of...
If the concentration of glucose (C6H12O6) in the blood is 0.9 g L-1, what will be the molarity of glucose in the blood? (i) 5 M (ii) 50 M (iii) 0.005 M (iv) 0.5 M
Correct Answer: (iii) 0.005 M Explanation: According to the molarity of a substance which is defined as the number of moles per volume of the solution in litres, the molarity of the glucose in blood...
The number of atoms present in one mole of an element is equal to Avogadro number. Which of the following element contains the greatest number of atoms? (i) 4g He (ii) 46g Na (iii) 0.40g Ca (iv) 12g He
Correct Answer: (iv) 12g He Explanation: The number of atoms present in 4g of Helium – 1 NA The number of atoms present in 46g of Sodium - 2 NA The number of atoms present in 0.04g of Calcium – 0.01...
If 500 mL of a 5M solution is diluted to 1500 mL, what will be the molarity of the solution obtained? (i) 1.5 M (ii) 1.66 M (iii) 0.017 M (iv) 1.59 M
Correct Answer: (ii) 1.66 M Explanation: According to the Using M1V1= M2V2 formula, the value of M2 is 1.66 M.
1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is extended from the state (1) to state (2) as displayed in Fig. 6.4. Ascertain the turn out accomplished for the development of gas from the state (1) to state (2) at 298 K.
solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} W=\text{ }\text{ }2.303nRT\text{ }log\text{ }\left( p1/p2 \right) \\ ~ \\ =\text{ }\text{ }2.303\text{ }\times \text{ }1\text{ }mol\text{ }\times \text{...
Enthalpy graph for a specific response is given in Fig. Is it conceivable to choose the immediacy of a response from the given chart? Clarify.
solution: From the given enthalpy outline it tends to be said the adjustment of enthalpy ∆H is positive for the response, for example it will be endothermic. In any case, when goes to the suddenness...
Address the likely energy/enthalpy change in the accompanying cycles graphically. (a) Throwing a stone starting from the earliest stage rooftop. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( b \right)\text{ }1/2\text{ }H2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }1/2\text{ }Cl2\left( g \right)\leftrightharpoons HCl\left( g \right)\Delta rH\Theta =92.32\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2732efbedd48f360b154aff012982f0c_l3.png)
In which of the cycles likely energy/enthalpy change is contributing variable to the immediacy?
solution: Among these two cycles, simultaneously or response (b) the expected energy/enthalpy change is contributing component to the immediacy.
How might you ascertain work done on an optimal gas in a pressure, when an adjustment of tension is completed in boundless advances?
solution: At the point when an optimal gas in a pressure, where the adjustment of tension is completed in boundless advances for example through a reversible interaction, the work done can be...
ideal gas encased in a chamber, when it is compacted by steady outer strain, pext in a solitary advance as displayed in Fig? Clarify graphically.
solution: From this chart we can get the be the work done on the ideal gas encased in the chamber in 1 stage: the region covered by P-V diagram (concealed locale) is the real worth of the...
An example of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a cyclic interaction of extension and pressure as displayed in Fig. What will be the worth of ∆H for the cycle in general?
solution: In the accompanying cyclic ( 1 → 2 →3 →1 ) measure the underlying and last point is something very similar (for example 1). Subsequently the enthalpy change or\[H=\text{ }0\]...
The strain volume work for an ideal gas can be determined by utilizing the articulation w= ʃPexdv. The work can likewise be determined from the pV–a plot by utilizing the region under the bend inside as far as possible. At the point when an ideal gas is compacted (a) reversibly or (b) irreversibly from volume Vi to Vf. pick the right alternative. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( I \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }=\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right) \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }<\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right) \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }>\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right) \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }=\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right)\text{ }+\text{ }pex.V \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cd21a1dca804f61b0640fc61b9848d76_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( I \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }=\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right) \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }<\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right) \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }>\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right) \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }w\text{ }\left( reversible \right)\text{ }=\text{ }w\text{ }\left( irreversible \right)\text{ }+\text{ }pex.V \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cd21a1dca804f61b0640fc61b9848d76_l3.png)
Arrangement: Alternative (ii) is the appropriate response. w (reversible) < w (irreversible) Region under the bend is more noteworthy in irreversible pressure than that of reversible...
An ideal gas is permitted to grow against a consistent strain of 2 bar from 10 L to 50 L in one stage. Compute the measure of work done by the gas. In the event that a similar development were done reversibly, will the work is done be higher or lower than the prior case? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( Considering\text{ }that\text{ }1\text{ }L\text{ }bar\text{ }=\text{ }100J \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8331e87f2ad28a3aa312920b78f9ba7f_l3.png)
solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Measure\text{ }of\text{ }work\text{ }done\text{ }=\text{ }-\text{ }pext\text{ }V \\ ~ \\ =\text{ }\text{ }2\text{ }bar\text{ }\times \text{ }\left(...
The enthalpy of response for the response : ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[2H2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }O2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2H2O\left( l \right)\text{ }is\text{ }Hr\Theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }572\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8d6c7a9cb211975cf0d634a1d03b0573_l3.png)
What will be standard enthalpy of development of H2O (l)?
solution: For the given response : \[2H2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }O2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to 2H2O\left( l \right)\] the standard enthalpy of response is \[Hr\Theta \text{ }=\text{...
The enthalpy of vapourisation of CCl4 is 30.5 kJ mol–1. Compute the warmth needed for the vapourisation of 284 g of CCl4 at steady tension. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( Molar\text{ }mass\text{ }of\text{ }CCl4\text{ }=\text{ }154\text{ }g\text{ }mol1 \right).\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-604d3d18d37df5c65742bf95bae2d83d_l3.png)
solution: The enthalpy of vapourisation is given \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} for\text{ }1\text{ }mole\text{ }of\text{ }CCl4\text{ }=\text{ }30.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\...
The net enthalpy change of a response is the measure of energy needed to break every one of the bonds in reactant atoms less the measure of energy needed to shape every one of the bonds in the item particles. What will be the enthalpy change for the accompanying response? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[H2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }Br2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2HBr\left( g \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6781e80aeb9eec44245bdbf15b422c68_l3.png)
Considering that Bond energy of H2, Br2 and HBr is 435 kJ mol–1, 192 kJ mol–1 and 368 kJ mol–1 separately.
solution: For the response \[H2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }Br2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to 2HBr\left( g \right)\] \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Enthalpy\text{ }change \\ ~ \\ =\text{...
On the off chance that the burning of 1g of graphite produces 20.7 kJ of warmth, what will be molar enthalpy change? Offer the meaning of the hint too.
solution: The warmth of ignition ∆Hc of graphite (for example carbon) is given as \[=\text{ }20.7\text{ }kJ\] for 1g of graphite (C). \[1\text{ }mole\text{ }of\text{ }Carbon\text{...
The contrast among CP and CV can be inferred utilizing the experimental connection ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[H\text{ }=\text{ }U\text{ }+\text{ }PV\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-30f978ca15c7de7187e41cd4fbcf8a4b_l3.png)
. Work out the distinction among CP and CV for 10 moles of an optimal gas.
solution: For an optimal gas, the distinction between these two \[is\text{ }CP\text{ }\text{ }CV\text{ }=\text{ }nR,\] the all inclusive gas consistent and \[where\text{ }n=\text{ }no.\text{...
If the charge on an electron is 1.6 × 10-19 coulombs, how many electrons should pass through a conductor in 1 second to constitute 1 ampere current?
Given, Charge moved $=1.6 \times 10^{-19}$ coulombs Current, I $=1 \mathrm{~A}$ Time taken, $t=1 \mathrm{~s}$ We know that, $\text{I}=\text{Q}/\text{t}$ $1=\text{Q}/1$ $\text{Q}=1\text{C}$ We also...
Warmth limit (Cp) is a broad property yet explicit warmth (c) is an escalated property. What will be the connection between Cpand c for 1 mol of water?
solution: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} For\text{ }water,\text{ }molar\text{ }warmth\text{ }limit\text{ }=\text{ }18\text{ }x\text{ }Specific\text{ }warmth\text{ }or \\ ~ \\ Cp~=\text{...
Development of gas in a vacuum is called free extension. Ascertain the work is done and the adjustment of inner energy when 1 liter of an ideal gas grows isothermally into a vacuum until its complete volume is 5 liter?
solution: Work done in vacuum is determined by : \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} -\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }Text\text{ }\left( Vinitial\text{ }\text{ }Vfinal\text{ } \right) \\ ~ \\...
Despite the fact that warmth is a way work yet warms consumed by the framework under certain particular conditions is free of way. What are those conditions? Clarify.
solution: Warmth is free of the way under 2 conditions: At the point when the volume of the framework is kept steady By first law of thermodynamics: ...
Foresee the adjustment of inward energy for a secluded framework at steady volume.
solution: For a disengaged framework \[q=0\text{ }and\text{ }w=0\] What's more, as indicated by first law of thermodynamics: \[U=\text{ }q\text{ }+\text{ }w\text{ }\left(...
Which amount out of ΔrG and ΔrGΘwill be zero at harmony?
solution: Gibbs energy for a response in which all reactants and items are in standard state. ΔrG° is identified with the harmony consistent of the response as follows ...
The molar enthalpy of vapourisation of CH3)2CO is not exactly that of water. Why?
solution: Water has solid hydrogen bonds and the high extremity likewise accumulates in coming about it to bubble at higher temperatures. Thus water has a higher molar enthalpy than CH3)2CO....
Distinguish the state capacities and way works out of the accompanying : enthalpy, entropy, heat, temperature, work, free energy.
solution: State capacities: enthalpy, entropy, temperature and free energy. Way works: Heat and work
The standard molar entropy of H2O (l ) is 70 J K–1 mol–1. Will the standard molar entropy of H2O(s) be more, or under 70 J K–1 mol–1?
solution: The standard molar entropy of H20 (1) is 70 J K-1 mol-1. The strong type of H20 is ice. In ice, atoms of H20 are less irregular than in fluid water. In this way, molar entropy of...
As warm harmony complies with the zeroth law of thermodynamics, temperature of framework and environmental elements will be a similar when they are in warm balance.
solution: For the given response \[N2O4\text{ }\left( g \right)\leftrightharpoons 2NO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }the\text{ }worth\text{ }of\text{ }Kp\text{ }=\text{ }0.98.\]...
Expansion in enthalpy of the environmental elements is equivalent to the lessening in enthalpy of the framework. Will the temperature of the framework and environmental elements be a similar when they are in warm balance?
solution: As warm balance submits to the zeroth law of thermodynamics, temperature of framework and environmental factors will be a similar when they are in warm balance.
The warmth affects a framework and temperature is the proportion of normal tumultuous movement of particles in the framework. Compose the numerical connection which relates these three boundaries.
solution: The numerical connection which relates these three boundaries is \[\Delta S\text{ }=\text{ }qrev/T\] where ΔS is the adjustment of entropy and T represents...
. Utilize the accompanying information to ascertain Δlattice Hθfor NaBr. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \Delta sub\text{ }H\theta for\text{ }sodium\text{ }metal\text{ }=\text{ }108.4\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ Ionization\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }sodium\text{ }=\text{ }496\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ Electron\text{ }acquire\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }bromine\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }325\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ Bond\text{ }separation\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }bromine\text{ }=\text{ }192\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \Delta f\text{ }H\theta for\text{ }NaBr\text{ }\left( s \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }360.1\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e26257ae943a58e5b93fe8059b1e1238_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \Delta sub\text{ }H\theta for\text{ }sodium\text{ }metal\text{ }=\text{ }108.4\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ Ionization\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }sodium\text{ }=\text{ }496\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ Electron\text{ }acquire\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }bromine\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }325\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ Bond\text{ }separation\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }bromine\text{ }=\text{ }192\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \Delta f\text{ }H\theta for\text{ }NaBr\text{ }\left( s \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }360.1\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e26257ae943a58e5b93fe8059b1e1238_l3.png)
solution: Sublimation of the metal(ΔsubHΘ) →Ionization of the metal (ΔiHΘ) →Dissociation of the non-metal (ΔdissHΘ) →Gain of electrons by the non-metal(ΔegHΘ) \[\Delta f\text{ }H\theta...
The enthalpy of atomisation for the response ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH4\left( g \right)\to \text{ }C\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }4H\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }is\text{ }1665\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-50889d40215348f358defd7ebfa19015_l3.png)
. What is the bond energy of the C–H bond?
solution: For 1 C-H bond, the bond energy will be equivalent to 1/4 that of the enthalpy of atomisation \[=\text{ }\left( 1665/4 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }416.25\text{ }kJ\text{...
. Enthalpy is a broad property. As a rule, if the enthalpy of a general response A→B along one course is Δr H and Δr H1, ΔrH2, ΔrH3 … .. address enthalpies of middle responses prompting item B. What will be the connection between ΔrH for generally speaking response and ΔrH1, ΔrH2… .. and so forth for moderate responses.
solution: For the response, A→B the development of B goes through a few middle of the road responses with various enthalpy esteems Δr H1, ΔrH2, ΔrH3… .., and the general enthalpy change is Δr...
. The worth of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\Delta fH\Theta for\text{ }NH3\text{ }is\text{ }\text{ }91.8\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1b9eb484f00117499f2332746d6bffcd_l3.png)
. Compute the enthalpy change for the accompanying response : ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[2NH3\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }N2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3H2\left( g \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-622a4b989965f3ae76c2a96693b81e2c_l3.png)
solution: Enthalpy change of a response is determined as : Σbond enthalpy of reactants-Σbond enthalpy of items for the deterioration \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2NH3\left( g...
Standard molar enthalpy of arrangement, Δf Hθis simply a unique instance of enthalpy of response, Δr Hθ. Is the Δr Hθfor the accompanying response same as Δf Hθ? Offer the justification behind your response. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CaO\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }CO2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CaCO3\left( s \right)\text{ };\text{ }\Delta fH\Theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }178.3\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-09765da93303511a8d85bc4ef9576452_l3.png)
solution: The given response \[CaO\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }CO2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to CaCO3\left( s \right)\] is demonstrating that it is happening in the standard type of 1 mole...
. One mole of CH3)2CO requires less warmth to disintegrate than 1 mol of water. Which of the two fluids has a higher enthalpy of vapourisation?
solution: Among the two fluids, water has a higher enthalpy of vapourisation (burning-through higher warmth energy). Thusly, ∆Hvapourisation (water) > ∆Hvapourisation...
18.0 g of water totally vapourises at 100°C and 1 bar pressure and the enthalpy change in the process is 40.79 kJ mol–1. What will be the enthalpy change for vapourising two moles of water under similar conditions? What is the standard enthalpy of vapourisation for water?
solution: Enthalpy change of vapourisation for \[1\text{ }mole\text{ }=\text{ }40.79\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\] enthalpy change of vapourisation for \[2\text{ }moles\text{ }of\text{ }water\text{...
. Think about the accompanying response among zinc and oxygen and pick the right alternatives out of the choices given underneath : ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[2\text{ }Zn\text{ }\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2\text{ }ZnO\text{ }\left( s \right)\text{ };\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }693.8\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-21eecefaac280bd02b037eefe5eb121b_l3.png)
(i) The enthalpy of two moles of ZnO is not exactly the absolute enthalpy of two moles of Zn and one mole of oxygen by 693.8 kJ. (ii) The enthalpy of two moles of ZnO is more than the absolute enthalpy of two moles of Zn and one mole of oxygen by 693.8 kJ. (iii) 693.8 kJ mol–1 energy is advanced in the response. (iv) 693.8 kJ mol–1 energy is caught up in the response.
solution: Choice (I) and (iii) are the appropriate responses
. For an optimal gas, crafted by reversible extension under isothermal condition can be determined by utilizing the articulation ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[w\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }nRT\text{ }ln\text{ }Vf/Vi\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-000900d27450b7c6bf2488384463f995_l3.png)
An example containing 1.0 mol of an ideal gas is extended isothermally and reversibly to multiple times of its unique volume, in two separate tests. The extension is completed at 300 K and 600 K separately. Pick the right alternative. (I) Work done at 600 K is multiple times the work done at 300 K. (ii) Work done at 300 K is double the work done at 600 K. (iii) Work done at 600 K is double the work done at 300 K. (iv) ∆U = 0 in the two cases.
solution: Alternative (iii) and (iv) are the appropriate responses. work done at 600 K is double the work done at 300 K. Since each case includes isothermal extension of an optimal gas, there...
The immediacy implies, having the capacity to continue without the help of an outer organization. The cycles which happen immediately are (I) stream of warmth from colder to hotter body. (ii) gas in a compartment contracting into one corner. (iii) gas extending to fill the accessible volume. (iv) consuming carbon in oxygen to give carbon dioxide.
solution: Alternative (iii) and (iv) are the appropriate responses. Gas grows or diffuses in accessible space suddenly, e.g., spillage of cooking gas gives smell of ethyl mercaptan...
In an exothermic response, heat is advanced, and the framework loses warmth to the encompassing. For such a framework (I) qp will be negative (ii) ∆rH will be negative (iii) qp will be positive (iv) ∆rH will be positive
solution: Choice (I) and (ii) are the appropriate responses. For an exothermic response\[,\text{ }qp~=\text{ }-\text{ }ve,\text{ }\gamma H\text{ }=\text{ }-\text{ }ve\]
. Thermodynamics essentially manages (I) interrelation of different types of energy and their change from one structure to another. (ii) energy changes in the cycles which rely just upon starting and last conditions of the minute frameworks containing a couple of particles. (iii) how and at what rate these energy changes are done. (iv) the framework in harmony state or moving from one balance state to another harmony state.
solution: Alternative (I) and (iv) are the appropriate responses. Thermodynamics manages interrelation of different types of energy and their change into one another. It additionally manages...
. Which of coming up next isn’t right? (I) ∆G is zero for a reversible response (ii) ∆G is positive for an unconstrained response (iii) ∆G is negative for an unconstrained response (iv) ∆G is positive for a non-unconstrained response
solution: Alternative (ii) is the appropriate response. ∆G gives a basis for suddenness at consistent strain and temperature. (I) If ∆G is negative (< 0). the cycle is...
. Enthalpy of sublimation of a substance is equivalent to (I) enthalpy of combination + enthalpy of vapourisation (ii) enthalpy of combination (iii) enthalpy of vapourisation (iv) double the enthalpy of vapourisation
solution: Choice (I) is the appropriate response. Enthalpy of sublimation of a substance is equivalent to enthalpy of combination + enthalpy of vapourisation. Sublimation is immediate...
The enthalpies of components in their standard states are taken as nothing. The enthalpy of arrangement of a compound (I) is consistently negative (ii) is consistently sure (iii) possibly certain or negative (iv) is rarely negative
solution: Choice (iii) is the appropriate response. Warmth of arrangement of a compound might be positive or negative.
. Consider the responses given beneath. Based on these responses discover which of the arithmetical relations given in choices (I) to (iv) is right? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( a \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }4\text{ }H\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CH4\text{ }\left( g \right);\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( b \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite,s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }2H2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CH4\text{ }\left( g \right);\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( I \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }2y \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }>\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }x\text{ }<\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-81745156192de5b4c48715895f94ae78_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( a \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }4\text{ }H\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CH4\text{ }\left( g \right);\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( b \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite,s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }2H2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CH4\text{ }\left( g \right);\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( I \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }2y \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }>\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }x\text{ }<\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-81745156192de5b4c48715895f94ae78_l3.png)
solution: Choice (iii) is the appropriate response. x > y because same bonds are formed in reactions (i) and (ii) but bonds between reactant molecules are broken only in reaction...
Based on thermochemical conditions (a), (b) and (c), discover which of the logarithmic connections given in alternatives (I) to (iv) is right. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( a \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite \right)\text{ }+\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( b \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite \right)\text{ }+12\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CO\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( c \right)\text{ }CO\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+12\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }z\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( I \right)\text{ }z\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }\text{ }z \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }+\text{ }z \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }y\text{ }=\text{ }2z\text{ }\text{ }x \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b40f2fc005f6abbd16305bc1f8b64ffb_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( a \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite \right)\text{ }+\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( b \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite \right)\text{ }+12\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CO\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( c \right)\text{ }CO\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+12\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH\text{ }=\text{ }z\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( I \right)\text{ }z\text{ }=\text{ }x\text{ }+\text{ }y \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }\text{ }z \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }x\text{ }=\text{ }y\text{ }+\text{ }z \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }y\text{ }=\text{ }2z\text{ }\text{ }x \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b40f2fc005f6abbd16305bc1f8b64ffb_l3.png)
solution: Choice (iii) is the appropriate response. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( a \right)\text{ }C\text{ }\left( graphite \right)\text{ }+\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to...
The entropy change can be determined by utilizing the articulation ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[S\text{ }=\text{ }qrev/T\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6bfe39a02f4a03c24c6a8eb9d86768e8_l3.png)
At the point when water freezes in a glass container, pick the right assertion among the accompanying : (I) ∆S (framework) diminishes however ∆S (environmental factors) stays as before. (ii) ∆S (framework) increments yet ∆S (environmental elements) diminishes. (iii) ∆S (framework) diminishes yet ∆S (environmental elements) increments. (iv) ∆S (framework) diminishes and ∆S (environmental factors) likewise diminishes.
solution: Alternative (iii) is the appropriate response. During the method involved with freezing energy is released,which is consumed by the environmental factors. Therefore,the entropy off...
In an adiabatic interaction, no exchange of warmth happens among framework and environmental elements. Pick the right choice with the expectation of complimentary extension of an optimal gas under adiabatic condition from the accompanying. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( I \right)\text{ }q\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }\ne \text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }q\text{ }\ne \text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }q\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }q\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }<\text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }\ne \text{ }0 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f414484974ac2116baf9c7e280488609_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( I \right)\text{ }q\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }\ne \text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }q\text{ }\ne \text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }q\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }=\text{ }0 \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }q\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }T\text{ }<\text{ }0,\text{ }w\text{ }\ne \text{ }0 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f414484974ac2116baf9c7e280488609_l3.png)
solution: Choice (iii) is the appropriate response. With the expectation of complimentary extension w = 0 For adiabatic cycle q = 0 From first law of thermodynamics, ...
. ∆fUᶱ of arrangement of CH4 (g) at certain temperature is – 393 kJ mol–1. The worth of ∆ fHᶱ is (I) zero (ii) < ∆f Uᶱ (iii) > ∆f Uᶱ (iv) equivalent to ∆f Uᶱ
solution: Choice (ii) is the appropriate response.
During complete burning of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of warmth is delivered. The thermochemical response for above change is ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( I \right)\text{ }2C4H10\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }13O2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }8CO2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }10H2O\left( l \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }2658.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }C4H10\left( g \right)\text{ }+13/2\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }4CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }5H2O\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }1329.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }C4H10\left( g \right)\text{ }+13/2\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }4CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }5H2O\text{ }\left( l \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }2658.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }C4H10\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+13/2\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }4CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }5H2O\text{ }\left( l \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }+2658.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77b9f5a9cfe475e02540c7538497ae67_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( I \right)\text{ }2C4H10\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }13O2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }8CO2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }10H2O\left( l \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }2658.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( ii \right)\text{ }C4H10\left( g \right)\text{ }+13/2\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }4CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }5H2O\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }1329.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( iii \right)\text{ }C4H10\left( g \right)\text{ }+13/2\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }4CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }5H2O\text{ }\left( l \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }2658.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ \left( iv \right)\text{ }C4H10\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+13/2\text{ }O2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }4CO2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }5H2O\text{ }\left( l \right)\text{ }cH\text{ }=\text{ }+2658.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-77b9f5a9cfe475e02540c7538497ae67_l3.png)
solution: Choice (iii) is the appropriate response. Exothermic reaction for combustion of one mole of butane is represented as \[\left( iii \right)\text{ }C4H10\left( g \right)\text{...
. The volume of gas is decreased to half from its unique volume. The particular warmth will be ______. (I) decrease to half (ii) be multiplied (iii) stay consistent (iv) increment multiple times
solution: Alternative (iii) is the appropriate response. The particular warmth of a substance is the warmth needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by one degree (1 K or 1...
The condition of a gas can be portrayed by citing the relationship between___. (I) pressure, volume, temperature (ii) temperature, sum, pressure (iii) the sum, volume, temperature (iv) pressure, volume, temperature, sum
solution: Alternative (iv) is the appropriate response. Condition of a framework can be portrayed by state capacities or state factors which are pressure, volume, temperature and measure of...
Which of the accompanying assertions is right? (I) The presence of responding species in a covered measuring utencil is an illustration of an open framework. (ii) There is a trade of energy just as a matter between the framework also, the environmental elements in a shut framework. (iii) The presence of reactants in a shut vessel made down of copper is an illustration of a shut framework. (iv) The presence of reactants in a canteen jar or some other shut protected vessel is an illustration of a shut framework.
solution: Alternative (iii) is the appropriate response. For a shut vessel made down of copper, regardless of can be traded between the framework and the environmental elements however energy trade...
Which of the following is the correct order of the size of the given species:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[~\left( \mathbf{i} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{I}\text{ }>\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{-}}>\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{+}}^{{}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7a8b80587c7e4bf72c9cd196715177bc_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{ii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{I}+>\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{-}}>\text{ }\mathbf{I}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a7464c368804f0a28cde1894bd32bb60_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iii} \right)\text{ }\mathbf{I}\text{ }>\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{+}}>\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{-}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-61edf3a246a74100367d9431971a553f_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( \mathbf{iv} \right)\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{-}}>\text{ }\mathbf{I}\text{ }>\text{ }{{\mathbf{I}}^{+}}^{{}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7de79f7e5e8187314bd7962083407d61_l3.png)
Option (iv) is the answer. The size of an anion, cation, and neutral species for a given element is in this order: anion>element>cation. Because of its higher z-effective, cation has the...
The elements in which electrons are progressively filled in 4f-orbital are called
(i) actinoids
(ii) transition elements
(iii) lanthanoids
(iv) halogens
Option (iii) is the answer. In lanthanoids, the 4f orbital is gradually filled with electrons. Lanthanoids have a broad electrical configuration. [Xe]4f 1-145d0-16s2.
The period number in the long form of the periodic table is equal to
(i) magnetic quantum number of any element of the period.
(ii) an atomic number of any element of the period.
(iii) maximum Principal quantum number of any element of the period.
(iv) maximum Azimuthal quantum number of any element of the period.
Option (iii) is the answer. Period number = maximum n of any element where 'n' stands for the principle quantum number. It determines the element's period number. Mg, for example, has a maximum main...
Explain the following terms with one example each. (a) Corrosion (b) Rancidity
Answer: (a) Corrosion occurs when oxygen oxidizes a refined metal to generate oxides. During corrosion, the metal steadily deteriorates. Iron rusting is a type of corrosion that converts iron to...
Oil and Fat containing food items are flushed with Nitrogen. Why?
Answer: The primary goal of flushing Nitrogen into food packages that contain oil and fat items is to prevent rancidity, which occurs when the oil or fat reacts with oxygen, releasing an unpleasant...
Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer: To keep iron goods from rusting, they are painted with a protective coating. When a metal surface is left unpainted, it comes into contact with the oxygen in the air and, in the presence of...
A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in the air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer: Copper is the metallic element with a gleaming brown sheen to it (Cu). When copper is heated in the presence of oxygen, copper oxide is formed as a result of the reaction with the oxygen in...
Explain the following in terms of gain of oxygen with two examples each. (a) Oxidation (b) Reduction
Answer: (a) When oxygen is added to an element to generate the element's respective oxide, the element being oxidised is the element being oxidised in the chemical reaction. Example: 4Na(s) + O2(g)...
What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Answer: When two soluble salt solutions are mixed, the ions are exchanged between the compounds in a twofold displacement reaction. When one of these chemicals is solid (insoluble in water), it...
In the refining of Silver, the recovery of silver from Silver nitrate solution involves displacement reaction by Copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer: Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s) Explanation: As the name implies, a displacement reaction involves the displacement of an atom by another atom. The general displacement response...
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write relevant equations for the above.
Answer: A displacement reaction occurs when a more reactive substance displaces a less reactive chemical from its salt solution, while a double displacement reaction occurs when two compounds...
Write one equation each for decomposition reactions in which energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity. Solution:
Answer: a) Thermochemical decomposition (Thermolysis) Potassium chlorate decomposes into potassium chloride and oxygen when heated to high temperatures. This reaction produces oxygen. 2KClO3 + Heat...
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of Combination reactions? Write equations for decomposition reactions.
Answer: A combination process occurs when two or more molecules combine to produce a larger molecule, whereas a decomposition reaction occurs when larger molecules break into two or more smaller...
Why is respiration considered to be an exothermic reaction?
Answer: We need the energy to live. We get this energy from our food. During digestion, food molecules are broken down into simpler molecules like glucose. These molecules react with oxygen in our...
What is meant by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer: When energy is taken from the surrounding environment in the form of heat, an endothermic process takes place. (For example, photosynthesis, ice melting, and evaporation are all examples of...
Write a balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction of each case
1. KBr + BaI2 → KI + BaBr2
2. ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
3. H2 + Cl → HCl
4. Mg + HCl → MgCl2 + H
Answer: When solving an equation for a chemical reaction, a balanced equation is one where the number of atoms for each element in the reaction, as well as the total charge, for both the reactants...
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following reactions.
1. Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide —-> Calcium carbonate + Water
2. Zinc + Silver nitrate —-> Zinc nitrate + Silver
3. Aluminium + Copper chloride —-> Aluminium chloride + Copper
4. Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate —-> Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer: When solving an equation for a chemical reaction, a balanced equation is one where the number of atoms for each element in the reaction, as well as the total charge, for both the reactants...
Balance the following chemical equations.
(a) 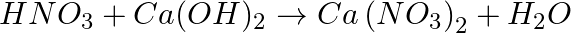 (b)
(b) 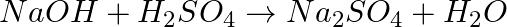 (c)
(c) 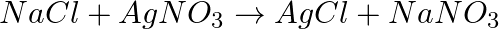 (d)
(d) 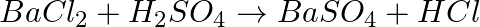
Answer: When solving an equation for a chemical reaction, a balanced equation is one where the number of atoms for each element in the reaction, as well as the total charge, for both the reactants...
Which of the following is not an actinoid?
(i) Curium (Z = 96)
(ii) Californium (Z = 98)
(iii) Uranium (Z = 92)
(iv) Terbium (Z = 65)
Option (iv) is the answer. Any group of 15 elements in the periodic table, ranging from actinium to lawrencium (atomic numbers 89–103), is known as an actinoid element. As evident from the...
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and balance them. (c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give Aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate. (d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and Hydrogen gas.
Answer: (c) Unbalanced: BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → AlCl3 + BaSO4 Balanced: 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4 (d) Unbalanced: K + H2O → KOH + H2 Balanced: 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH +...
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
Answer: (a) Unbalanced: H2 + N2 → NH3 Balanced: 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3 (b) Unbalanced: H2S + O2 → H2O + SO2 Balanced: 2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O + 2SO2
What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should a chemical equation be balanced?
Answer: When there are the same number of distinct atoms on both the reactant and product sides of an equation, it is said to be "balanced." It is required to have a balanced chemical equation in...
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? Tick the correct answer.
1. Hydrogen gas and Iron chloride are produced.
2. Chlorine gas and Iron hydroxide are produced.
3. No reaction takes place.
4. Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer: Option 1) is correct. An explanation is given below. The Chlorine from Hydrogen chloride is displaced by the Iron fillings, resulting in the subsequent reaction. 2HCl + Fe → FeCl2 +...
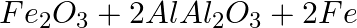
The above reaction is an example of a) Combination reaction. Double displacement reaction. Decomposition reaction. Displacement reaction.
Answer: Option d) This displacement of oxygen from the ferrous oxide to the aluminum metal forms Aluminium Oxide. Aluminum reacts faster than Fe in this reaction. So Al displaces Fe from its oxide....
Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect? 2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced
(b) Carbon Dioxide is getting oxidised
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all
Answer: With the aforementioned reaction, lead oxide (PbO) is reduced to lead and carbon (C) is oxidised to form carbon dioxide (CO2). As a result, both statements (a) and (b) are correct. As a...
Identify the substances that are oxidized and that are reduced in the following equation. i) 4Na(s) + 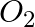 (g) →
(g) → 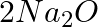 (s) ii) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
(s) ii) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l)
Answer: The chemical that has been oxidised is referred to as a reduction agent. The chemical that has been reduced is referred to as an oxidising agent. (i) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s) Oxidized...
Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Answer: Reaction It is possible to have a double displacement reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl) in certain circumstances. It is discovered that negative and positive...
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Answer: A copper sulphate solution is formed when an iron nail is dipped in it, and the iron displaces the copper from the copper sulphate solution due to the fact that iron is more reactive than...
Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes in Activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas
Answer: In activity 1.7, the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes is twice the amount collected in the other, due to the hydrolysis of water, which results in the release of H2 and O2...
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing. (i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
Answer: (i) The whitewashing solution is calcium oxide (CaO), often known as quicklime. Quicklime is used for whitewashing because it combines with water to form calcium hydroxide (CaOH) and absorbs...
Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions
i) Solutions of Barium chloride and Sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble Barium sulphate and solution of Sodium chloride.
ii) Sodium hydroxide solution in water reacts with hydrochloric acid solution to produce Sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer: A chemical equation represents a chemical process as a collection of substances. A balanced chemical equation has the same number of atoms on both sides of the equation. i) BaCl2 + Na2SO4 →...
Write a balanced equation for the following chemical reactions: iii) Sodium + Water —-> Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer: A chemical equation represents a chemical process as a collection of substances. A balanced chemical equation has the same number of atoms on both sides of the equation. (iii) 2Na(s) + 2H2O...
Write a balanced equation for the following chemical reactions. i) Hydrogen + Chloride —-> Hydrogen chloride ii) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate —> Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
A chemical equation represents a chemical process as a collection of substances. A balanced chemical equation has the same number of atoms on both sides of the equation. (i) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl...
An element X belongs to group 2 and another element Y belongs to group 15 of the periodic table: (a) What is the number of valence electrons in X? (b) What is the valency of X? (c) What the number of valence electrons in Y? (d) What is the valency of Y? Explain how you have arrived at your answers.
(a) 2. For the group 1 and 2, the number of valence electrons is equal to the group number and in the 2nd group, it is equal to 2. (b) 2. Valency is determined by the number of valence electrons...
Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the periodic table. Write the electronic configurations of these two elements. Which of these will be more electronegative? Why?
The electronic configuration of nitrogen and phosphorous are as follows: N = (2,5) ; P = (2, 8, 5) Nitrogen will have more electronegativity because its atom has small size due to which the...
Fill in the blanks in the following statements: (a) The horizontal rows in a periodic table are called _______. (b) In going across a period (right to left) in periodic table, the atomic size of the atom _______. (c) On moving from right to left in the second period, the number of valence electrons _______. (d) On going down in a group in the periodic table, the metallic character of elements _______. (e) The tendency to gain an electron_______ on moving down in a group of the periodic table.
(a) Periods (b) Increases (c) Decreases (d) Increases (e) Decreases
Rewrite the following statements after correction, if necessary: (i) Elements in the same period have equal valency. (ii) The metallic character of elements in a period increases gradually on moving from left to right.
(i) Elements in the same group have equal valency. (ii)The metallic character of elements in a period decreases gradually on moving from left to right.
A metal salt MX when exposed to light splits up to form metal M and a gas X2. Metal M is used in making ornaments whereas gas X2 is used in making bleaching powder. The salt MX is itself used in black and white photography.
(a) What do you think metal M is?
(b) What could be gas X2?
(c) Name the metal salt MX.
(d) Name any two salt solutions which on mixing together can produce a precipitate of salt MX.
(e) What type of chemical reaction takes place when salt MX is exposed to light? Write the equation of the reaction.
(a) Silver is the metal X. (a) When MX salt is exposed to light, chlorine is produced as a gas. (c) MX is the metal salt silver chloride that is employed in black and white photography. (d) Silver...
When a strip of red-brown metal X is placed in a colourless salt solution YNO3 then metal Y is set free and a blue coloured salt solution X(NO3)2 is formed. The liberated metal Y forms a shining white deposit on the strip of metal X.
(a) What do you think metal X is?
(b) Name the salt YNO3.
(c) What could be metal Y?
(d) Name the salt X(NO3)2
(e) What type of reaction takes place between metal X and salt solution YNO3?
(a) Copper is the red-brown strip of metal X. (b) Silver nitrate is a colourless salt solution with the formula YNO3. (c) Silver is the metal that forms a shining white deposit on the strip metal X...
A red-brown metal X forms a salt XSO4. When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of XSO4, then a black precipitate of XS is formed along with sulphuric acid solution.
(a) What could the salt XSO4 be?
(b) What is the colour of salt XSO4?
(c) Name the black precipitate XS
(d) By using the formula of the salt obtained in (a) above, write an equation of the reaction which takes place when hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through its aqueous solution.
(e) What type of chemical reaction takes place in this case?
(a) Copper sulphate is be the salt formed named as XSO4. (b) The salt is blue in colour as it is copper sulphate (c) Copper sulphide is responsible for the black precipitate XS. (d) Chemical...
Two metals X and Y form the salts XSO4 and Y2SO4, respectively. The solution of salt XSO4 is blue in colour whereas that of Y2SO4 is colourless. When barium chloride solution is added to XSO4 solution, then a white precipitate Z is formed along with a salt which turns the solution green. And when barium chloride solution is added to Y2SO4 solution, then the same white precipitate Z is formed along with colourless common salt solution.
(a) What could the metals X and Y be?
(b) Write the name and formula of salt XSO4.
(c) Write the name and formula of salt Y2SO4.
(d) What is the name and formula of white precipitate Z?
(e) Write the name and formula of the salt which turns the solution green in the first case.
(a)Metal X is Copper and Metal Y is Sodium. Both produce sulphate salts on reaction. (b) XSO4 is Copper sulphate, CuSO4 , the salt formed which is blue in colour. (c) Y2SO4 is Sodium sulphate,...
A metal X forms a water soluble salt XNO3. When an aqueous solution of XNO3 is added to common salt solution, then a white precipitate of compound Y is formed alongwith sodium nitrate solution. Metal X is said to be the best conductor of electricity and it does not evolve hydrogen when put in dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) What is metal X ?
(b) What is salt XNO3?
(c) Name the compound Y.
(d) Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place on reacting XNO3 solution and common salt solution giving the physical states of all the reactants and products.
(e) What type of chemical reaction is illustrated by the above equation?
(a) Silver (Ag) is a conductor of electricity that does not produce hydrogen when exposed to dilute hydrochloric acid. (b) Silver nitrate (AgNO3) is XNO3 which reacts with NaCl (common salt) to give...
When a black metal compound XO is heated with a colourless gas Y2, then metal X and another compound Y2O are formed. Metal X is red-brown in colour which does not react with dilute acids at all. Gas Y2 can be prepared by the action of a dilute acid on any active metal. The compound Y2O is a liquid at room temperature which can turn anhydrous copper sulphate blue.
(a) What do you think is metal X?
(b) What could be gas Y 2?
(c) What is compound XO?
(d) What is compound Y2O?
(e) Write the chemical equation of the reaction which takes place on heating XO with Y2.
(f) What type of chemical reaction is illustrated in the above equation?
(a) Metal X is Copper (Cu) which is red-brown in colour and does not react with dilute acids. (b) Colorless gas Y2 is Hydrogen (H2). (c) Compound XO, a black metal compound is a Copper oxide (CuO)...
A strip of metal X is dipped in a blue coloured salt solution YSO4. After some time, a layer of metal Y from the salt solution is formed on the surface of metal strip X. Metal X is used in galvanisation whereas metal Y is used in making electric wires. Metal X and metal Y together form an alloy Z.
(a) What could metal X be?
(b) What could metal Y be?
(c) Name the metal salt YSO4
(d) What type of chemical reaction takes place when metal X reacts with salt solution YSO4? Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved.
(e) Name the alloy Z.
(a) Zn undergoes displacement reaction and is also used for galvanization. The evidences suggest that metal X is Zinc (Zn). (b) Copper is more reactive than Zn and displaces it while interacting....
When hydrogen burns in oxygen, water is formed and when water is electrolysed, then hydrogen and oxygen are produced. What type of reaction takes place?
(a) In the first case?
(b) In the second case?
(a) The formation of water as a result of a reaction involving hydrogen burning in oxygen gas is a type of combination reaction. (b) The decomposition reaction takes place in the second case...
A colourless lead salt, when heated, produces a yellow residue and brown fumes.
(a) Name the lead salt.
(b) Name the brown fumes.
(c) Write a chemical equation of the reaction involved
(a) Lead salt here is Lead nitrate. (b) Brown fumes are produced due to the production of Nitrogen dioxide. (c) Chemical equation for the reaction involved is: 2Pb(NO3)2→ 2PbO + 4NO2
When a green iron salt is heated strongly, its colour finally changes to brown and odour of burning sulphur is given out.
(a) Name the iron salt.
(b) Name the type of reaction that takes place during the heating of iron salt.
(c) Write a chemical equation for the reaction involved.
(a) Ferrous sulphate. (b) Decomposition reaction. Anhydrous ferrous sulphate is formed when a ferrous sulphate crystal loses water. It decomposes into ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide, and sulphur...
You are given the following chemical equation:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{Mg}\left( \mathbf{s} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{CuO}\left( \mathbf{s} \right)~\to \mathbf{MgO}\left( \mathbf{s} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{Cu}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{s} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6f995beaa02cb60c6c6f41fd202b467a_l3.png)
(a) Decomposition reaction as well as displacement reaction
(b) Combination reaction as well as double displacement reaction
(c) Redox reaction as well as displacement reaction
(d) Double displacement reaction as well as Redox reaction
The answer is option(c). Because magnesium is oxidised here and copper is reduced, a redox reaction. Also, Magnesium being more reactive displaces copper in the solution. As a result, displacement...
Consider the reaction:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{KBr}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{aq} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{AgN}{{\mathbf{O}}_{\mathbf{3}~}}\left( \mathbf{aq} \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }\mathbf{KN}{{\mathbf{O}}_{\mathbf{3}~}}\left( \mathbf{aq} \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\mathbf{AgBr}\text{ }\left( \mathbf{s} \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1426359ca96caabcf611532f6230d500_l3.png)
This is an example of:
(a) Decomposition reaction
(b) Combination reaction
(c) Double displacement reaction
(d) Displacement reaction
Option (c) is the correct response. The given reaction is a type of double displacement reaction, in which ions are exchanged between both the reactants.
