Solution: Cyclo-octatetraene isn't planar yet is tub-molded. It is, in this manner, a non-planar framework having 8 n-electrons. In this manner, the atom isn't sweet-smelling as it doesn't contain a...
Clarify why the accompanying framework isn’t fragrant?
Solution: Because of the presence of sp3–hybridized carbon, the framework isn't planar. Further, it contains just four n-electrons, subsequently, the framework isn't fragrant on the grounds that it...
Clarify why the accompanying framework isn’t fragrant?
Solution: Because of the presence of a sp3-hybridized carbon, the framework isn't planar. It contains six n-electrons yet the framework isn't completely formed since all the six n-electrons don't...
What are the important conditions for any framework to be sweet-smelling?
Solution: The fundamental conditions for any fragrant framework are as per the following: (I) Firstly, the compound course of action or construction ought to be planar. (ii) The n-electrons are...
For what reason is benzene exceptionally steady however it contains three twofold bonds?
Solution: Benzene is a mixture of the resounding designs and it is displayed as: Every one of the six carbon molecules in benzene are hybridized to sp2.In benzene, every carbon particle's two...
Draw the cis and trans constructions of hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher b.p. what’s more, why?
Solution: Hex-2-ene is addressed as displayed beneath: Mathematical isomers of hex-2-ene are as per the following: A cis intensifies dipole second is equivalent to the amount of the C – CH3...
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Toluene
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Hexyne
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Pentene
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Compose synthetic conditions for the burning response of Butane
Solution: Burning responses might be characterized as an oxygen or oxygen response of a compound.
Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis results of an alkene? What is the primary equation of the alkene?
Solution: From the given data, the two ozonolysis results of an alkene are pentan-3-one and propanal. Assume the alkene given is A. The converse of the ozonolysis response is the thing that we get,...
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Compose IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Solution: From the data given it gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u when ' A ' goes through ozonolysis. The arrangement of an aldehyde's two moles recommends that the presence of...
An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a combination of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Compose construction and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Throughout ozonolysis, an ozonide is created as a halfway that has a cyclic construction; it goes through cleavage to give the eventual outcomes. Ethanal and pentan-3-one are acquired from the...
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis 1 – Phenylbut-1-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of 1 – Phenylbut-1-ene is displayed as The resulting IUPAC names of the items are : Item (I) benzaldehyde, and Item (II) propanal
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis 2-Ethylbut-1-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of 2-Ethylbut-1-ene is displayed as: The resulting IUPAC names of the items are: Item (I) pentan-3-one, and Item (II) methanal
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis 3, 4 – Dimethyl-hept-3-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of 3, 4-Dimethylhept-3-ene is displayed as: The item names resulting to IUPAC are: Item (I) butan-2-one, and Item (II) Pentan-2-one
Compose IUPAC names of the items acquired by the ozonolysis Pent-2-ene
Solution: Ozonolysis of Pent-2-ene is displayed as: The accompanying Product IUPAC names are: Item (I) ethanal, and Item (II) propanal.
compose primary equations and IUPAC names for all potential isomers having the quantity of the twofold or triple bond as demonstrated C5H8 (one triple bond)
Solution: The resulting primary isomers are likely for C5H8 with one triple bond: The IUPAC name of Compound (I) is Pent-1-yne, Compound (II) is Pent-2-yne, and Compound (III) is...
compose primary equations and IUPAC names for all potential isomers having the quantity of the twofold or triple bond as demonstrated C4H8 (one twofold bond)
Solution: The subsequent primary isomers with one twofold bond are plausible for C4H8: The IUPAC name of Compound (I) is But-1-ene, Compound (II) is But-2-ene, and Compound (III) is...
Write the IUPAC names of
Solution: 4-Ethyldeca-1, 5, 8-triene is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC names of
Solution: 5-(2-Methylpropyl)- decane is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC name of
Solution: 2-Methyl phenol is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC name of
Solution: 4-Phenyl but-1-ene is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC name of
Solution: 1, 3-Butadiene or Buta-1,3-diene is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC names of
Solution: Pen-1-ene-3-yne is the necessary IUPAC name
Write the IUPAC nameof ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}~\mathbf{CH}\text{ }=\text{ }\mathbf{C}\text{ }{{(\mathbf{C}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}})}_{\mathbf{2}}}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c63b9b35d0c7e5500238909182cb534b_l3.png)
Solution: 2-Methylbut-2-ene is the necessary IUPAC name
How would you represent the arrangement of ethane during chlorination of methane?
Solution: The methane chlorination measure works through a free extreme chain instrument. Stage 1: Initiation: The outcome starts with the hemolytic cleavage of Cl – Cl bond as: Stage 2:...
Before the neutrino hypothesis, the beta decay process was thought to be the transition 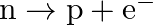 . If this was true, show that if the neutron was at rest, the proton and electron would emerge with fixed energies and calculate them. Experimentally, the electron energy was found to have a large range.
. If this was true, show that if the neutron was at rest, the proton and electron would emerge with fixed energies and calculate them. Experimentally, the electron energy was found to have a large range.
It is given that neutron was at rest before $\beta$ decay from neutron. So, energy of neutron $=$ $\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{n}}=\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{n}} \mathrm{c}^{2}$. Momentum of neutron...
Deuteron is a bound state of a neutron and a proton with a binding energy B = 2.2 MeV. A γ -ray of energy E is aimed at a deuteron nucleus to try to break it into a (neutron + proton) such that the n and p move in the direction of the incident γ-ray. If E = B, show that this cannot happen. Hence calculate how much bigger than B must E be for such a process to happen.
The binding energy of a deuteron is given as $B = 2.2 MeV$ The kinetic energies of neutron and proton be $K_n$ and $K_p$ $p_n$ and $p_p$ are the momentum of neutron and proton $E - B = K_n + K_p$ B...
Are the nucleons fundamental particles, or do they consist of still smaller parts? One way to find out is to probe a nucleon just as Rutherford probed an atom. What should be the kinetic energy of an electron for it to be able to probe a nucleon? Assume the diameter of a nucleon to be approximately 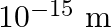 .
.
$\lambda=\mathrm{h} / \mathrm{p}$ and, kinetic energy $=$ potential energy $\mathrm{E}=\mathrm{hc} / \lambda$ Kinetic energy of an electron can be calculated as, $\mathrm{KE}=\mathrm{PE}=\mathrm{hc}...
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 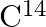 activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The
activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 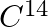 activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given the half-life of
activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given the half-life of 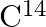 is 5760 years.
is 5760 years.
$\mathrm{C}^{14}$ activity of a piece of wood from the ruins is given as $\mathrm{R}=12 \mathrm{dis} / \mathrm{min}$ per gram $\mathrm{C}^{14}$ activity of a living wood is given as...
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. 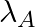 and
and 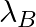 are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
(a) Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and 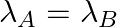
(b) Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and 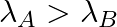
(c) Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and 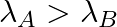
(d) Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at 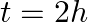 and
and 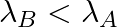
The correct options are: (b) Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and $\lambda _A>\lambda_B$ (d) Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at...
In a nuclear reactor, moderators slow down the neutrons which come out in a fission process. The moderator used to have light nuclei. Heavy nuclei will not serve the purpose because
(a) they will break up
(b) elastic collision of neutrons with heavy nuclei will not slow them down
(c) the net weight of the reactor would be unbearably high
(d) substances with heavy nuclei do not occur in a liquid or gaseous state at room temperature
The correct option is: (b) elastic collision of neutrons with heavy nuclei will not slow them down
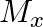 and
and 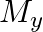 denote the atomic masses of the parent and the daughter nuclei respectively in a radioactive decay. The Q-value for a
denote the atomic masses of the parent and the daughter nuclei respectively in a radioactive decay. The Q-value for a 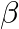 – decay is
– decay is 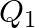 and that for a
and that for a 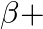 decay is
decay is 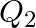 . If me denotes the mass of an electron, then which of the following statements is correct?
. If me denotes the mass of an electron, then which of the following statements is correct?
(a) 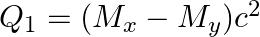 and
and 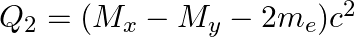
(b) 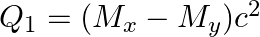 and
and 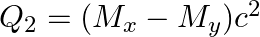
(c) 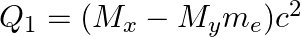 and
and 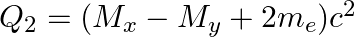
(d) 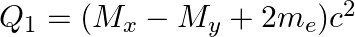 and
and 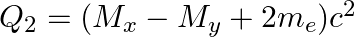
The correct option is: (a) $Q_ 1=(M _x-M_ y) c^{2}$ and $Q_ 2=(M _x-M_ y-2 m_ e) c^{2}$
Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
Answer: When two separate atoms join to form a covalent connection, their electrons are not shared equally. A more electronegative atom's nucleus attracts the bond pair. In this case, an...
Define electronegativity. How does it differ from electron gain enthalpy?
Answer: Sr. No Electronegativity Electron affinity 1 The electronegativity of an atom in a chemical compound refers to its proclivity to attract the shared pairs of electrons that are present in the...
Explain the important aspects of resonance with reference to the 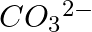 ion.
ion.
Answer: Although the properties of the carbonate ion cannot be described by a single structure, they can be described by two or more resonance structures. The carbonate ion's true structure is a...
Although geometries of NH3 and H2O molecules are distorted tetrahedral, bond angle in water is less than that of Ammonia. Discuss.
Answer: Ammonia's central atom (N) has 1 lone pair and 3 bond pairs. Water's central atom (O) has two lone pairs and two bond pairs. The two lone pairs on the O- atom of water reject the two bond...
Write the favourable factors for the formation of an ionic bond.
Answer: An ionic link is formed by moving electrons from one atom to another. This means that ionic bond formation is dependent on neutral atom flexibility. The lattice energy of the molecule...
Define the octet rule. Write its significance and limitations
Answer: "Atoms can combine either by transferring or sharing valence electrons to achieve the closest inert gas configuration," says the Octet Rule. Octet rule describes how chemical bonds occur...
Explain the formation of a chemical bond.
Answer: “A chemical bond is an attractive force that binds chemical elements together.” Many theories exist for forming chemical bonds, including valence shell electron pair repulsion, electronic,...
Think about the components: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the component that displays neither negative nor positive oxidation state?
Solution: Ne displays neither negative nor positive oxidation no. That is 0.
Think about the components: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the component that displays both negative and positive oxidation states.
Solution: I displays both negative and positive oxidation no. That is - 1, +1, +3, +5 and +7.
Consider the elements: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the element that exhibits only positive oxidation.
Solution: Cs displays just certain oxidation no. That is +1.
Think about the components: Cs, Ne, I and F Identify the component that displays just adverse oxidation.
Solution: F exhibits only negative oxidation number. That is -1.
Assign oxidation number to the underlined elements 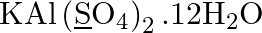
Solution: $\mathrm{KAl}\left(\underline{\mathrm{S}} \mathrm{O}_{4}\right)_{2} .12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ Let expect oxidation number of S is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component 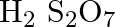
Solution: $\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}$ Let accept oxidation number of S is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }O\text{ }=\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component NaBH4
Solution: NaBH4 Let accept oxidation number of B is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Na\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z-direction is given by 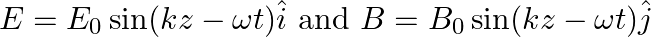
a) Use equation 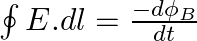 to prove
to prove 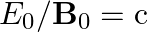
b) by using a similar process and the equation 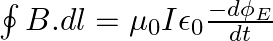 , prove that
, prove that 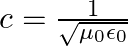
a) Substituting the above equations in the following equation we get ${c} \oint E . d l=-\frac{d \phi_{B}}{d t}=-\frac{d}{d t} \oint B \cdot d s$ So, $E_{0} / B_{0}=0$ b) We get $c=1 /...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component CaO2
Solution: CaO2 Let expect oxidation number of O is x. \[Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Ca\text{ }=\text{ }+2\] Then, at that point, we have: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}}...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component K2MnO4
Solution: K2MnO4 Let expect oxidation number of Mn is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }K\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component H4P2O7
Solution: H4P2O7 Let expect oxidation number of P is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component NaHSO4
Solution: NaHSO4 Let expect oxidation number of S is x. \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Na\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\ Oxidation\text{ }number\text{...
Assign the oxidation number to the underlined component NaH2PO4
Solution: NaH2PO4 Let expect oxidation number of P is x. We realize that, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} Oxidation\text{ }number\text{ }of\text{ }Na\text{ }=\text{ }+1 \\ ~ \\...
Thermodynamically the most steady type of carbon is (a) Diamond (b) Graphite (c) Fullerenes (d) Coal
Solution: (b) Graphite is thermodynamically the most steady type of carbon.
An infinitely long thin wire carrying a uniform linear static charge density 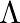 is placed along the z-axis. The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity
is placed along the z-axis. The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity 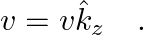 Calculate the pointing vectors
Calculate the pointing vectors 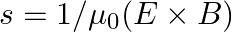
The electric field in an infinitely long thin wire is given by the expression, $\vec{E}=\frac{\lambda \hat{e}_{s}}{2 \pi \epsilon_{0} a} \hat{j}$ Magnetic field due to the wire is given by the...
The kind of hybridization of boron in diborane is (a) sp (b)sp2 (c) sp3 (d) dsp2
Solution: (c) Boron in diborane is sp3 hybridized.
A watery arrangement of borax is (a) Neutral (b) Amphoteric (c) Basic (d) Acidic
Solution: (b) Borax is a strong base salt (NaOH) and a frail corrosive (H3BO3). Accordingly, it is an essential thing in nature.
What do you comprehend by Catenation?
Solution: Catenation A few components or particles (like carbon) may interface with one another through solid covalent bonds to shape long chains or branches. This trademark is known as catenation....
What do you comprehend by Allotropy
Solution: Allotropy Allotropy is the presence of a component in more than one structure, having distinctive actual properties yet similar synthetic properties. The various types of a component are...
What do you comprehend by Inert pair impact
Solution: Inert pair impact As one actions down the gathering, s-block electrons decline their propensity to take part in substance holding. This impact is known as the dormant pair impact. The...
In a portion of the responses, thallium takes after aluminum, while in others it looks like with the gathering I metals. Backing this assertion by giving some proof.
Solution: Thallium is a piece of the intermittent table gathering 13. For this gathering, the most widely recognized oxidation state is + 3. Heavier individuals from this gathering, nonetheless,...
Clarify why would that be an incredible decline in ionization enthalpy from carbon to silicon?
Solution: Carbon ionizing enthalpy (the principal component in bunch 14) is exceptionally high (1086 kJ/mol). That is normal due to its little size. Nonetheless, there is a sharp decline in enthalpy...
Give reasons: Aluminium wire is utilized to make transmission links.
Solution: Aluminum wire is utilized to make transmission links. Aluminium wires are good conductors of electricity and also it is cheap metal easily available, light in weight and also very ductile....
Give reasons: Aluminum utensils ought not be kept in water for the time being.
Solution: Aluminum utensils ought not be kept in water for the time being. The oxygen in water responds to make a dainty layer of aluminum oxide with aluminum. This layer keeps further response from...
Give reasons: Aluminum compounds are utilized to make airplane body.
Solution: Aluminum compounds are utilized to make airplane body. Aluminum has a high protection from elastic and is light. It might likewise be alloyed to various metals like Si, Mg, Cu, Mn and Zn....
Give reasons: Diamond is utilized as a rough
Solution: Diamond is utilized as a rough Carbon is sp3 hybridized in Diamond. With the assistance of solid covalent bonds, every carbon molecule is bound to four other carbon iotas. These covalent...
Give reasons: Graphite is utilized as the grease.
Solution: Graphite is utilized as the grease. Graphite has a layered construction, and the powers of frail van der Waals tie various layers of graphite together. These layers might slide one over...
Give reasons: A combination of weaken NaOH and aluminum pieces is utilized to open channel.
Solution: A combination of weaken NaOH and aluminum pieces is utilized to open the channel. Sodium hydroxide and aluminum respond to shape aluminate (III) sodium tetra hydroxy and hydrogen gas....
Give reasons: Conc.HNO3 can be moved in an aluminum holder.
Solution: Conc.HNO3 can be shipped in an aluminum holder. As it responds with aluminum to frame a slight defensive oxide layer on the aluminum surface, concentrated HNO3 can be put away and shipped...
How is the exorbitant substance of CO2 answerable for a dangerous atmospheric devation?
Solution: Carbon dioxide is a gas that is vital for our endurance. The expanded CO2 content in the climate, nonetheless, represents a genuine danger. An increment in petroleum product ignition,...
Recommend an explanation with regards to why CO is toxic.
Solution: Given its capacity to frame a complex with hemoglobin, carbon monoxide is profoundly toxic. The previous hinders restricting with oxygen by Hb. Subsequently, an individual passes on...
You are given a 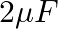 parallel plate capacitor. How would you establish an instantaneous displacement current of
parallel plate capacitor. How would you establish an instantaneous displacement current of 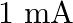 in the space between its plates?
in the space between its plates?
The capacitance of the capacitor is given by $\mathrm{C}=2 \mu \mathrm{F}$ Displacement current is given as $I_{d}=1 \mathrm{~mA}$ Hence, Charge in capacitor will be, $q=C V$ $\mathrm{dV} /...
Give a short portrayal of the standards of the accompanying procedures taking a model. Chromatography
Solution: Chromatography It is generally utilized for the partition and cleansing of natural mixtures. Rule: The guideline on which it works is that singular parts of a blend move at various speeds...
Give a short portrayal of the standards of the accompanying procedures taking a model. Distillation
Solution: Distillation This strategy is utilized to isolate non-unpredictable fluids from unstable pollutants. It is likewise utilized when the parts have an extensive distinction in their edges of...
Give a short portrayal of the standards of the accompanying procedures taking a model. Crystallization
Solution: Crystallization Crystallization is utilized to decontaminate strong natural mixtures. Standard: The guideline on which it works is the distinction in the dissolvability of the compound and...
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit. 
Solution: Substitution (nucleophilic) response since modification of particles happens.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit. 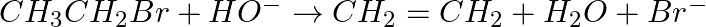
Solution: Elimination (bimolecular) response since response hydrogen and bromine are taken out to shape ethene.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.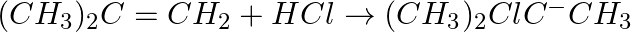
Solution: Addition (electrophilic) response since two reactant particles joins to shape a solitary item.
Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.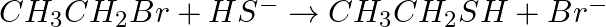
Solution: Substitution (nucleophilic) response since bromine bunch gets subbed by – SH bunch.
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles: 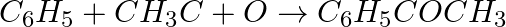
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core adoring reagent. An electrophile is a reagent which needs an electron pair and is...
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles: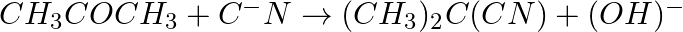
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core adoring reagent. An electrophile is a reagent which needs an electron pair and is...
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles: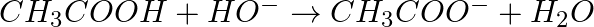
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core adoring reagent. An electrophile is a reagent which needs an electron pair and is...
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Clarify with models.
Solution: A nucleophile is a reagent that has an electron pair and will give it away. It is otherwise called a core cherishing reagent. Ex: NC–, OH–, R3C–(carbanions), and so on An electrophile is a...
Which of the two: O2NCH2CH2O–or CH3CH2O–is relied upon to be more steady and why?
Solution: Since NO2 has a place with the electron-pulling out bunch, it shows – I impact. NO2 attempts to diminish the negative charge on the compound by pulling out the electrons toward it. This...
Draw recipes for the initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the accompanying mixture H–CH=CH2
Solution: The initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the given mixtures are H–CH=CH2: Ethene CH3–CH=CH2: Propene CH3–CH2–CH=CH2: 1-Butene CH3–CH2–CH2–CH=CH2: 1-Pentene...
Draw recipes for the initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the accompanying mixture CH3COCH3
Solution: CH3COCH3: Propanone CH3COCH2CH3: Butanone CH3COCH2CH2CH3 : Pentan-2-one CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3: Hexan-2-one CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 : Heptan-2-one
Poynting vectors 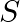 is defined as a vector whose magnitude is equal to the wave intensity and whose direction is along the direction of wave propagation. Mathematically, it is given by
is defined as a vector whose magnitude is equal to the wave intensity and whose direction is along the direction of wave propagation. Mathematically, it is given by 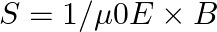 . Show that nature of
. Show that nature of 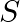 versus
versus 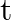 graph.
graph.
Draw recipes for the initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the accompanying mixture H–COOH
Solution: The initial five individuals from each homologous series starting with the given mixtures are H–COOH: Methanoic corrosive CH3–COOH: Ethanoic corrosive CH3–CH2–COOH: Propanoic corrosive...
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? But-3-yn-1-ol or But-4-ol-1-yne
Solution: Out of the two utilitarian gatherings present in the given compound, the alcoholic gathering is the central practical gathering. Consequently, the parent chain will have an – ol postfix....
The charge on a parallel plate capacitor varies as 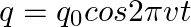 . The plates are very large and close together. Neglecting the edge effects, find the displacement current through the capacitor?
. The plates are very large and close together. Neglecting the edge effects, find the displacement current through the capacitor?
Displacement current through the capacitor is given as, $\mathrm{Id}=\mathrm{Ic}=\mathrm{dq} / \mathrm{dt}$ Given, $q=q_{0} \cos 2 \pi v t$ On putting the values, we get $\mathrm{Id}=\mathrm{Ic}=-2...
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane or 4-Chloro-2-methylpentane
Solution: If the substituents in the chain are in identical positions, then, at that point, the lower number is given to the substituent bunch in sequential request. Along these lines, the right...
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? 2,4,7-Trimethyloctane or 2,5,7-Trimethyloctane
Solution: The locant number should begin from the base. Here, 2,4,7 is lower than 2,5,7. Subsequently, the right IUPAC name would be 2,4,7-Trimethyloctane.
Which of the accompanying addresses the right IUPAC name for the mixtures concerned? 2,2-Dimethylpentane or 2-Dimethylpentane
solution: The prefix di shows that there are two methyl bunches in the chain. Along these lines, the right IUPAC name would be 2,2-Dimethylpentane.
Why is the orientation of the portable radio with respect to broadcasting station important?
As electromagnetic waves are plane polarised, the antenna must be parallel to the vibration of the fields of the wave. The orientation of the portable radio with respect to the transmitting station...
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[C6H6\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-250e7c087123a8d0267c095925b18800_l3.png)
Solution: C6H6 All the 6 carbon particles in benzene are sp2 hybridized
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH2=CHCN\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-52ef84ac98a604743dfb23732dfbb165_l3.png)
Solution: C-1 is sp2 hybridized. C-2 is sp2 hybridized. C-3 is sp hybridized.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\left( CH3 \right)2CO\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a2bea77220b7e99546204fa04a862cfa_l3.png)
Solution: C - 1 and C-3 are sp3 hybridized. C-2 is sp2 hybridized.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH3CH=CH2\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6a2ef16862caa7e37fd3861c7df53de4_l3.png)
Solution: C-1 is sp3 hybridized. C-2 is sp2 hybridized. C-3 is sp2 hybridized.
What are the hybridisation conditions of every carbon molecule in the accompanying compound? ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CH2=C=O\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3ffdae7fcb2301f4db1b66d768c446ab_l3.png)
Solution: C-1 is sp2 hybridized. C-2 is sp hybridized.
A plane electromagnetic wave propagating along 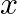 -direction can have the following pairs of
-direction can have the following pairs of 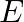 and
and 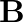
a) 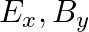
b) 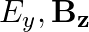
c) 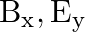
d) 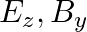
The correct options are: b) $E_y, \mathbf{B_ z}$ d) $E_z, B_y$
An electromagnetic wave travelling along the 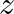 -axis is given as:
-axis is given as: 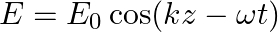 . Choose the correct options from the following a) the associated magnetic field is given as
. Choose the correct options from the following a) the associated magnetic field is given as 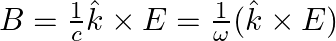
b) the electromagnetic field can be written in terms of the associated magnetic field as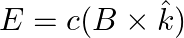
c)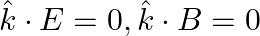
d)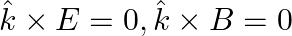
a) the associated magnetic field is given as $B=\frac{1}{c} \hat{k} \times E=\frac{1}{\omega}(\hat{k} \times E)$ b) the electromagnetic field can be written in terms of the associated magnetic field...
One requires 11eV of energy to dissociate a carbon monoxide molecule into carbon and oxygen atoms. The minimum frequency of the appropriate electromagnetic radiation to achieve the dissociation lies in
a) visible region
b) infrared region
c) ultraviolet region
d) microwave region
c) ultraviolet region
In the LCR circuit the ac driving voltage is v = vm sin ωt.
Describe subsequent motion of charges.
R must be short-circuited in order for the circuit to become an LC oscillator. The capacitor will continue to drain, and all of the energy will be transferred to L and back. Energy will oscillate...
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is
(a) 5 √2 A
(b) 5 √3/2 A
(c) 5/6 A
(d) 5/ √2 A
(b) 5 √3/2 A
Considering the elements F, Cl, O and N, the correct order of their chemical reactivity in terms of oxidizing property is : (a) F > Cl > O > N (b) F > O > Cl > N (c) Cl > F > O > N (d) O > F > N > Cl
Answer: (b) F > O > Cl > N During a period, as we move from left to right, the non-metallic characteristics of the elements become more prominent. As a result, F > O > N.
Considering the elements B, C, N, F, and Si, the correct order of their non-metallic character is : a) B > C > Si > N > F b) Si > C > B > N > F c) F > N > C > B > Si d) F > N > C > Si > B
Answer: c) F > N > C > B > Si While moving from left to right in a period, the nonmetallic property of the elements reduces as we move from left to right in the period. As a result, F...
Considering the elements B, Al, Mg, and K, the correct order of their metallic character is : (a) B > Al > Mg > K (b) Al > Mg > B > K (c) Mg > Al > K > B (d) K > Mg > Al > B
Answer: d) K > Mg > Al > B During a period, the metallic nature of the components diminishes as we move from left to right in the period. As a result, Mg > Al. With each group we...
Which one of the following statements is incorrect in relation to ionization enthalpy? (a) Ionization enthalpy increases for each successive electron. (b) The greatest increase in ionization enthalpy is experienced on the removal of an electron from core noble gas configuration. (c) End of valence electrons is marked by a big jump in ionization enthalpy. (d) Removal of an electron from orbitals bearing lower n value is easier than from orbital having higher n value
Answer: (d) is a false statement When comparing orbitals with a lower value of 'n' to orbitals with a higher value of 'n,' it is easier to remove an electron from the lower value of 'n' orbital....
The size of isoelectronic species F–, Ne and Na+ is affected by (a) nuclear charge (Z ) (b) valence principal quantum number (n) (c) electron-electron interaction in the outer orbitals (d) none of the factors because their size is the same.
Answer: (a) Nuclear charge (Z) Because, in the case of isoelectronic species, the atomic size decreases as the number of nuclear charge increases (Z). e.g. the arrangement according to increasing...
“Anything that influences the valence electrons will affect the chemistry of the element”. Which of the factors given below is not affecting the valence shell? (a) Valence Principal quantum number (n) (b) Nuclear charge (Z) (c) Nuclear mass (d) Number of core electrons
Answer: Option c) Because the nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons, the mass of the nucleus has no effect on the valence shell. Protons, or nuclear charges, have an effect on the valence...
Which of the following statements related to the modern periodic table is incorrect? (a) The p-block has 6 columns because a maximum of 6 electrons can occupy all the orbitals in a p-shell. (b) The d-block has 8 columns because a maximum of 8 electrons can occupy all the orbitals in a d-subshell. (c) Each block contains a number of columns equal to the number of electrons that can occupy that subshell. (d) The block indicates the value of an azimuthal quantum number (l) for the last subshell that received electrons in building up the electronic configuration.
Answer: Correcting the incorrect statement is represented by option (b). It explains that "the d-block has 8 columns because a maximum of 8 electrons can occupy all of the orbitals in a d-subshell,"...
In the modern periodic table, the period indicates the value of : (a) atomic number (b) atomic mass (c) principal quantum number (d) azimuthal quantum number.
Answer: (c) The period in the Modern periodic table indicates the value of ‘n’ i.e. a principal quantum number. A periodic table's period reflects the value of a particular element's major quantum...
Predict the formulas of the stable binary compounds that would be formed by the combination of the following pairs of elements. (a) Lithium and oxygen (b) Magnesium and nitrogen (c) Aluminium and iodine (d) Silicon and oxygen (e) Phosphorus and fluorine (f) Element 71 and fluorine
Answer: i) $Li_2O$ is formed when the alkali metal lithium (with one valence electron) and group 16 element oxygen (with two valence electrons) mix. (ii) The alkaline earth metal magnesium (which...
The first 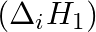 and the second
and the second 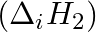 ionization enthalpies (in
ionization enthalpies (in 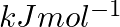 ) and the
) and the 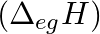 electron gain enthalpy (in
electron gain enthalpy (in 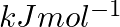 ) of a few elements are given below: Which of the above elements is likely to be : (a) the least reactive element. (b) the most reactive metal. (c) the most reactive non-metal. (d) the least reactive non-metal. (e) the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2 (X=halogen). (f) the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen)?
) of a few elements are given below: Which of the above elements is likely to be : (a) the least reactive element. (b) the most reactive metal. (c) the most reactive non-metal. (d) the least reactive non-metal. (e) the metal which can form a stable binary halide of the formula MX2 (X=halogen). (f) the metal which can form a predominantly stable covalent halide of the formula MX (X=halogen)?
Elements (\Delta _{i}H_{1})(ΔiH1) (\Delta _{i}H_{2})(ΔiH2) (\Delta _{eg}H)(ΔegH) 1 520 7300 -60 2 419 3051 -48 3 1681 3374 -328 4 1008 1846 -295 5 2372 5251 +48 6 738 1451 -40 Answer:...
Assign the position of the element having outer electronic configuration (i) 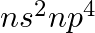 for
for 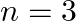 (ii) (n1)
(ii) (n1) 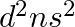 for
for 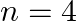 , and (iii)
, and (iii) 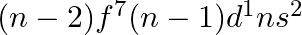 for
for 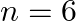 , in the periodic table.
, in the periodic table.
Answer: i) Since n = 6, the element is in period 6. f-block element because the last electron enters f-orbital. They are in the third group. So, 54 + 7 + 2 + 1 Equals 64. So Gadolinium is required....
Write the general outer electronic configuration of s-, p-, d- and f- block elements.
Answer: The general outer electronic configuration of s block elements is $ns ^{(1-2)}$. The general outer electronic configuration of p block elements is $ns ^{2} np ^{(1-6)}$. The general outer...
The increasing order of reactivity among group 1 elements is Li < Na < K < Rb Cl > Br > I. Explain.
Answer: Group 1 elements have only one valence electron. So they tend to expel this electron to form a stable inert gas. The ionization enthalpies of the elements drop in group 1. Expulsion of the...
Use the periodic table to answer the following questions. (a) Identify an element with five electrons in the outer subshell. (b) Identify an element that would tend to lose two electrons. (c) Identify an element that would tend to gain two electrons. (d) Identify the group having metal, non-metal, liquid as well as gas at the room temperature
Answer: (a) The electrical configuration of an element with 5 electrons in the outer subshell is ns2np5. The electrical configuration of the Halogen group is the same. As a result, the elements...
What are the major differences between metals and non-metals?
Answer: Metals lose electrons to produce cations. Metals have low ionization, negative electron, and electronegativities enthalpies. ionic compounds and basic oxides Non-metals readily take...
Would you expect the first ionization enthalpies for two isotopes of the same element to be the same or different? Justify your answer
Answer: The ionization enthalpy of any atom is determined by the number of protons and electrons in the atom. However, the isotopes of any element have the same number of electrons and protons as...
Describe the theory associated with the radius of an atom as it (a) gains an electron (b) loses an electron
Answer: a) An atom loses one electron when it expels one, but the nuclear charge remains the same. In an atom, electron-electron repulsion reduces. So the effective nuclear charge increases. As a...
How would you react to the statement that the electronegativity of N on the Pauling scale is 3.0 in all the nitrogen compounds?
Answer: Electronegativity is a property of any element that is subject to change. Electronegativity varies depending on the substance being studied. The following statement is erroneous: "The...
What is the basic difference between the terms electron gain enthalpy and electronegativity?
Answer: Electron gain enthalpy Electronegativity It is the common tendency of an atom to attract outside electrons It is the general tendency of an atom to attract shared pair of electrons It is the...
Would you expect the second electron gain enthalpy of O as positive, more negative or less negative than the first? Justify your answer
Answer: Oxygen is in p block element group 16. It is the first of 16 members. It is a non-metal found in the earth's crust. When an electron is added to an O atom, it releases energy. O has a...
Which of the following pairs of elements would have a more negative electron gain enthalpy? (i) O or F (ii) F or Cl
Answer: i) O and F are from the same period. As the electron is inserted in the same shell, the atomic size of O-atom is larger than F-atom. It has one less proton than F-atom. So an O-atom nucleus...
The first ionization enthalpy values (in kJ/mol) of group 13 elements are given below. How would you explain this deviation from the general trend?
B Al Ga In Tl 801 577 579 558 589 Answer The ionization enthalpy decreases with group size. B and Al agree. Ga has a higher ionization enthalpy than Al. Tend electrons in the inner shell of...
Molecules in the air in the atmosphere are attracted by the gravitational force of the earth. Explain why all of them do not fall into the earth just like an apple falling from a tree.
The gravitational force of the earth attracts molecules in the atmosphere, yet they do not descend into the earth since they are in random motion, whereas an apple moves downhill.
What are the various factors due to which the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements tends to decrease down a group?
Answer: The factors that cause the ionization enthalpy to drop as we travel down the main group are as follows: 1. “Inner shells increase in number as we proceed down the group.” The nucleus' inner...
How would you explain the fact that the first ionization enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium but its second ionization enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
Answer: Because magnesium has a larger 1st ionization enthalpy than sodium, Magnesium has bigger atoms than sodium. A higher effective nuclear charge than sodium, Magnesium So sodium requires less...
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne. Explain Why {i}Be has higher ΔH than B (ii) O has lower ΔH than N and F?
Answer: i) The electron that can be evacuated from Be(beryllium) atom is 2s, but the electron that can be expelled from boron is 2p. 2s – electron, and nucleus attract more strongly than 2s –...
Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is 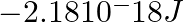 . Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
. Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
Answer: Given that, the electron of hydrogen is having $-2.18 * 10^{-18} J$ in the ground state. Thus, To eject an electron from the ground state in a $H ($ hydrogen $)-$ atom, a certain amount of...
If the law of gravitation, instead of being inverse-square law, becomes an inverse-cube-law
a) planets will not have elliptic orbits
b) circular orbits of planets is not possible
c) projectile motion of a stone thrown by hand on the surface of the earth will be approximately parabolic
d) there will be no gravitational force inside a spherical shell of uniform density
The correct options are a) planets will not have elliptic orbits c) projectile motion of a stone thrown by hand on the surface of the earth will be approximately parabolic Explanation: The planets...
What is the significance of the terms — ‘isolated gaseous atom’ and ‘ground state’ while defining the ionization enthalpy and electron gain enthalpy?
Answer: In the ground state of an isolated gaseous atom, ionisation enthalpy is required to eject an electron. Even though the atoms are far separated in the gaseous state, there are some attraction...
Explain why cation is smaller and anions larger in radii than their parent atoms?
Answer: It possesses less electrons than the parent atom, but the overall nuclear charge remains the same, resulting in greater attraction of electrons to the nucleus. Cations have smaller radii...
Consider the following species : 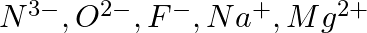 , and
, and 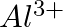 (a) What is common in them? (b) Arrange them in the order of increasing ionic radii.
(a) What is common in them? (b) Arrange them in the order of increasing ionic radii.
Answer: (a) All of the species have the same number of electrons, i.e. 10 electrons. They are, therefore, isoelectronic species. (b) The following is the arrangement of the given ions in ascending...
As observed from earth, the sun appears to move in an approximately circular orbit. For the motion of another planet like mercury as observed from earth, this would
a) be similarly true
b) not be true because the force between earth and mercury is not inverse square law
c) not be true because the major gravitational force on mercury is due to sun
d) not be true because mercury is influenced by forces other than gravitational forces
The correct option is c) not be true because the major gravitational force on mercury is due to sun
The earth is an approximate sphere. If the interior contained matter which is not of the same density everywhere, then on the surface of the earth, the acceleration due to gravity
a) will be directed towards the centre but not the same everywhere
b) will have the same value everywhere but not directed towards the centre
c) will be same everywhere in magnitude directed towards the centre
d) cannot be zero at any point
The correct option is d) cannot be zero at any point
How does H2 O2 act as a dying specialist?
Solution: Hydrogen peroxide goes about as a solid oxidizing specialist both in fundamental and acidic media. When added to a material, it breaks the substance obligations of the chromophores...
Knowing the properties of H2O and D2O, do you imagine that D2O can be utilized for drinking purposes?
Solution: D2O is referred to as weighty water which goes about as an arbitrator (dials back the pace of response). Because of this property, it can't be utilized for drinking reason since it dials...
Portray the helpfulness of water in biosphere and organic frameworks.
Solution: Water is extremely important for all types of life which establish 65% of human body and 95% of plants.it assumes an indispensable part in the biosphere because of its → Thermal...
Is demineralised or refined water valuable for drinking purposes? If not, how might it be made valuable?
Solution: Water is extremely fundamental for our life. It comprises of many broke down supplements that are needed for ourselves and furthermore for plants and creatures. Demineralised water is...
What is implied by ‘demineralised’ water and how might it be acquired ?
Solution: This water is liberated from every one of the solvent mineral salts and it doesn't contain any cation or anion. It is acquired progressively by going the water through anion trade and...
What causes the impermanent and super durable hardness of water?
Solution: Because of the presence of dissolvable salts of magnesium and calcium as chlorides in water, hardness stays super durable in water. Because of the presence of dissolvable salts of calcium...
Portray the construction of the normal type of ice.
Solution: For the most part, ice is the translucent type of water. It visibles in a hexagonal structure in case it is solidified at climatic strain. At the point when the temperature is...
Analyze the designs of H2O and H2 O2.
Solution: The water atom will be shown with a bond point of 104 .5o has a bowed structure in vaporous stage. The O-H bond length is 95.7 pm. Structure : Hydrogen peroxide has a non-planar design...
Organize the accompanying NaH, MgH2 and H2O arranged by expanding diminishing property.
Solution: Ionic hydrides are solid diminishing specialists. NaH can undoubtedly give its electrons. Henceforth, it is most diminishing in nature. Both, MgH2 and H2O are covalent hydrides. H2O is...
Organize the accompanying H–H, D–D and F–F arranged by expanding bond separation enthalpy.
Solution: The bond pair in D–D bond is more emphatically drawn in by the core than the bond pair in H–H bond. This is a direct result of the greater atomic mass of D2. The more grounded the...
Organize the accompanying LiH, NaH and CsH arranged by expanding ionic person.
Solution: The ionic person of a bond is reliant upon the electro negativities of the molecules in question. The higher the distinction between the electro negativities of molecules, the more modest...
Organize the accompanying CaH2, BeH2 and TiH2 arranged by expanding electrical conductance.
Solution: The electrical conductance of an atom chiefly relies upon its covalent or ionic nature. CaH2 is an ionic hydride, which conducts power in the liquid state. Titanium hydride, TiH2 is...
Among NH3, H2O and HF, which would you hope to have most noteworthy greatness of hydrogen holding and why?
Solution: The degree of hydrogen holding predominantly relies upon (I) Electronegativity (ii) Number of hydrogen iotas accessible for holding. Among oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen, the expanding...
How does the nuclear hydrogen or oxy-hydrogen light capacity for cutting and welding purposes ? Clarify.
Solution: The nuclear hydrogen light is otherwise called oxy-hydrogen light. These molecules are delivered through dihydrogen separation with the assistance of an electric circular segment which...
How would you anticipate that the metallic hydrides should be valuable for hydrogen stockpiling? Clarify
Solution: Metallic hydrides are hydrogen inadequate. They don't keep the law of consistent structure. It has been set up that in the hydrides of Pd, Ac, Ni, and Ce, hydrogen possesses the...
What do you comprehend by the expression “non-stoichiometric hydrides”? Do you anticipate that this type of the hydrides should be framed by soluble base metals? Legitimize your reply.
Solution: Non-Stoichiometric hydrides are hydrogen-insufficient mixtures which is framed by the response of dihydrogen with d-square and f-block components. These hydrides don't observe the law of...
Do you expect the carbon hydrides of the sort (Cn H2n+2 ) to go about as ‘Lewis’ base or corrosive? Legitimize.
Solution: For carbon hydrides which have a place with type (Cn H2n+2), the accompanying hydrides are feasible for \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} n\text{ }=\text{ }1\Rightarrow CH4 \\ ~ \\...
What do you comprehend by (I) electron rich – mixtures of hydrogen, (ii) electron-exact, and (iii) electron-lacking? Give avocation appropriate models.
Solution: Sub-atomic hydride is grouped based on the presence of the bonds and absolute number of electrons in their Lewis structures as: Electron-inadequate hydrides Electron-exact hydrides...
Talk about the results of high enthalpy of H–H bond as far as synthetic reactivity of dihydrogen
Solution: The ionization enthalpy of H–H bond is higher (1312 kJ mol–1 ) which shows that hydrogen has a low propensity to frame H+ particles. Its ionization enthalpy esteem is equivalent to that of...
For what reason does hydrogen happen in a diatomic structure instead of in a monoatomic structure under ordinary conditions?
Solution: The ionization enthalpy of hydrogen molecule is higher. In this manner, it is more enthusiastically to eliminate its electron. This outcomes its propensity to exist in the low monoatomic...
Legitimize the situation of hydrogen in the intermittent table based on its electronic design.
Solution: The first component in the occasional table is hydrogen. Hydrogen shows double conduct since it has just 1 electron on its one 'S' shell.(i.e.,) hydrogen takes after the two incandescent...
Work out the entropy change in environmental elements when 1.00 mol of H2O(l) is shaped under standard conditions. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[f\text{ }H0=\text{ }\text{ }286\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1.\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0876268cab5e7e19237ca8d099603274_l3.png)
Solution: It is given that 286 kJ mol–1 of warmth is advanced on the development of 1 mol of H2O(l). Accordingly, an equivalent measure of warmth will be consumed by the environmental elements....
Comment on the thermodynamic stability of NO(g), given
Solution: The positive worth of ∆rH demonstrates that warmth is assimilated during the development of NO(g). This implies that NO(g) has higher energy than the reactants (N2 and O2)....
The harmony steady for a response is 10. What will be the worth of ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[G0?\text{ }R\text{ }=\text{ }8.314\text{ }JK1\text{ }mol1,\text{ }T\text{ }=\text{ }300\text{ }K.\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c5355a31e6d1d5f6327e806c31f733f0_l3.png)
Solution: From the articulation, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} G\theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }2.303\text{ }RT\text{ }logKeq \\ ~ \\ G\theta \text{ }for\text{ }the\text{ }response,\text{ }=\text{...
For the response ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2A\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }B\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2D\left( g \right) \\ ~ \\ U\theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }10.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }and\text{ }S\theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }44.1\text{ }JK1\text{ }. \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cbc82328853f02bdc578b87abcbd9b11_l3.png)
Compute ∆Gθ for the response, and anticipate whether the response might happen suddenly.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2A\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }B\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2D\left( g \right) \\ ~ \\ U\theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }10.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }and\text{ }S\theta \text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }44.1\text{ }JK1\text{ }. \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cbc82328853f02bdc578b87abcbd9b11_l3.png)
Solution: For the given response, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2\text{ }A\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }B\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2D\left( g \right) \\ ~ \\ ng\text{ }=\text{...
For the response, 2Cl(g) → Cl2(g), what are the indications of ∆H and ∆S ?
Solution: ∆H and ∆S are negative The given response addresses the development of chlorine particle from chlorine molecules. Here, bond development is occurring. Along these lines, energy is being...
For the response at 298 K, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2A\text{ }+\text{ }B\text{ }\to \text{ }C\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }400\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ what's\text{ }more,\text{ }S\text{ }=\text{ }0.2\text{ }kJ\text{ }K1\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dda209e4073843cae616fbc6002155e5_l3.png)
At what temperature will the response become unconstrained believing ∆H and ∆S to be consistent over the temperature range?
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} 2A\text{ }+\text{ }B\text{ }\to \text{ }C\text{ }H\text{ }=\text{ }400\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ ~ \\ what's\text{ }more,\text{ }S\text{ }=\text{ }0.2\text{ }kJ\text{ }K1\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-dda209e4073843cae616fbc6002155e5_l3.png)
Solution: From the articulation, \[G\text{ }=\text{ }H\text{ }\text{ }TS\] Expecting the response at balance, ∆T for the response would be: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( G\text{...
For a segregated framework, ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[U\text{ }=\text{ }0\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e877d1035c3edbb47c89fe48897ae3da_l3.png)
what will be ∆S?
Solution: ∆S will be positive i.e., more noteworthy than nothing \[Since\text{ }U\text{ }=\text{ }0,\] ∆S will be positive and the response will be unconstrained.
Ascertain the enthalpy change for the interaction ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[CCl4\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }C\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }4Cl\left( g \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2f50a987d1e8f6ebc394f6ed04c1c2b4_l3.png)
furthermore, ascertain bond enthalpy of C–Cl in CCl4(g). ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} vapH\theta \text{ }\left( CCl4 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }30.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }. \\ ~ \\ fH\theta \text{ }\left( CCl4 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }135.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }. \\ ~ \\ aH\theta \text{ }\left( C \right)\text{ }=\text{ }715.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }, \\ ~ \\ where\text{ }aH\theta \text{ }is\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }atomisation \\ ~ \\ aH\theta \text{ }\left( Cl2 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }242\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-183416d42bdde6938df21980fb24335b_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} vapH\theta \text{ }\left( CCl4 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }30.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }. \\ ~ \\ fH\theta \text{ }\left( CCl4 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }\text{ }135.5\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }. \\ ~ \\ aH\theta \text{ }\left( C \right)\text{ }=\text{ }715.0\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }, \\ ~ \\ where\text{ }aH\theta \text{ }is\text{ }enthalpy\text{ }of\text{ }atomisation \\ ~ \\ aH\theta \text{ }\left( Cl2 \right)\text{ }=\text{ }242\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-183416d42bdde6938df21980fb24335b_l3.png)
Solution: The synthetic conditions suggesting to the given upsides of enthalpies are:
Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CH3OH(l) from the following data:
Solution: The response that happens during the arrangement of CH3OH(l) can be composed as: \[C\left( s \right)\text{ }+\text{ }2H2O\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }\left( 1/2...
Given ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[N2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3H2\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }2NH3\text{ }\left( g \right)\text{ };\text{ }rH0=\text{ }\text{ }92.4\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d81c6dc91c7c744bc321c09dcfa91bab_l3.png)
What is the standard enthalpy of development of NH3 gas?
Solution: Standard enthalpy of development of a compound is the adjustment of enthalpy that happens during the arrangement of 1 mole of a substance in its standard structure from its constituent...
Enthalpies of development of CO (g), CO2 (g), N2O (g) and N2O4(g) are – 110, – 393, 81 and 9.7 kJ mol–1 individually. Discover the worth of ∆rH for the response: ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[N2O4\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3CO\left( g \right)\to \text{ }N2O\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3\text{ }CO2\left( g \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-84c70293d06a7f15cf0337e2f45f3df8_l3.png)
Solution: ∆rH for a response is characterized as the contrast between ∆fH worth of items and ∆fH worth of reactants.
What do you understand by isoelectronic species? Name a species that will be isoelectronic with each of the following atoms or ions. (i) 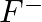 (ii)
(ii) 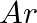 (iii)
(iii) 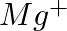 (iv)
(iv) 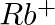
Answer: Isoelectronic species have the same number of electrons as one another. i) The elements $F^-$ and $O_2$ each have ten electrons. As a result, they are considered isoelectronic. (ii) The...
How do atomic radius vary in a period and in a group? How do you explain the variation?
Answer: A period's left to right movement reduces atomic radius. Because external electrons are available in a comparable valence shell, the atomic number increases from left to right, increasing...
Enthalpy of burning of carbon to CO2 is – 393.5 kJ mol–1. Compute the warmth endless supply of 35.2 g of CO2 from carbon and dioxygen gas.
Solution: Arrangement of CO2 from carbon and dioxygen gas can be addressed as: \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} \left( 1\text{ }mole\text{ }=\text{ }44\text{ }g \right) \\ ~ \\ Warmth\text{...
What does atomic radius and ionic radius really mean to you?
Answer: The atomic radius is the size of an atom. It measures an atom's size. If an element is a metal, its radius is metallic, and if it is not a metal, its radius is covalent. The metallic radius...
Why do elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties?
Answer: The number of valence electrons in any element determines the chemical and physical properties of that element. When elements in the same group of the periodic table have the same number of...
Which element do you think would have been named by (i) Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory (ii) Seaborg’s group?
Answer: (i) Lawrencium (Lr), which has an atomic number of Z=103, and Berkelium (Bk), which has an atomic number of Z=97, are the two elements with the highest atomic numbers. (ii) Seaborgium (Sg),...
What is the atomic number of element keeping in mind both the cases given below; i) Element is in 3rd period of the periodic table. ii) Element is in 17th group of the periodic table.
Answer: The first phase has two elements, while the second period has eight. As a result, element Z = 11 starts the third phase. The third period currently has eight elements. As a result, the 18th...
In terms of period and group where would you locate the element with Z =114?
Answer: The seventh period of the periodic table contains elements with atomic numbers Z = 87–114. The element with Z = 114 is thus available in the seventh period. In the seventh period, the first...
Work out the enthalpy change on freezing of 1.0 mol of water at 10.0°C to ice at – 10.0°C. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} fusH\text{ }=\text{ }6.03\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }at\text{ }0{}^\circ C. \\ ~ \\ Cp\left[ H2O\left( l \right) \right]\text{ }=\text{ }75.3\text{ }J\text{ }mol1\text{ }K\text{ }\text{ }1 \\ ~ \\ Cp\left[ H2O\left( s \right) \right]\text{ }=\text{ }36.8\text{ }J\text{ }mol1\text{ }K\text{ }\text{ }1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ae9ce04526cb31bbc938dd00ac9ef2b9_l3.png)
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} fusH\text{ }=\text{ }6.03\text{ }kJ\text{ }mol1\text{ }at\text{ }0{}^\circ C. \\ ~ \\ Cp\left[ H2O\left( l \right) \right]\text{ }=\text{ }75.3\text{ }J\text{ }mol1\text{ }K\text{ }\text{ }1 \\ ~ \\ Cp\left[ H2O\left( s \right) \right]\text{ }=\text{ }36.8\text{ }J\text{ }mol1\text{ }K\text{ }\text{ }1 \\ \end{array}\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ae9ce04526cb31bbc938dd00ac9ef2b9_l3.png)
Solution: Complete enthalpy change engaged with the change is the amount of the accompanying changes: (a) Energy change engaged with the change of 1 mol of water at 10°C to 1 mol of water at 0°C....
On the basis of quantum numbers, justify that the sixth period of the periodic table should have 32 elements.
Answer: For the outermost shells of a periodic table, a period shows the value of the main quantum number (n). Each period begins with the primary quantum number (n). And n for the 6th period is 6....
What is the basic difference in approach between the Mendeleev’s Periodic Law and the Modern Periodic Law?
Answer: Mendeleev’s Approach for periodic law Modern approach for the periodic law Periodic functions of the atomic mass of the corresponding elements determine the chemical and physical properties...
Which important property did Mendeleev use to classify the elements in his periodic table and did he stick to that?
Answer: Mendeleev arranged the elements in his periodic table by atomic weight. Mendeleev classified the elements into groups and periods based on atomic weight. Mendeleev grouped elements with...
What is the basic theme of organization in the periodic table?
Answer: It divides items into periods and groups based on their qualities. This method simplifies and organizes the study of elements and their compounds. Elements with similar characteristics are...
Work out the quantity of kJ of warmth important to raise the temperature of 60.0 g of aluminum from 35°C to 55°C. Molar warmth limit of Al is 24 J mol–1 K–1
solution: From the statement of warmth (q), \[q\text{ }=\text{ }m.\text{ }c.\text{ }T\] Where, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} c\text{ }=\text{ }molar\text{ }warmth\text{ }limit \\ ~ \\...
Which of the following are the correct reasons for the anomalous behaviour of lithium? (i) The exceptionally small size of its atom (ii) Its high polarising power (iii) It has a high degree of hydration (iv) Exceptionally low ionisation enthalpy
Answer: Option i) & ii) Lithium exhibits a high ionization enthalpy in addition to a high degree of hydration. This is owing to the fact that it is so little.
Choose the correct statements from the following. (i) Beryllium is not readily attacked by acids because of the presence of an oxide film on the surface of the metal. (ii) Beryllium sulphate is readily soluble in water as the greater hydration enthalpy of Be2+ overcomes the lattice enthalpy factor. (iii) Beryllium exhibits coordination number more than four. (iv) Beryllium oxide is purely acidic.
Answer: Option i) & ii) Be mimics Al (diagonal relationship), and together they create a protective film of oxide that is resistant to acid assault. Because of the high hydration enthalpy of...
When Zeolite, which is hydrated sodium aluminium silicate is treated with hard water, the sodium ions are exchanged with which of the following ion(s)? (i) 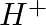 ions (ii)
ions (ii) 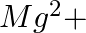 ions (iii)
ions (iii) 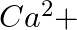 ions (iv)
ions (iv) 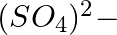 ions
ions
Answer: Option ii) & iii) Because of this, when zeolite, which is sodium aluminium silicate, reacts with hard water, the sodium ion of zeolite is swapped for calcium and magnesium ions.
The response of cyanamide, NH2CN(s), with dioxygen was done in a bomb calorimeter, and ∆U was observed to be – 742.7 kJ mol–1 at 298 K. Ascertain enthalpy change for the response at 298 K. ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[NH2CN\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }3/2\text{ }O2\left( g \right)\text{ }\to \text{ }N2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }CO2\left( g \right)\text{ }+\text{ }H2O\left( l \right)\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6cb518a194b0305964737ad87e3d7289_l3.png)
Solution: Enthalpy change for a response (∆H) is given by the articulation, \[H\text{ }=\text{ }U\text{ }+\text{ }ngRT\] Where, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} U\text{ }=\text{ }change\text{...
Metallic elements are described by their standard electrode potential, fusion enthalpy, atomic size, etc. The alkali metals are characterised by which of the following properties? (i) High boiling point (ii) High negative standard electrode potential (iii) High density (iv) Large atomic size
Answer: Option ii) & iv) Periods begin with alkali metals. For their period, alkali metals have the biggest atomic radius. They have low density due to their huge size and low bulk. Alkali...
Dehydration of hydrates of halides of calcium, barium and strontium i.e., CaCl26H2O, BaCl2.2H2O, SrCl2.2H2O, can be achieved by heating. These become wet on keeping in air. Which of the following statements is correct about these halides? (i) act as dehydrating agent (ii) can absorb moisture from the air (iii) The tendency to form hydrate decreases from calcium to barium (iv) All of the above
Answer: Option iv) Because they are hygroscopic in nature, the calcium, barium, and strontium halides operate as a dehydrating agent in the body. They are capable of absorbing moisture....
In a cycle, 701 J of warmth is consumed by a framework and 394 J of work is finished by the framework. What is the adjustment of interior energy for the cycle?
solution: As per the principal law of thermodynamics, \[U\text{ }=\text{ }q\text{ }+\text{ }W\text{ }\left( I \right)\] Where, \[\begin{array}{*{35}{l}} U\text{ }=\text{ }change\text{...
Which of the following statements is true about Ca(OH)2? (i) It is used in the preparation of bleaching powder (ii) It is a light blue solid (iii) It does not possess disinfectant property. (iv) It is used in the manufacture of cement.
Answer: Option i) Slaked lime is formed by combining quicklime and water to form a paste. Because quicklime can be used in the manufacture of cement, slaked lime can be used in the manufacture of...
A response ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[,\text{ }A\text{ }+\text{ }B\text{ }\to \text{ }C\text{ }+\text{ }D\text{ }+\text{ }q\]](https://www.learnatnoon.com/s/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f134f882cde1f21a1a7d40a02e8eec6e_l3.png)
is found to have a positive entropy change. The response will be (I) conceivable at high temperature (ii) conceivable just at low temperature (iii) unrealistic at any temperature (iv) conceivable at any temperature
Solution: For a response to be unconstrained, ∆G ought to be negative. \[G\text{ }=\text{ }H\text{ }\text{ }TS\] As indicated by the inquiry, for the given response, ...
The formula of soda ash is (i) Na2CO3.10H2O (ii) Na2CO3.2H2O (iii) Na2CO3.H2O (iv) Na2CO3
Answer: Option iv) The formula for soda ash is $Na_2CO_3$ that is sodium carbonate.
Which of the following elements does not form hydride by direct heating with dihydrogen? (i) Be (ii) Mg (iii) Sr (iv) Ba
Answer: Option i) When heated, all of the elements, with the exception of beryllium, mix with hydrogen to create their hydrides.
Suspension of slaked lime in water is known as (i) lime water (ii) quick lime (iii) milk of lime (iv) an aqueous solution of slaked lime
Answer: Option iii) Calcium hydroxide dissociates in an aqueous solution, releasing calcium cations and hydroxide anions. Calcium oxide is the chemical compound known as quicklime. Milk of lime is a...
The enthalpy of burning of methane, graphite and dihydrogen at 298 K are, – 890.3 kJ mol–1 – 393.5 kJ mol–1 , and – 285.8 kJ mol–1 individually. Enthalpy of arrangement of CH4(g) will be (I) – 74.8 kJ mol–1 (ii) – 52.27 kJ mol–1 (iii) +74.8 kJ mol–1 (iv) +52.26 kJ mol–1 .
solution: As indicated by the inquiry, Subsequently, the ideal condition is the one that addresses the development of CH4 (g) i.e., Enthalpy of arrangement of\[~CH4\left( g \right)\text{...
Dead burnt plaster is (i) CaSO4 (ii) CaSO4.1/2 H2O (iii) CaSO4.H2O (iv) CaSO4.2H2O
Answer: Option i) When plaster of Paris is heated to 200°C, it transforms into anhydrous calcium sulphate, often known as dead plaster, which lacks setting properties since it absorbs water at a...
By adding gypsum to cement (i) setting time of cement becomes less. (ii) setting time of cement increases. (iii) colour of cement becomes light. (iv) the shining surface is obtained.
Answer: Option ii) The addition of gypsum serves only to slow down the setting process of the cement, allowing it to solidify to a sufficiently hard state before use.
When sodium is dissolved in liquid ammonia, a solution of deep blue colour is obtained. The colour of the solution is due to (i) ammoniated electron (ii) sodium ion (iii) sodium amide (iv) ammoniated sodium ion
Answer: option i) The concentration of these solvated ions in the sodium in liquid ammonia solution changes the color to copper. So the ammoniated electron is responsible for the solution's color.
